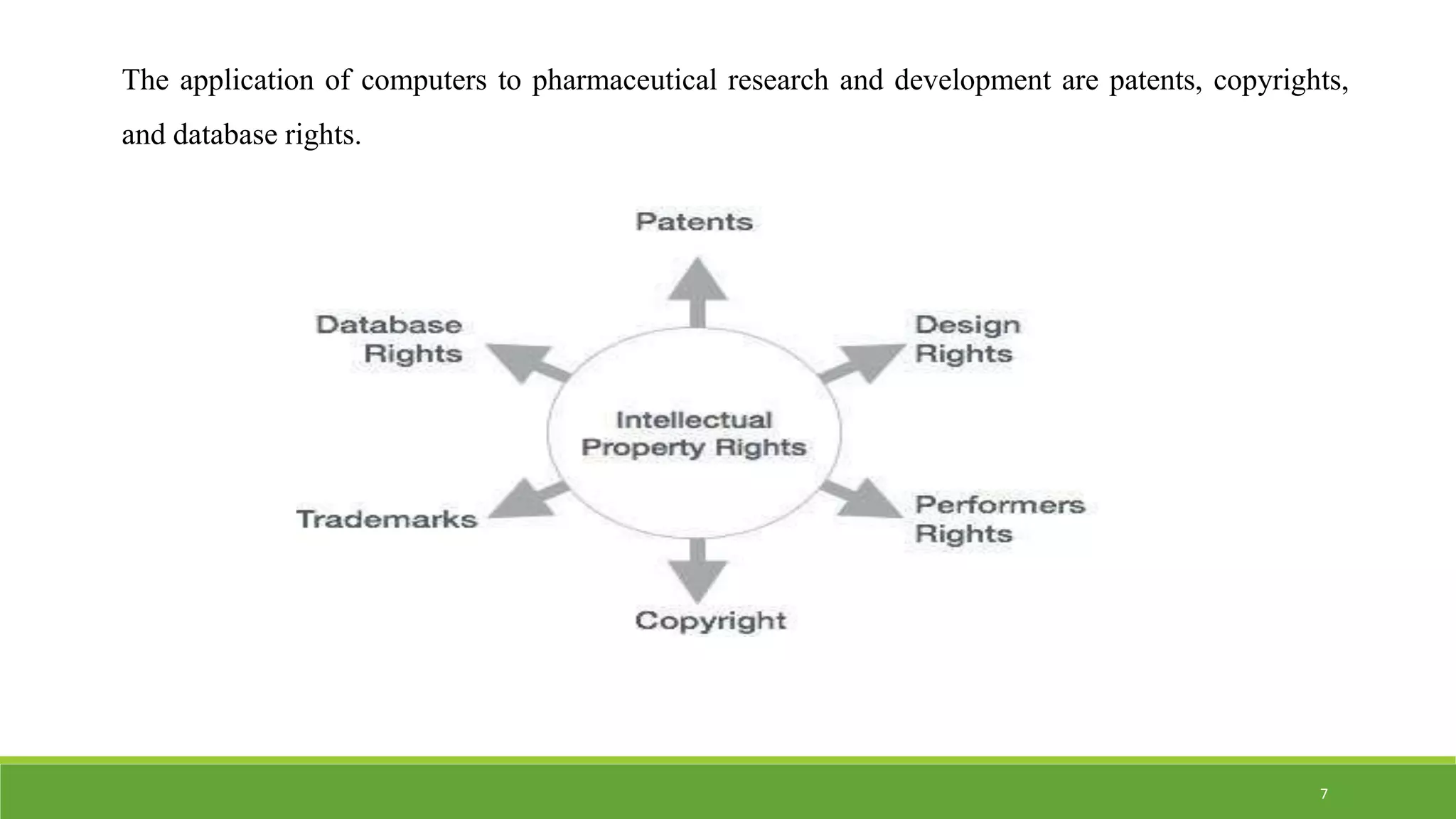
The document discusses the legal protection of innovative computer uses in pharmaceutical research and development, emphasizing the need for combined intellectual property (IP) strategies from pharmacology and computer science. It covers various types of IP rights, including patents, copyrights, and trade secrets, and highlights the challenges in patenting algorithms and bioinformatics. The conclusion notes the prevalence of computers in drug development and the importance of enforcing IP rights in this field.