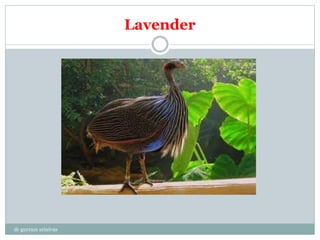
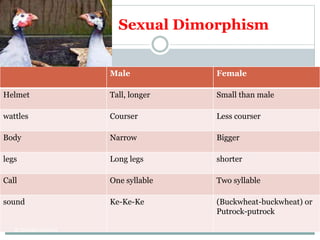
This document discusses rearing guinea fowl, a bird native to Africa that is raised for both meat and eggs. It describes guinea fowl's hardiness and disease resistance compared to other poultry. There are three main varieties - pearl, lavender, and white - as well as hybrids. Guinea fowl reach sexual maturity later than chickens, lay fewer eggs per year, and have lower productivity overall but richer meat. Their management requires less intensive housing and feeding than other poultry due to their foraging ability but still benefits from standard brooding and feeding practices. Guinea fowl have higher innate disease resistance than other poultry.