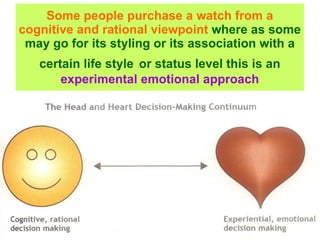
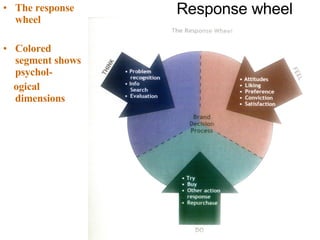
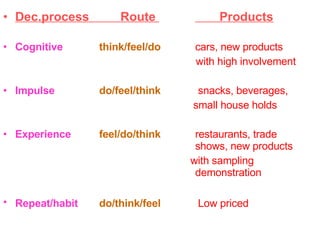
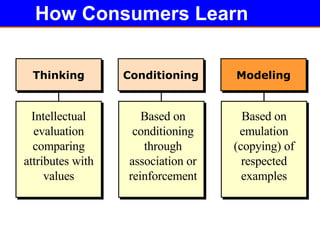
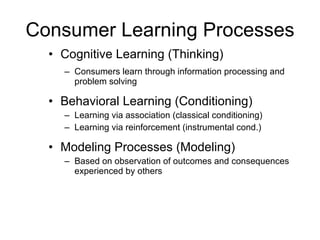
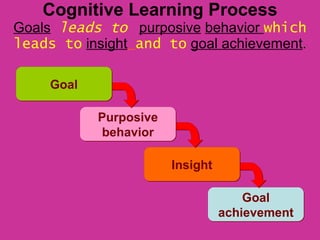
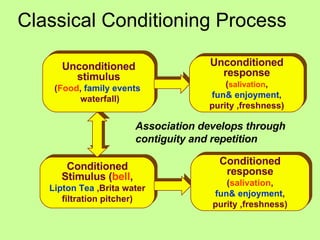
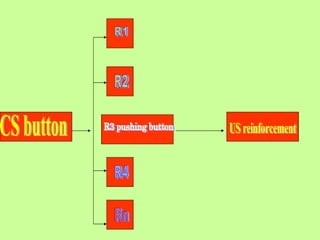
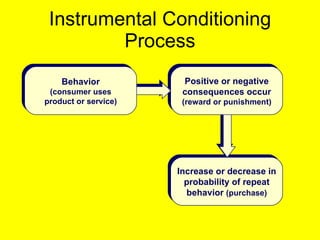
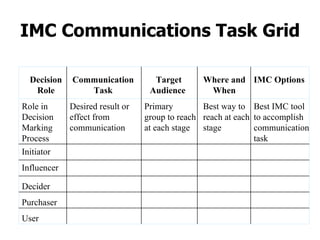
Variations in consumer decision making depend on the type of product and level of involvement. People learn through different processes such as cognitive learning, behavioral learning through conditioning, and modeling from others. Marketers aim to influence consumer learning and decision making through various tools and strategies. Cultural and social factors also impact consumer behavior.