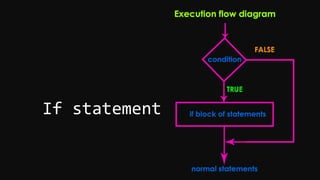
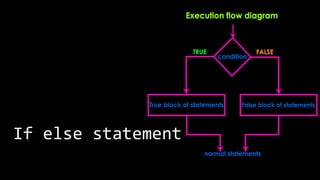
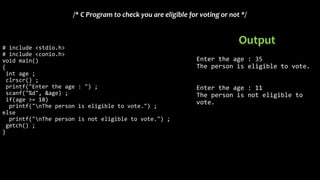
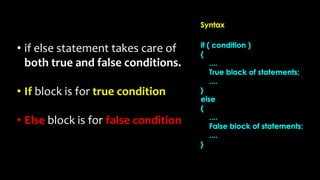
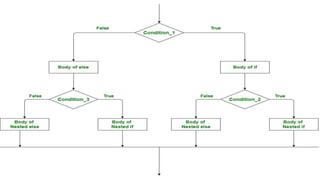
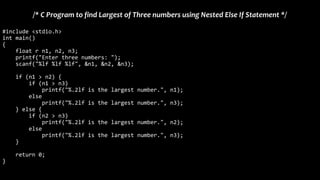
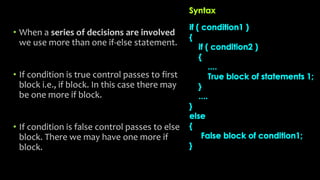
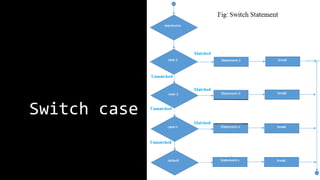
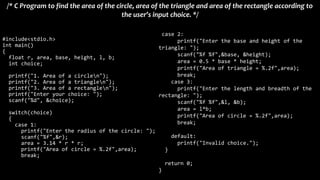
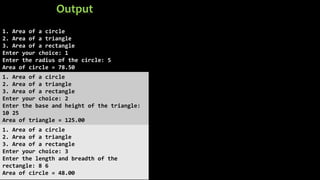
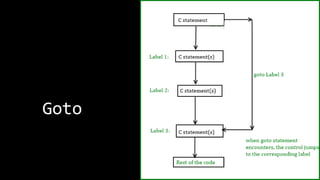
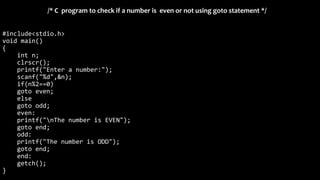
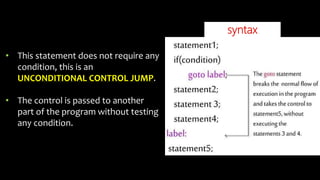
The document explains various branching statements in programming, particularly focusing on C language constructs for decision-making like 'if', 'else', 'switch-case', and 'goto'. It provides code examples for each statement type to demonstrate their application in determining control flow based on conditions, such as checking voting eligibility and calculating areas of geometric shapes. Additionally, it describes nested if statements for more complex decision-making scenarios.