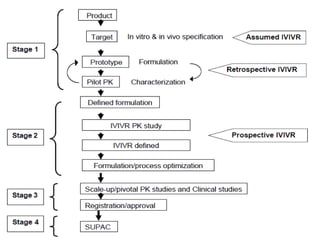
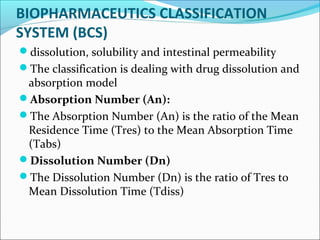
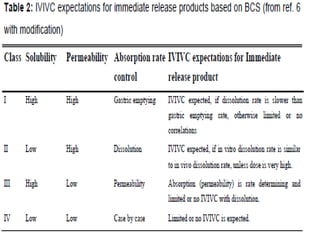
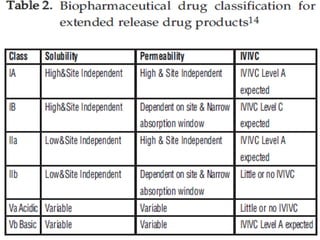
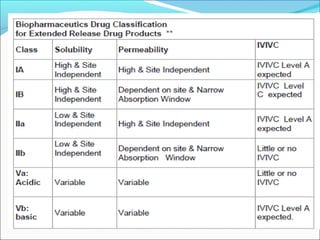
The document discusses In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation (IVIVC), outlining its definitions, correlation levels, and applications in pharmaceutical development to minimize human testing. It describes five correlation levels, from Level A, which establishes a direct relationship between in vitro and in vivo data, to Level D, which is a qualitative analysis. Additionally, it introduces the Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) focusing on drug dissolution, solubility, and absorption metrics.