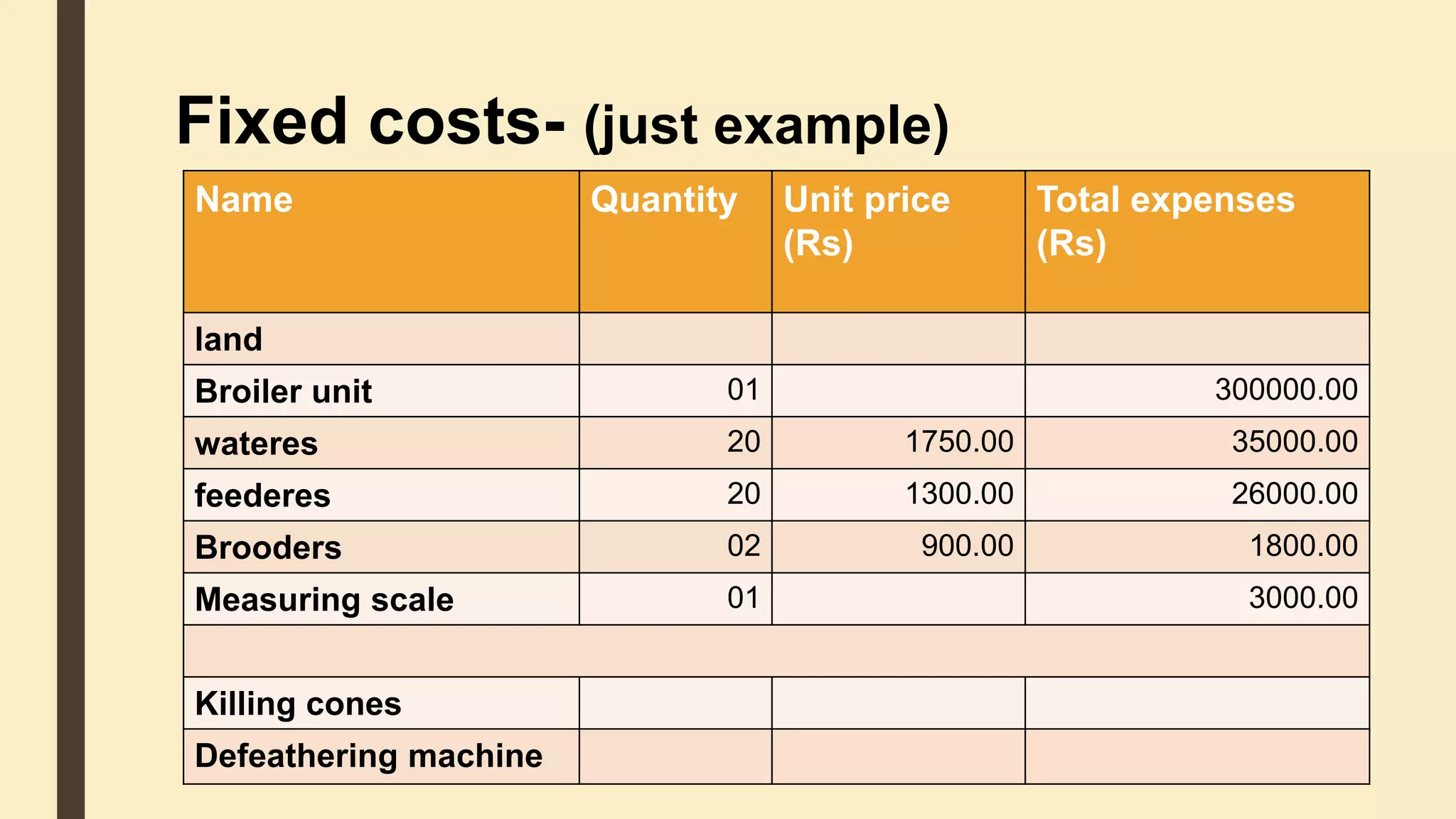
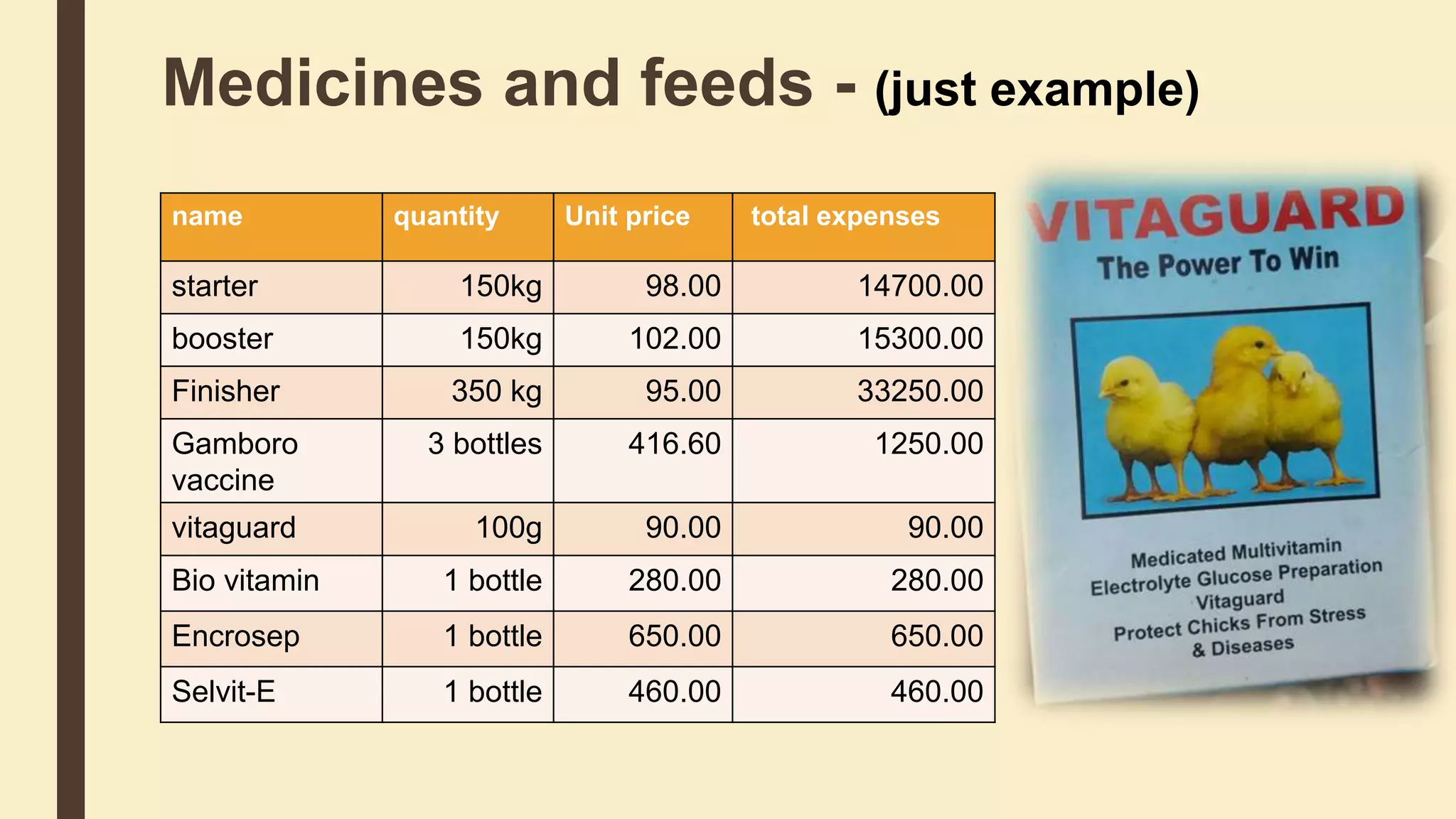
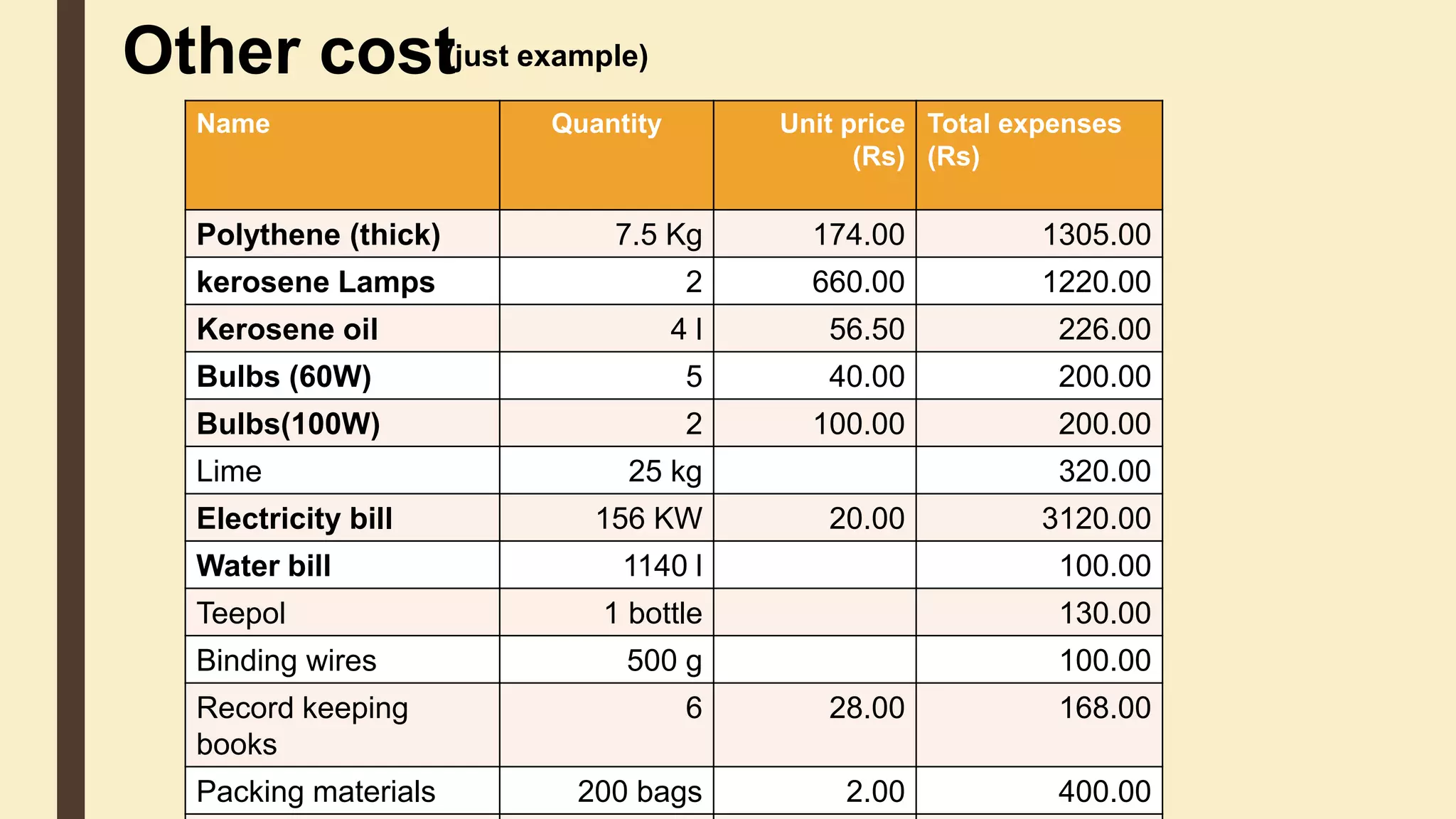
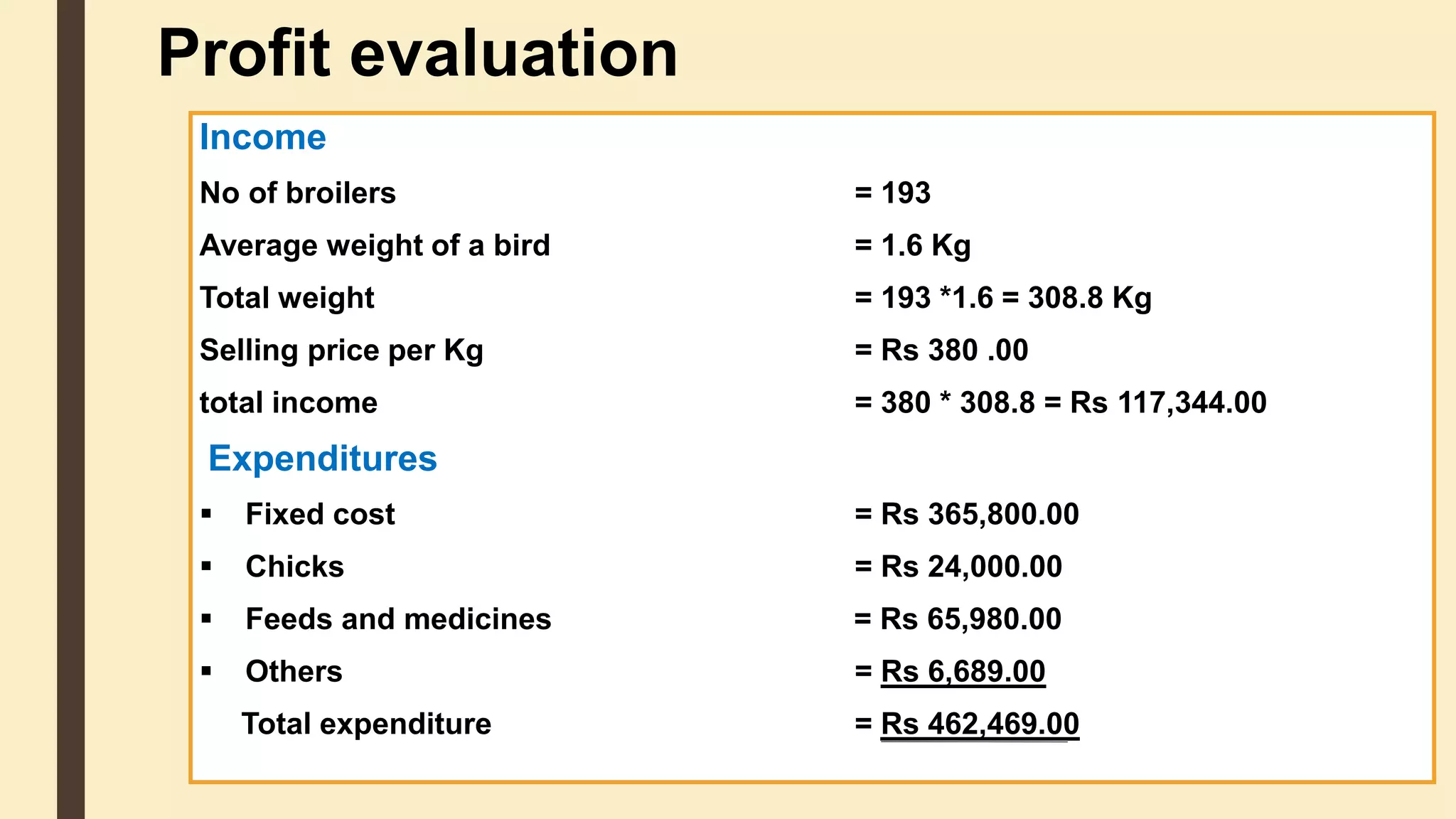
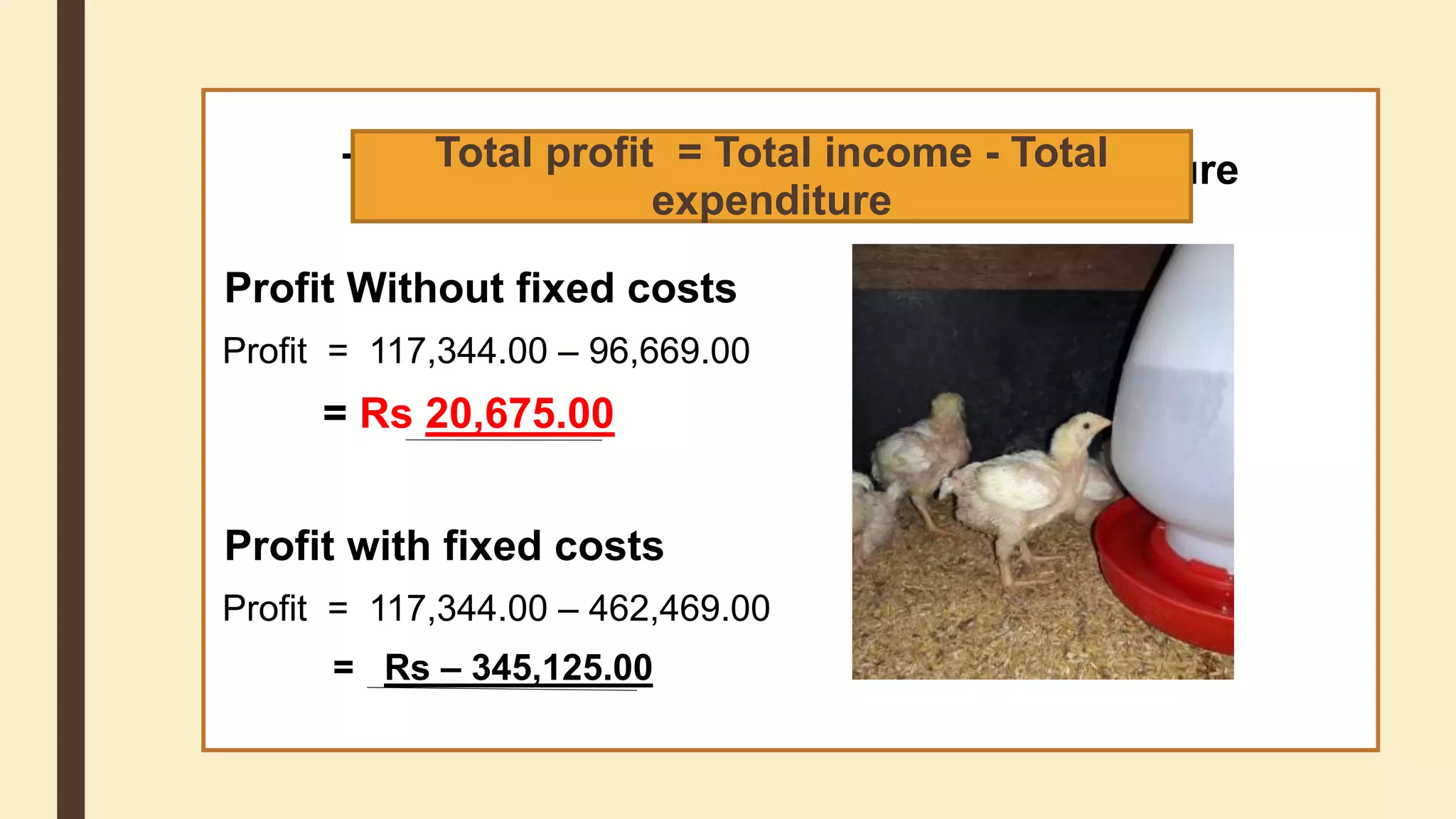
This document discusses the importance of cost analysis for broiler farming projects. It provides examples of fixed costs like land and equipment, and variable costs like feed and chicks. Calculating total expenditures allows farmers to establish goals, reduce risks, and evaluate profits. For the example broiler project, total income was around Rs. 117,344 while total expenditures were approximately Rs. 462,469, resulting in a loss of Rs. 345,125 when factoring in fixed costs like land. Proper management can help reduce costs and improve profits over time.