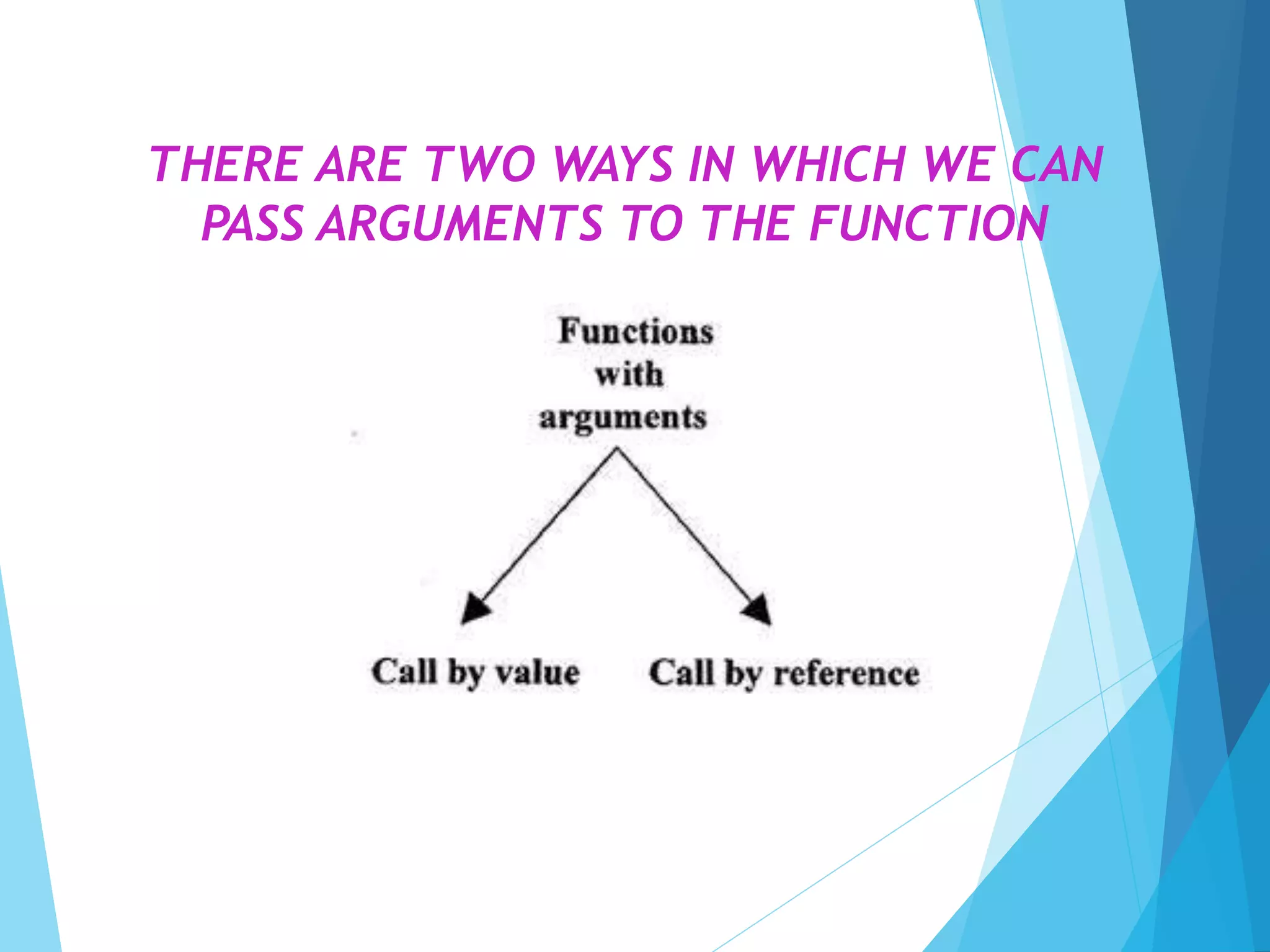
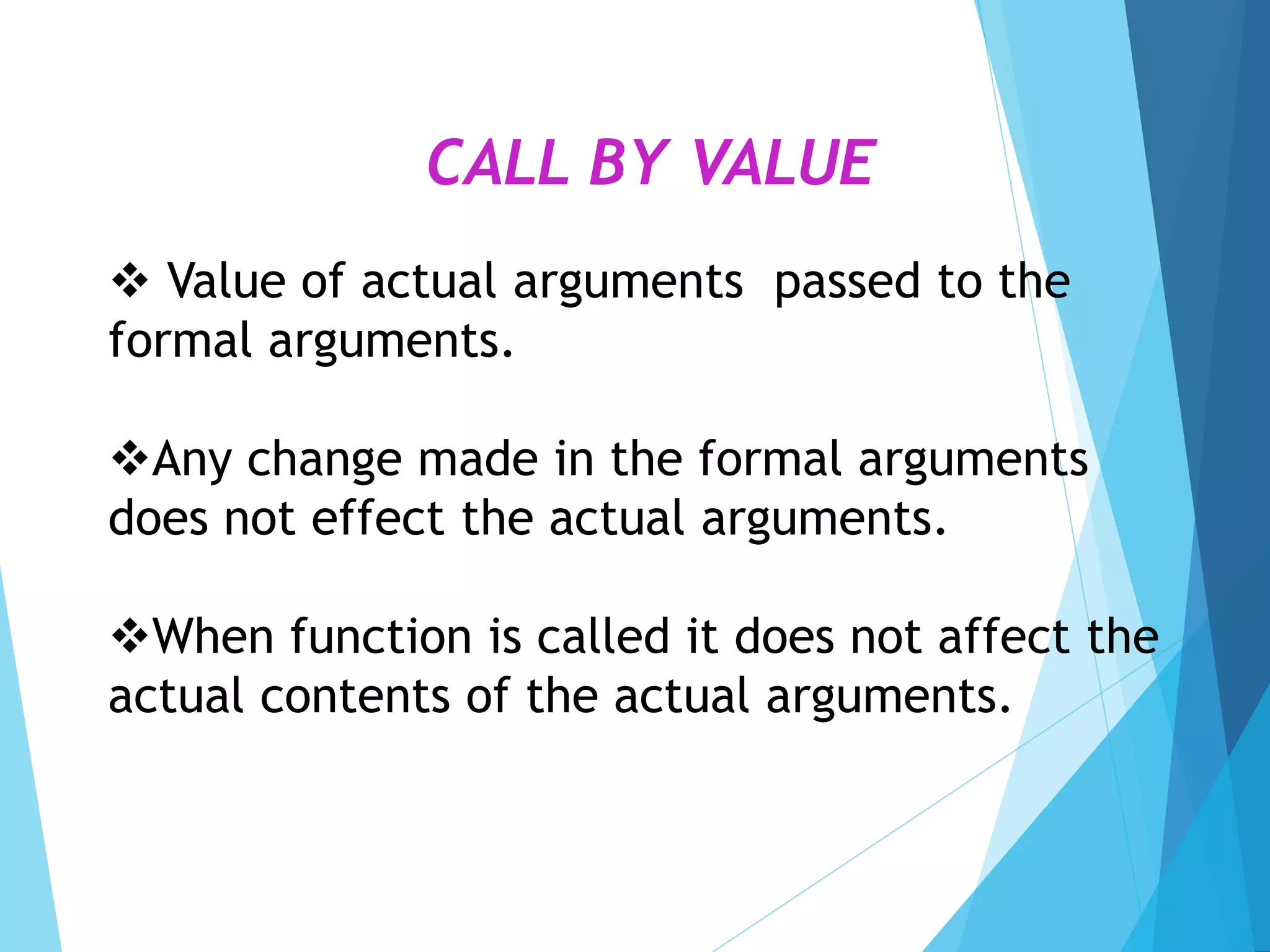
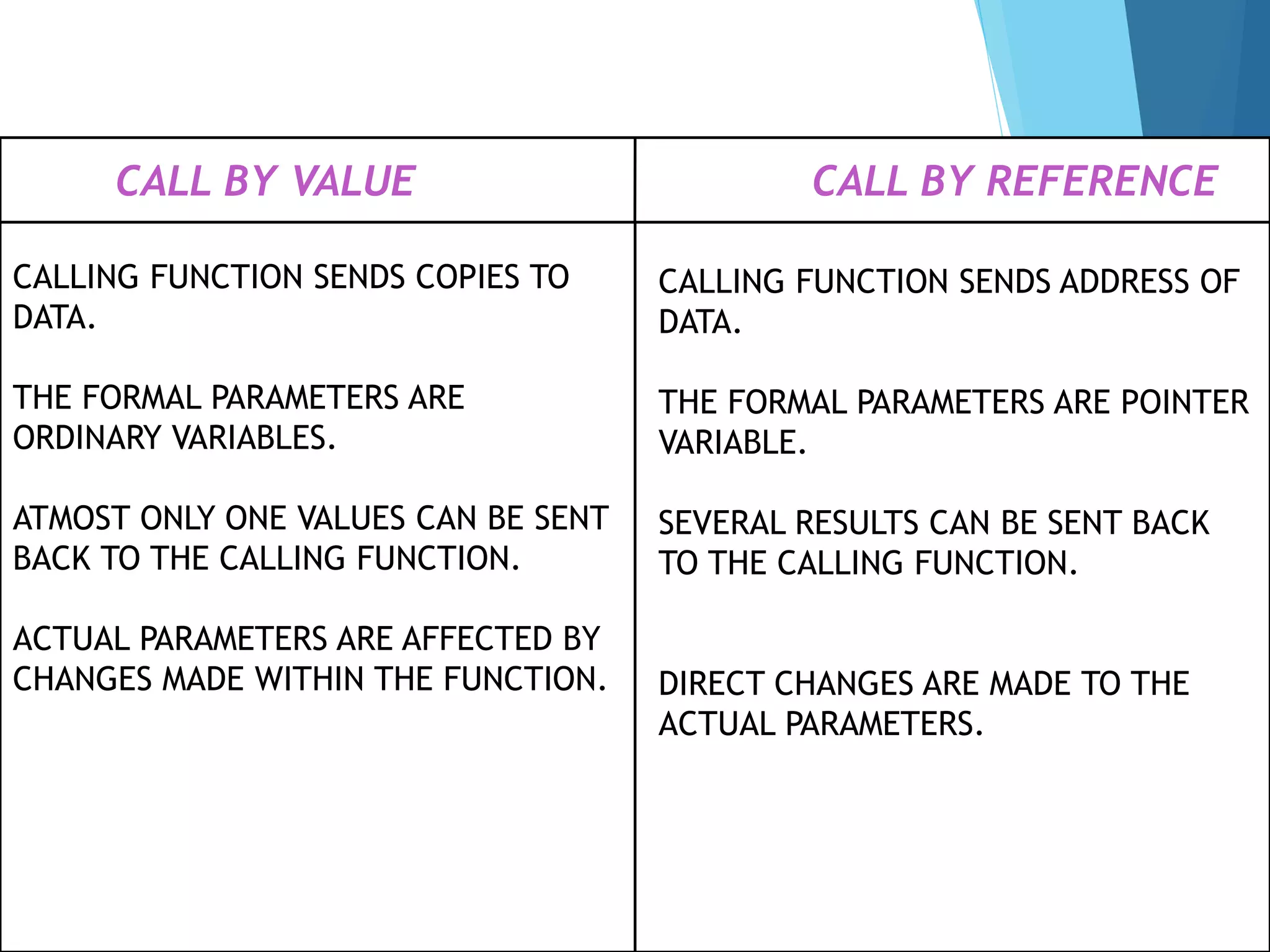
The document discusses call by value and call by reference in functions. Call by value passes the actual value of an argument to the formal parameter, so any changes made to the formal parameter do not affect the actual argument. Call by reference passes the address of the actual argument, so changes to the formal parameter do directly modify the actual argument. An example program demonstrates call by value, where changing the formal parameter does not change the original variable.