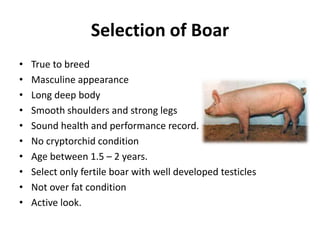
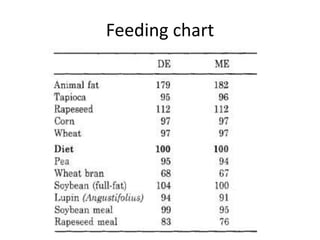
Breeding management for swine involves selecting breeds based on factors like prolificacy, growth ability, temperament, and disease resistance. Key factors in selecting breeding stock include litter size, strength, milking ability, and temperament. Common breeding systems are inbreeding, outbreeding, outcrossing, and crossbreeding between two breeds. Guidelines cover the normal reproduction cycle including age of puberty, breeding, gestation period, litter size, weaning, and farrowing interval. Management involves flushing sows before mating to improve physical condition and increase ovulation and litter size. Heat is detected through vulval changes, discharge, restlessness and immobility to back pressure.