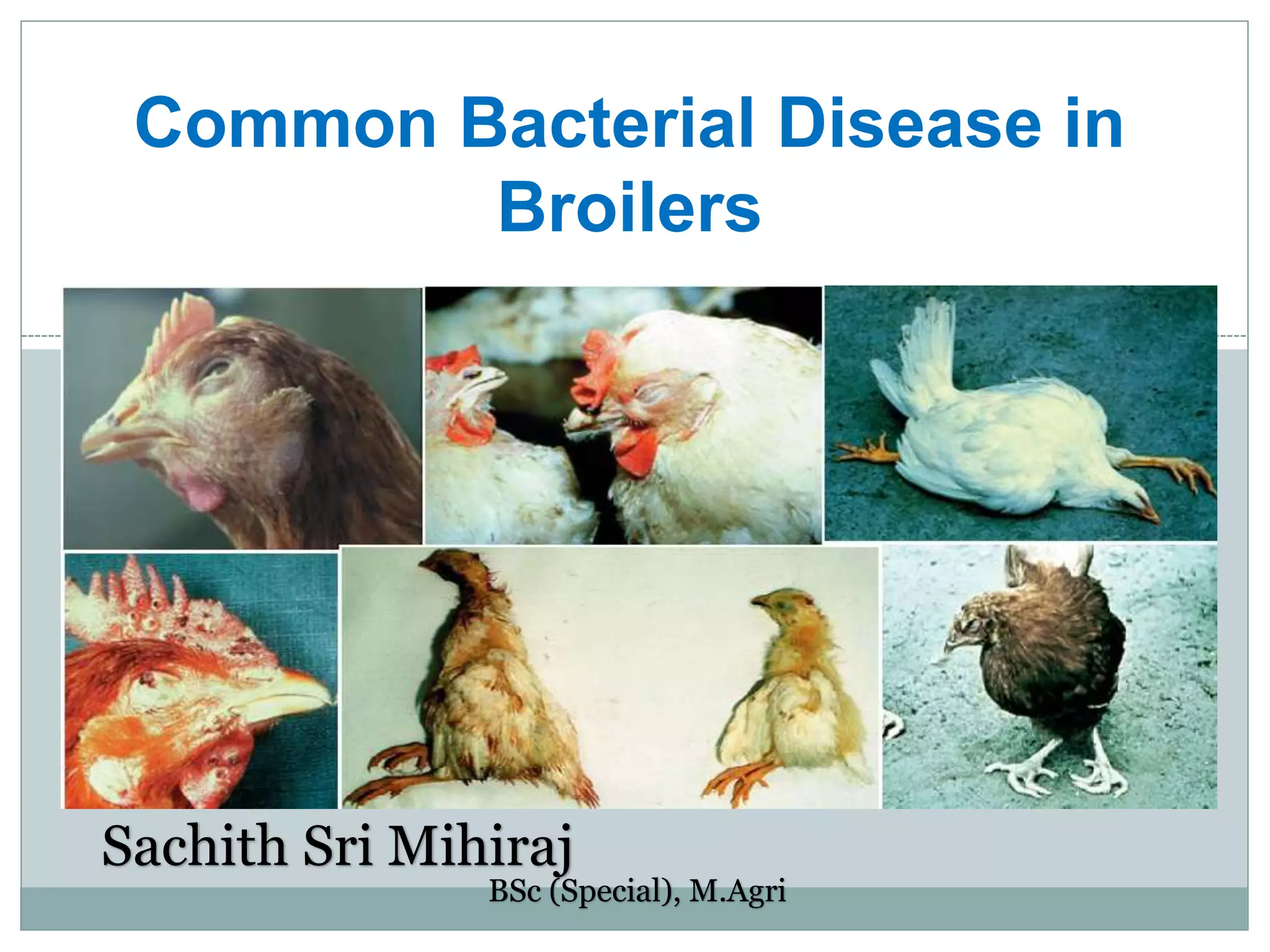
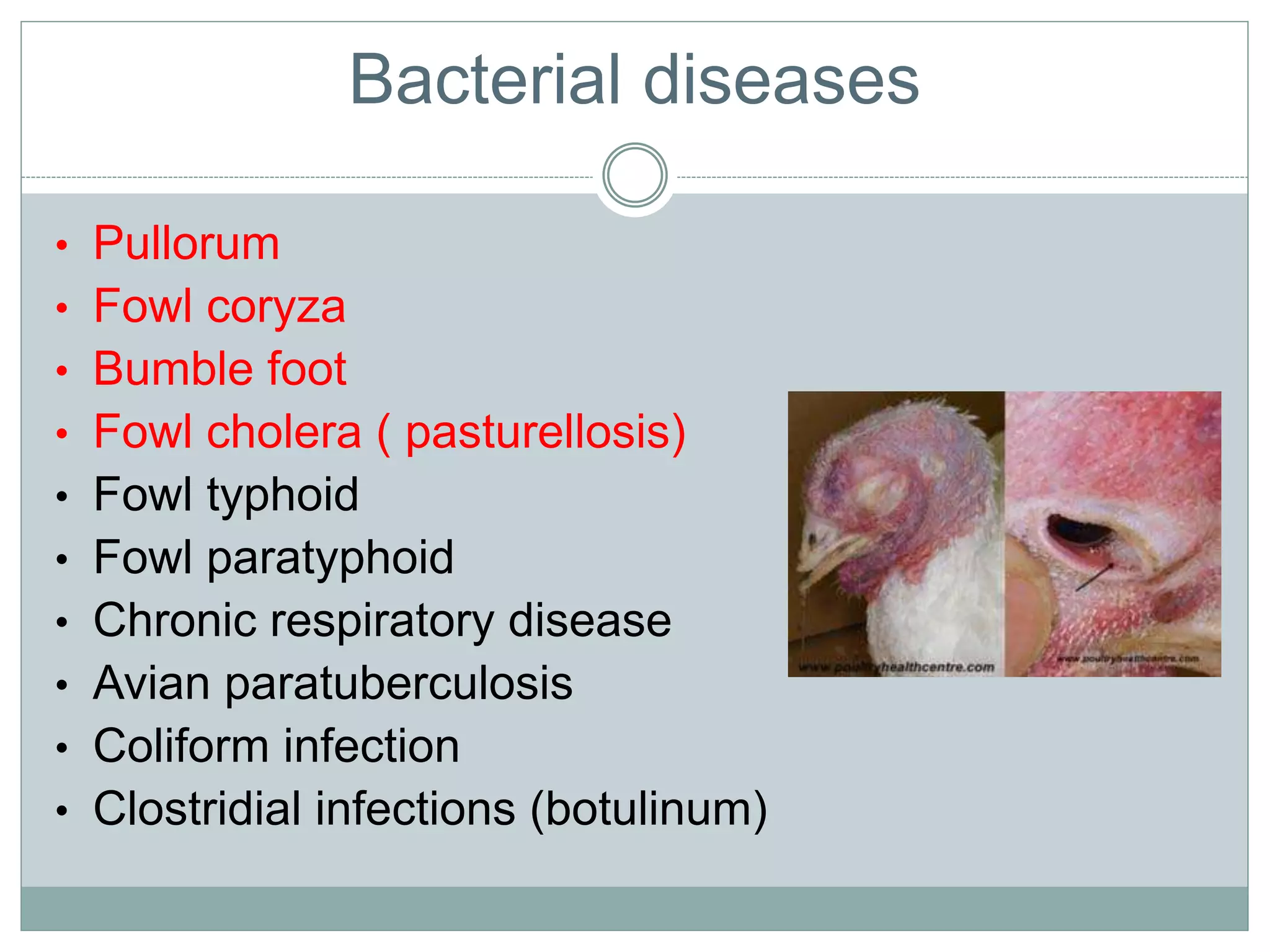
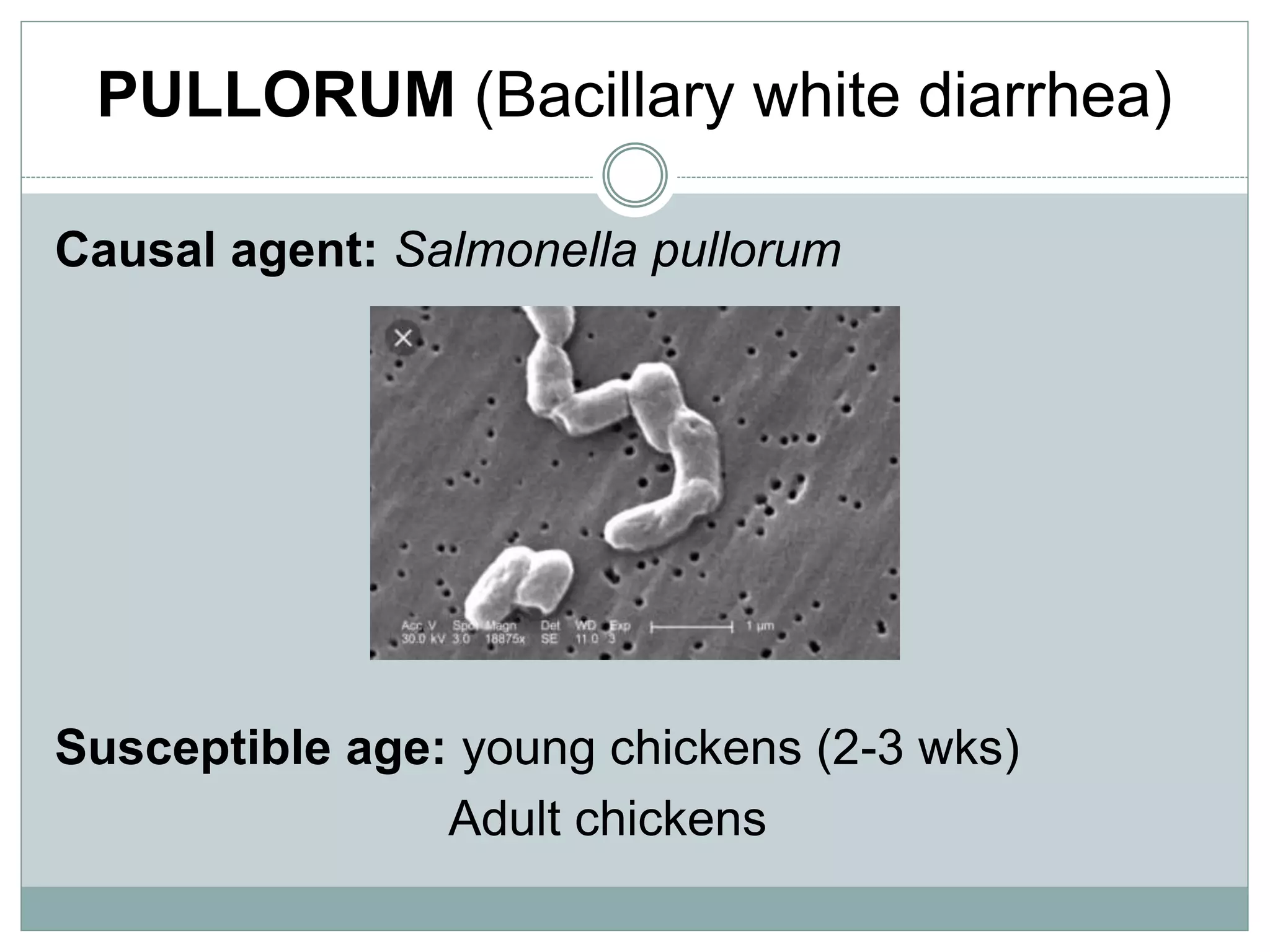
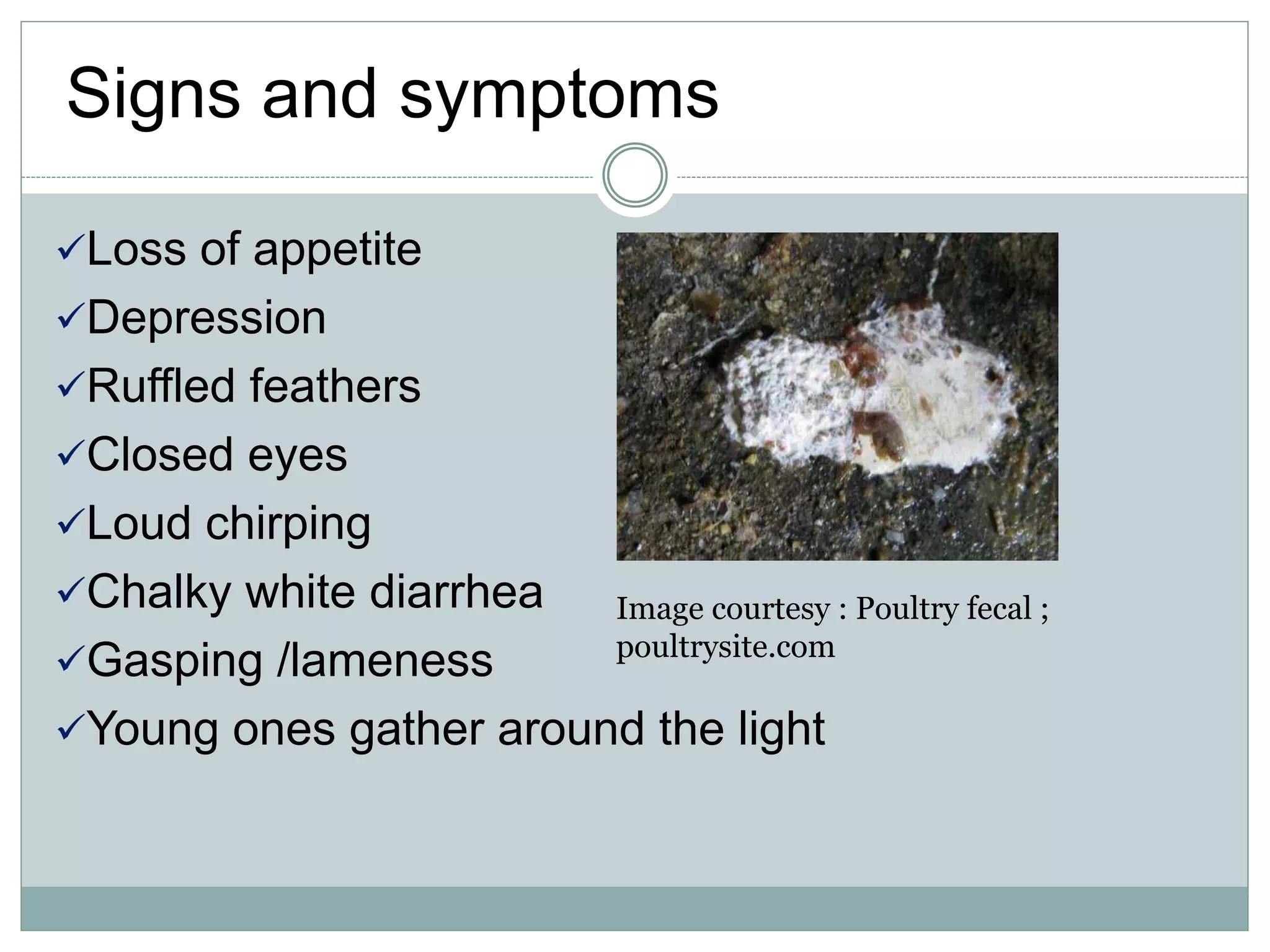
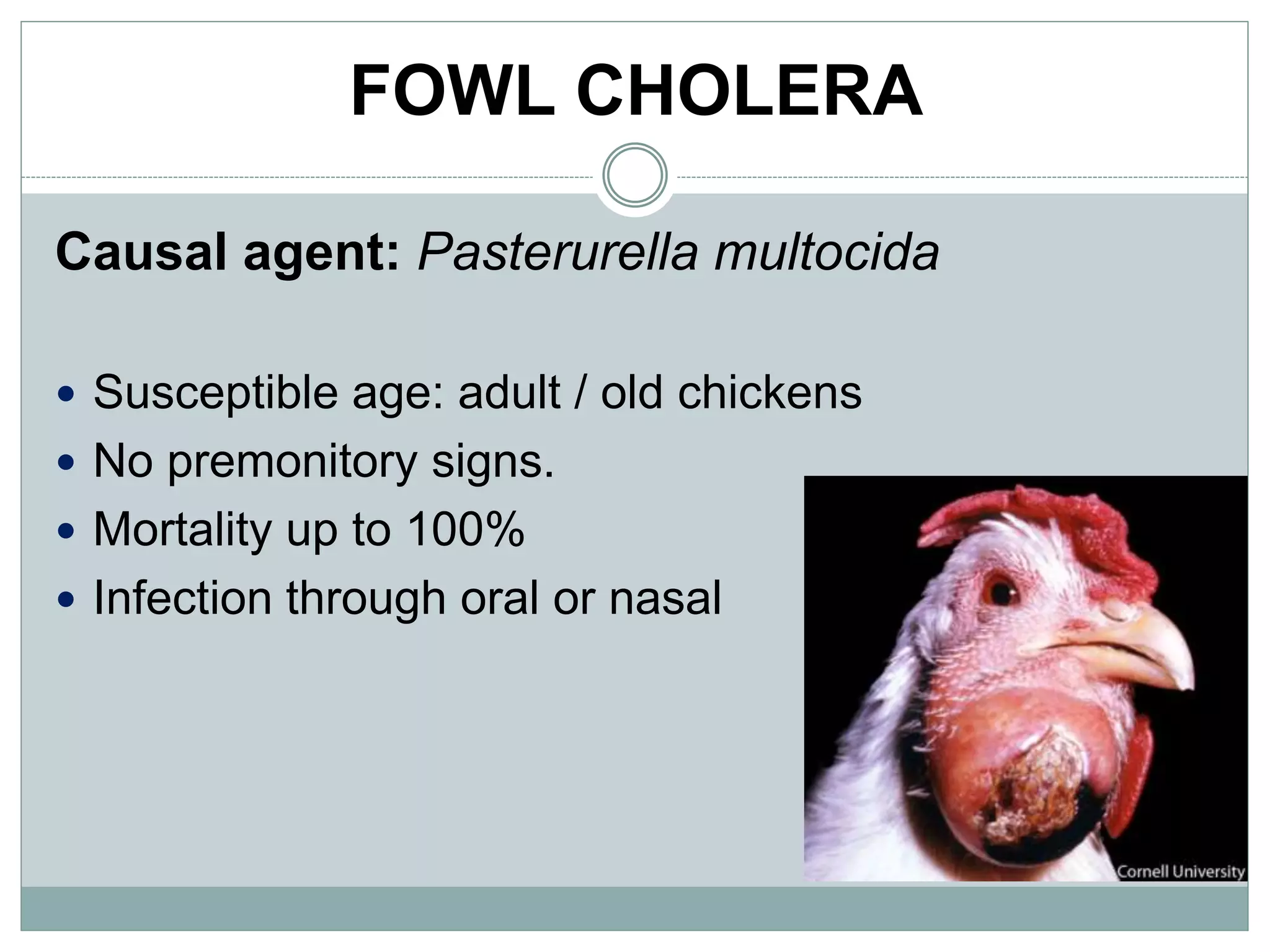
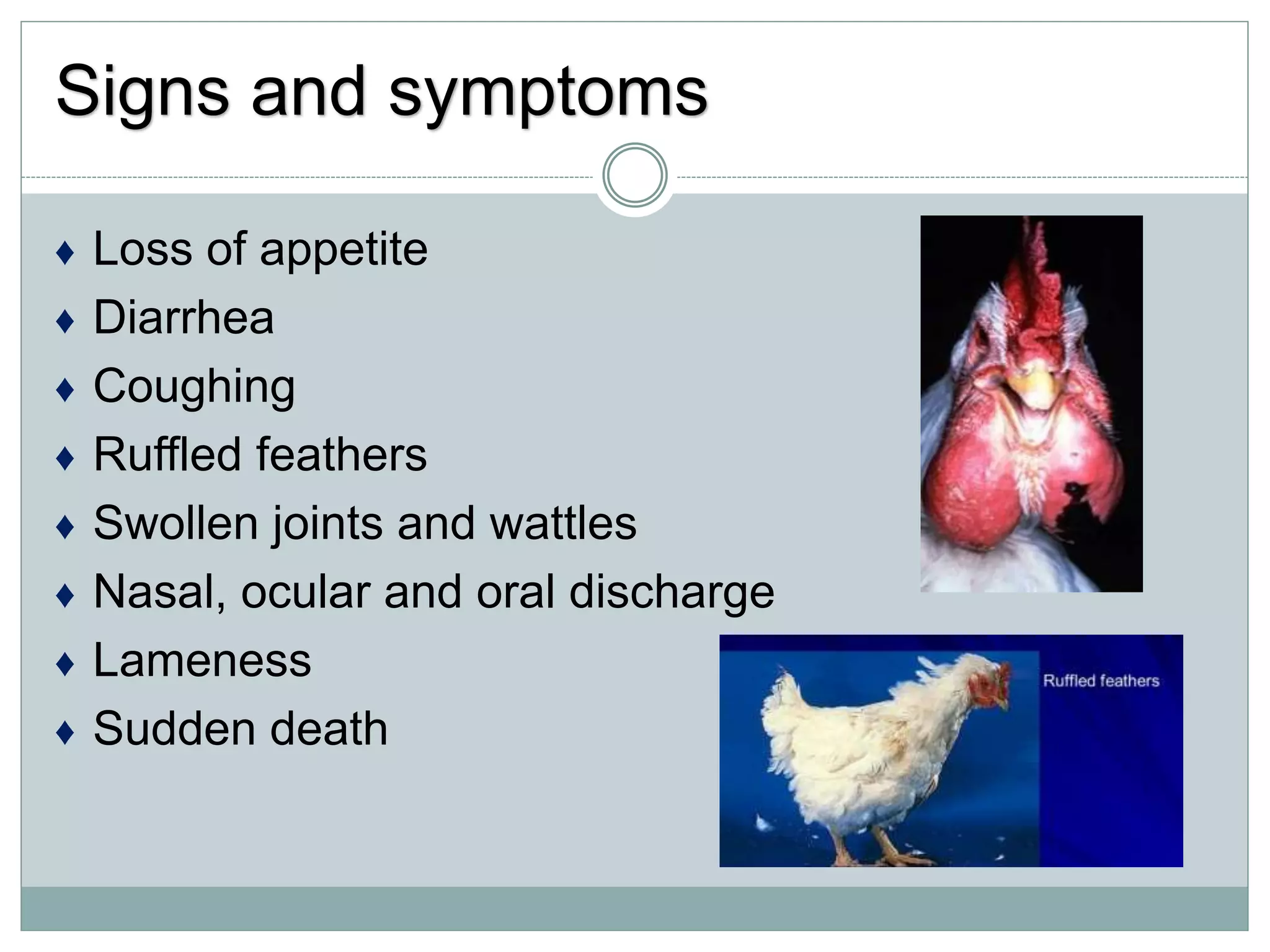
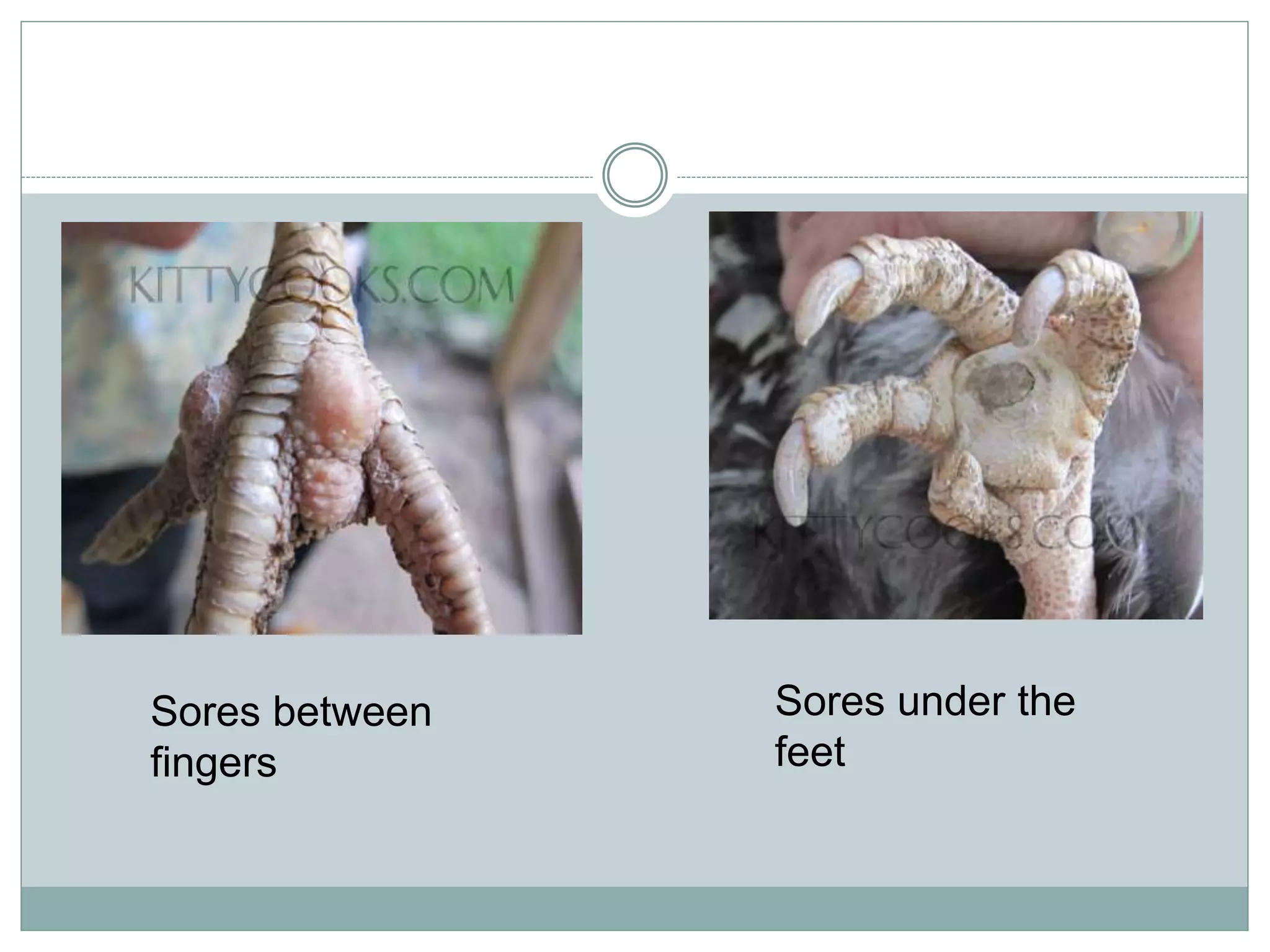
The document discusses common bacterial diseases in broilers, including their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. It highlights specific diseases such as pullorum, fowl cholera, fowl coryza, and bumble foot, detailing the pathogens involved and the preventive measures needed. Treatment methods include antibiotics, vaccinations, and maintaining proper sanitation to control outbreaks.