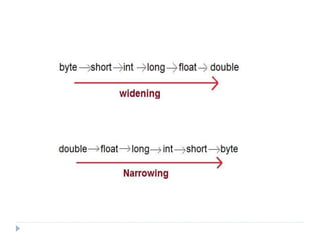
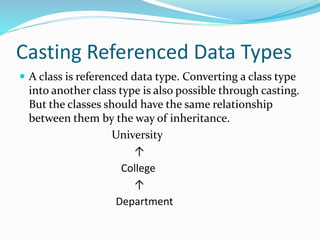
Type casting is the process of converting an object or variable from one data type to another, with widening being the safe conversion from a lower to a higher data type, and narrowing being the potentially unsafe conversion from a higher to a lower data type. Data types are categorized into primitive and referenced types, with type casting possible between classes that have an inheritance relationship. Generalization and specialization describe the phenomena of promoting subclasses to superclasses and narrowing superclasses to subclasses, respectively.






![Widening in referenced data
types
ClassTest
{
public static void main{String args[]}
{
One o;
o = (One) newTwo();
o.show1();
}
}
Note : we are able to access show1() method of the super
class. But in this case, it is not possible to call show2().](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typecasting-190704071938/85/Type-casting-9-320.jpg)
