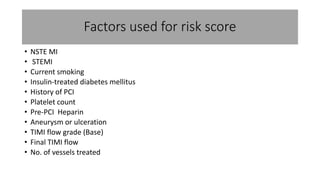
This document discusses coronary stent thrombosis, a serious complication of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). It outlines risk factors and prevention strategies. Key points include:
- Stent thrombosis is a nightmare for cardiologists and can have various causes, including patient factors, lesion characteristics, technical issues, and non-adherence to dual antiplatelet therapy.
- Prevention through optimal stent deployment, complete coverage of the lesion, and adherence to prolonged dual antiplatelet therapy are critical to minimizing the risk of stent thrombosis.
- Intravascular imaging can help identify issues like incomplete stent expansion or apposition that may lead to thrombosis.
- Large clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of newer antiplatelet regimens like











![TECHNIQUE
• Newer generation stent(OK)
• Expansion[No residue]
• Apposition [full length]
• Dissections[No residual-IVUS]
• Provisional stenting[Preferred]
• Crush and Culotte[Discourage]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coronarystentthrombosis-141024131056-conversion-gate01/85/Coronary-stent-thrombosis-13-320.jpg)


![Subha Diwali 2014
• Light for ST is not enough what is
given here,You have to light it for
yourself from today[23-10-2014]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coronarystentthrombosis-141024131056-conversion-gate01/85/Coronary-stent-thrombosis-16-320.jpg)