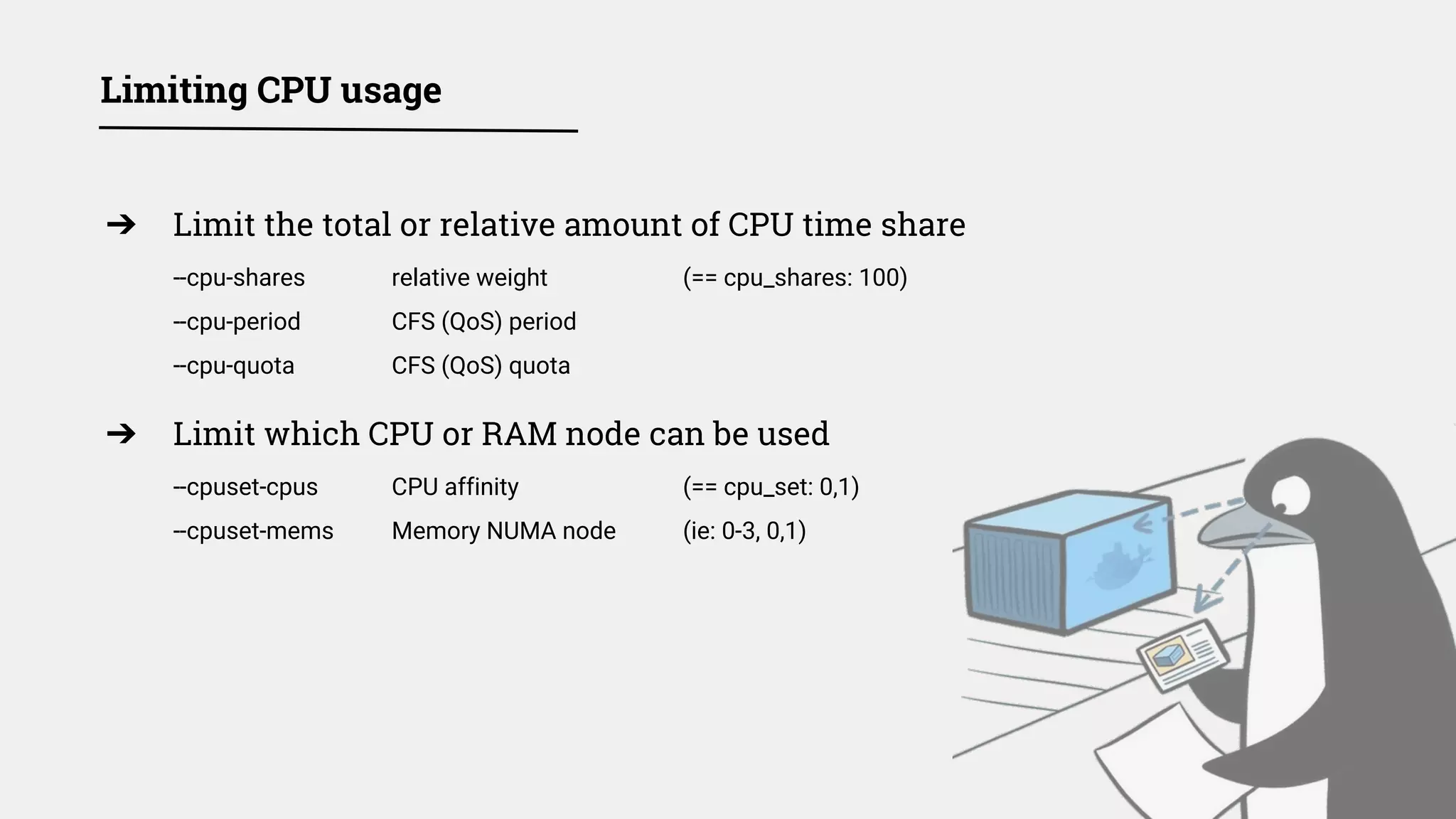
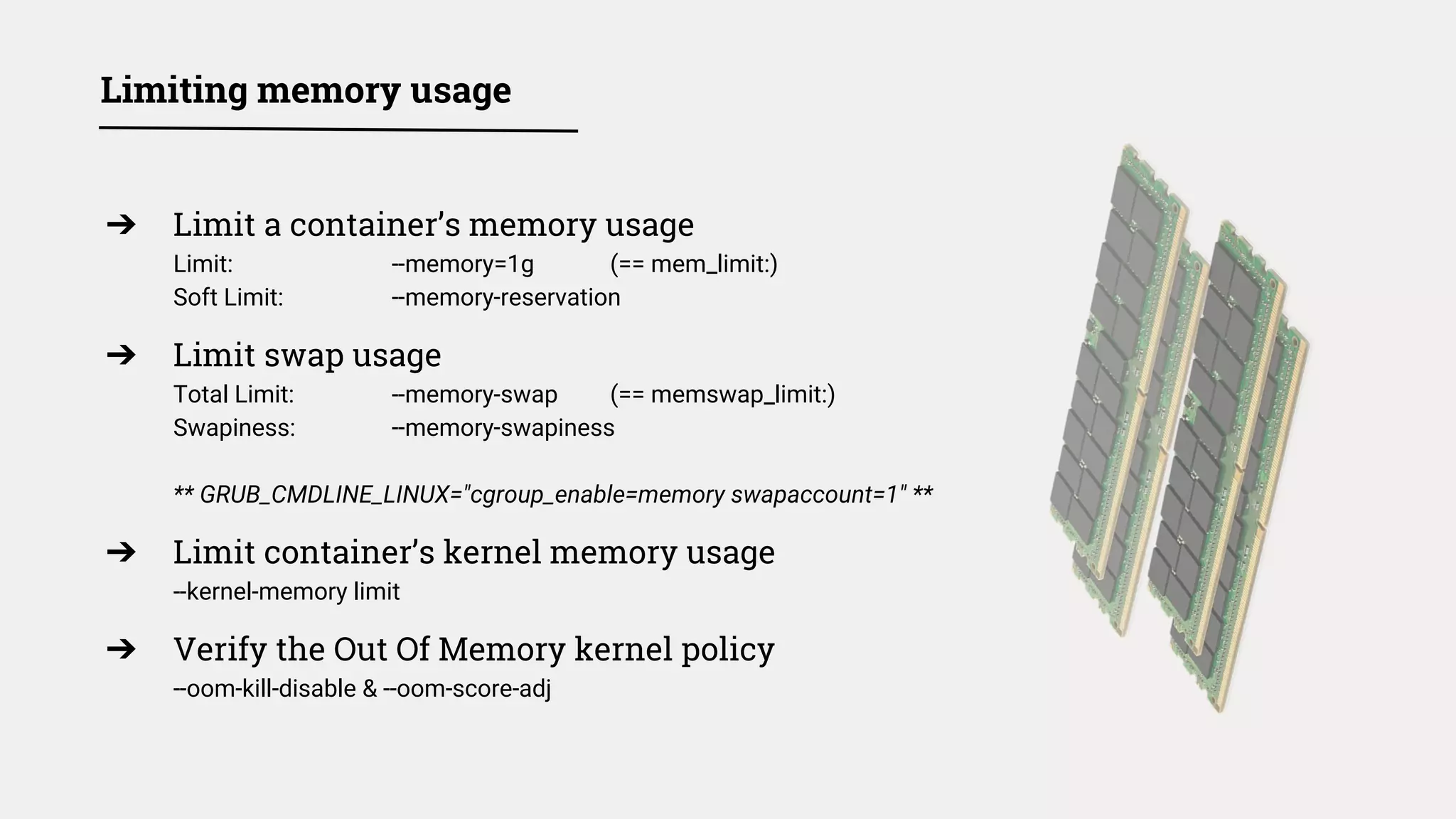
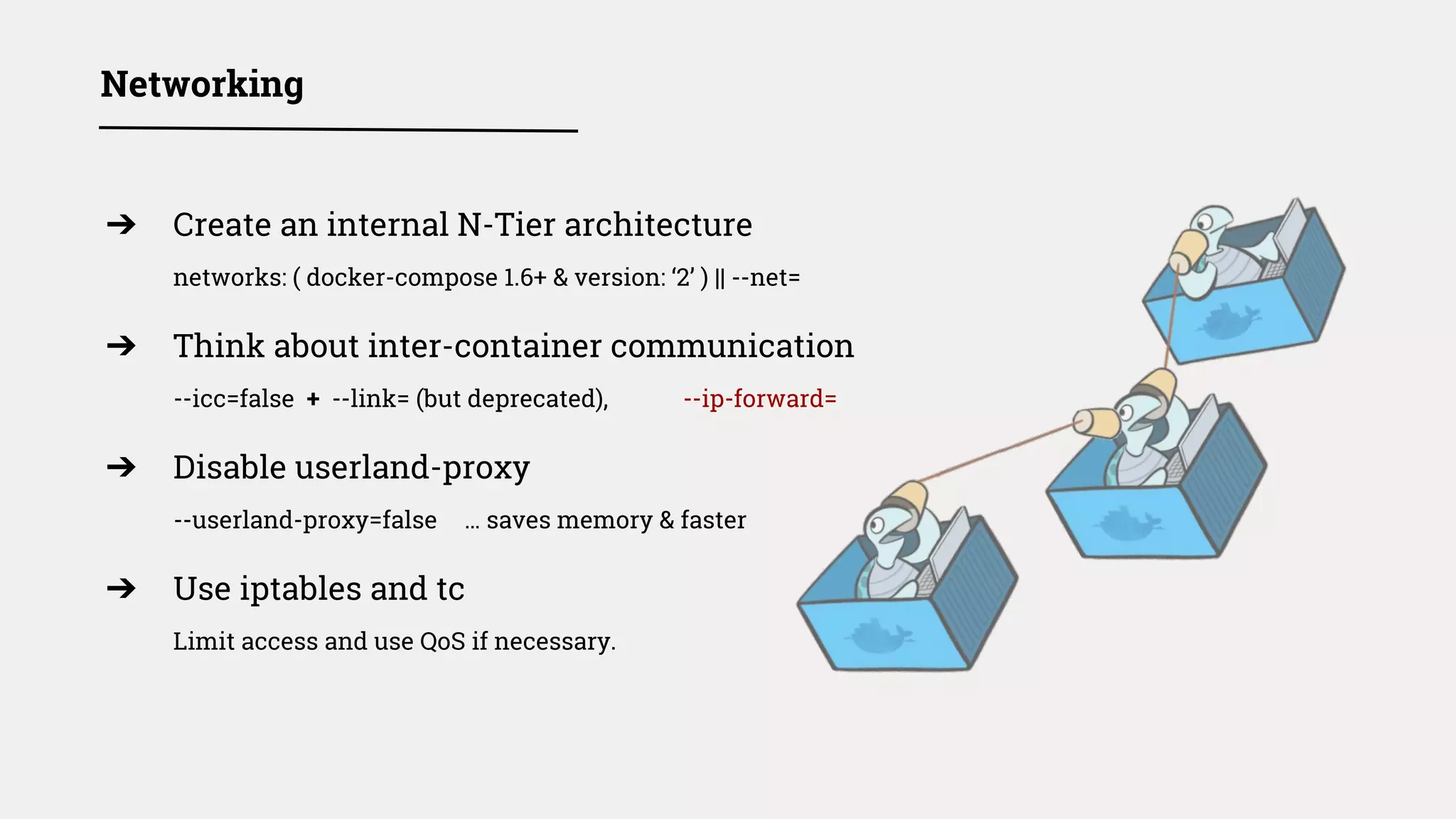
The document discusses various security measures and best practices for ensuring Docker security in production environments, particularly within CI/CD pipelines. It covers topics such as container orchestration, secret management, resource limits, and the importance of keeping binaries updated. The document emphasizes the need for monitoring, proper configuration, and a robust defense against potential vulnerabilities and attacks.






![➔ Swarm init / join
Expose master nodes carefully (hold cluster’s secrets)
Mutually auth. TLS, AES-GCM, 12 hours key rotation (Gossip / Raft)
➔ Use overlay network encryption
docker network create -d overlay -o encrypted mynet
- Keys shared with tasks & services, but not «docker run»
➔ Mutually authenticate your microservices too
Microservices should not rely on overlay encryption:
Authenticate & Encrypt [container ↔ container] communications
➔ «docker-compose bundle» - experimental status
Lacks support for most useful runtime security options, maybe in 1.13+?
Swarm Networking [1.12+]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dockersecurity2016-160902182951/75/Docker-Security-in-Production-Overview-16-2048.jpg)


