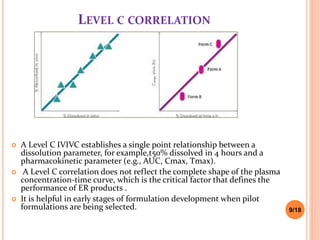
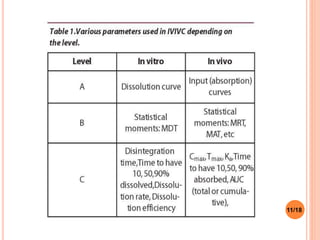
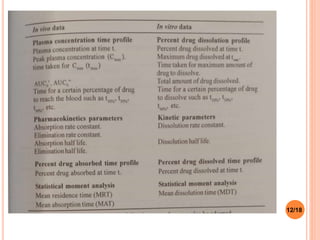
This document discusses the correlation of in vivo drug data with in vitro dissolution data. It begins by defining in vitro-in vivo correlation (IVIVC) as a predictive mathematical model relating an in vitro property like dissolution rate to an in vivo response like plasma drug concentration. The objectives of IVIVC include reducing human testing and regulatory burdens. There are different levels of IVIVC - Level A provides the closest correlation while Level D is only qualitative. Level A correlates dissolution directly to absorption rate while Level C relates a parameter like AUC to a dissolution parameter. IVIVC can be used to justify formulation and process changes without additional human studies.