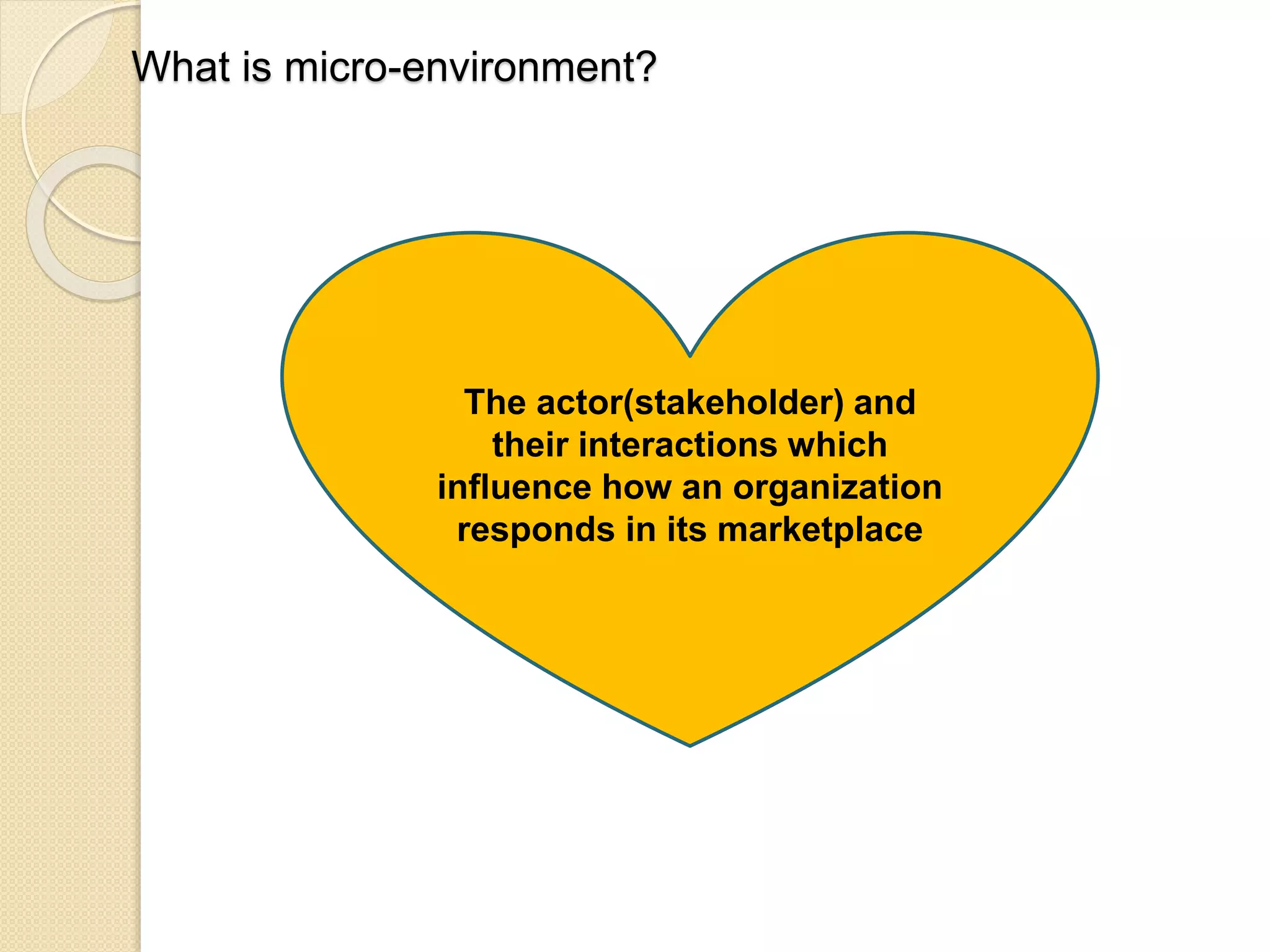
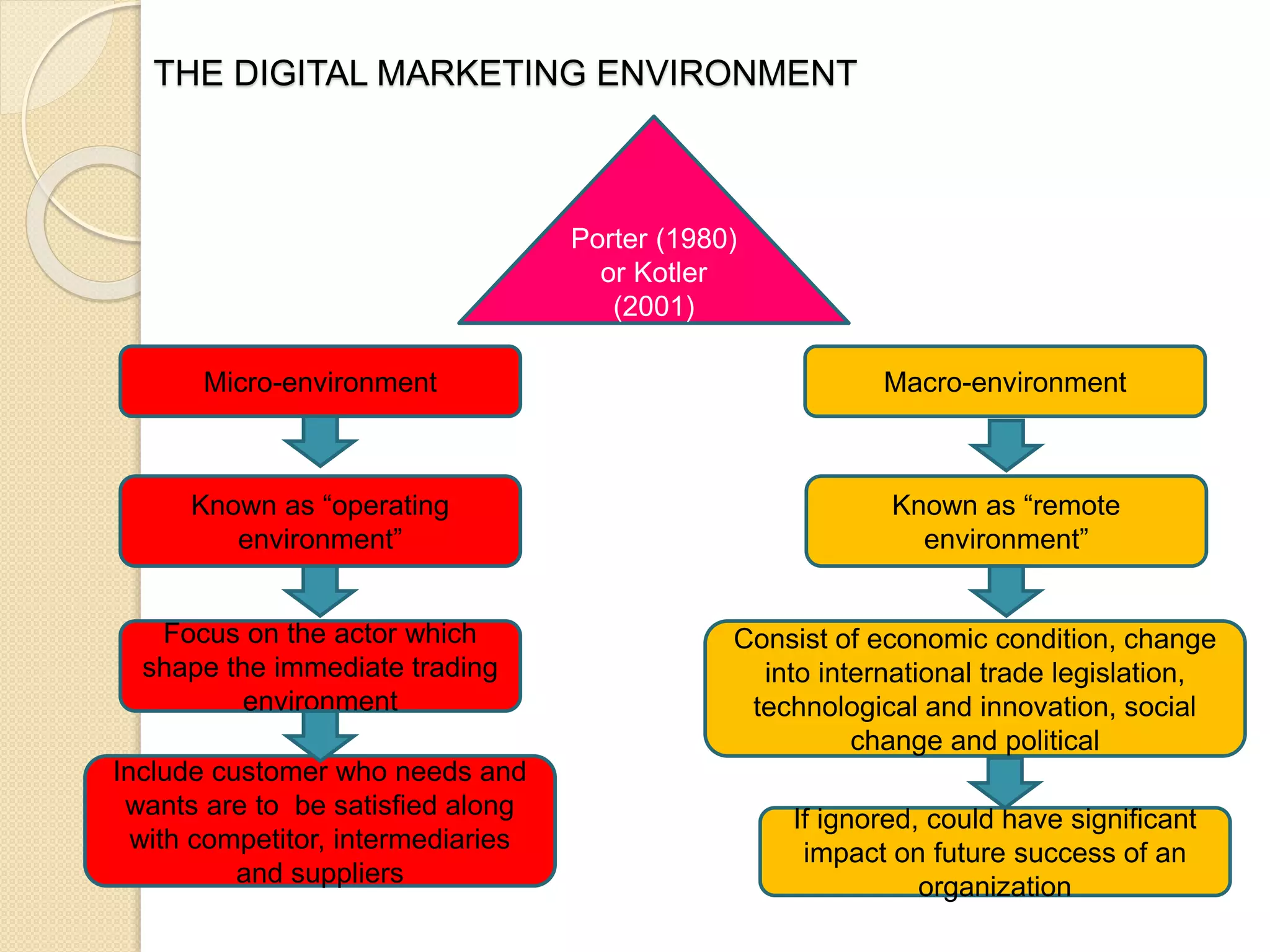
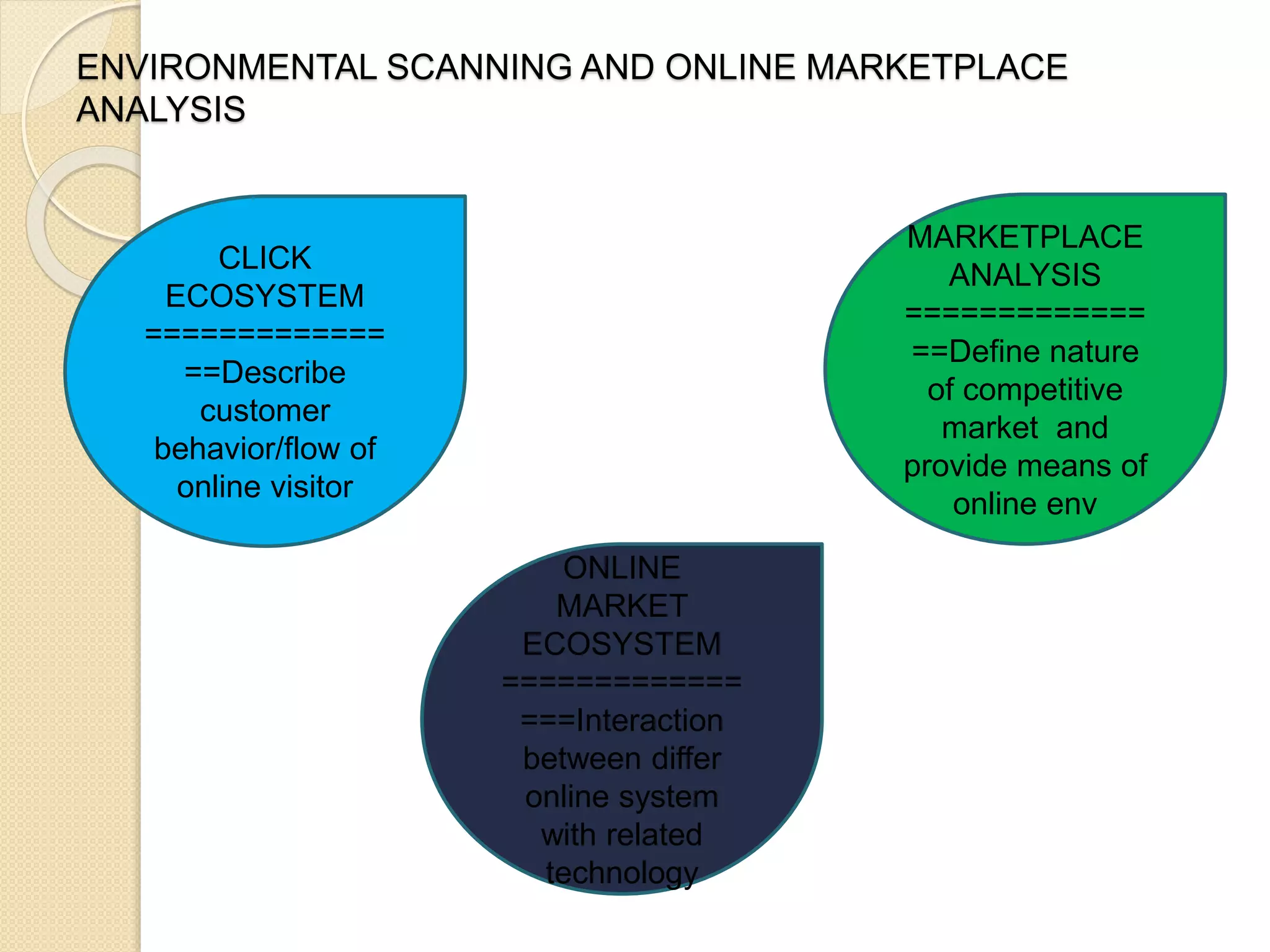
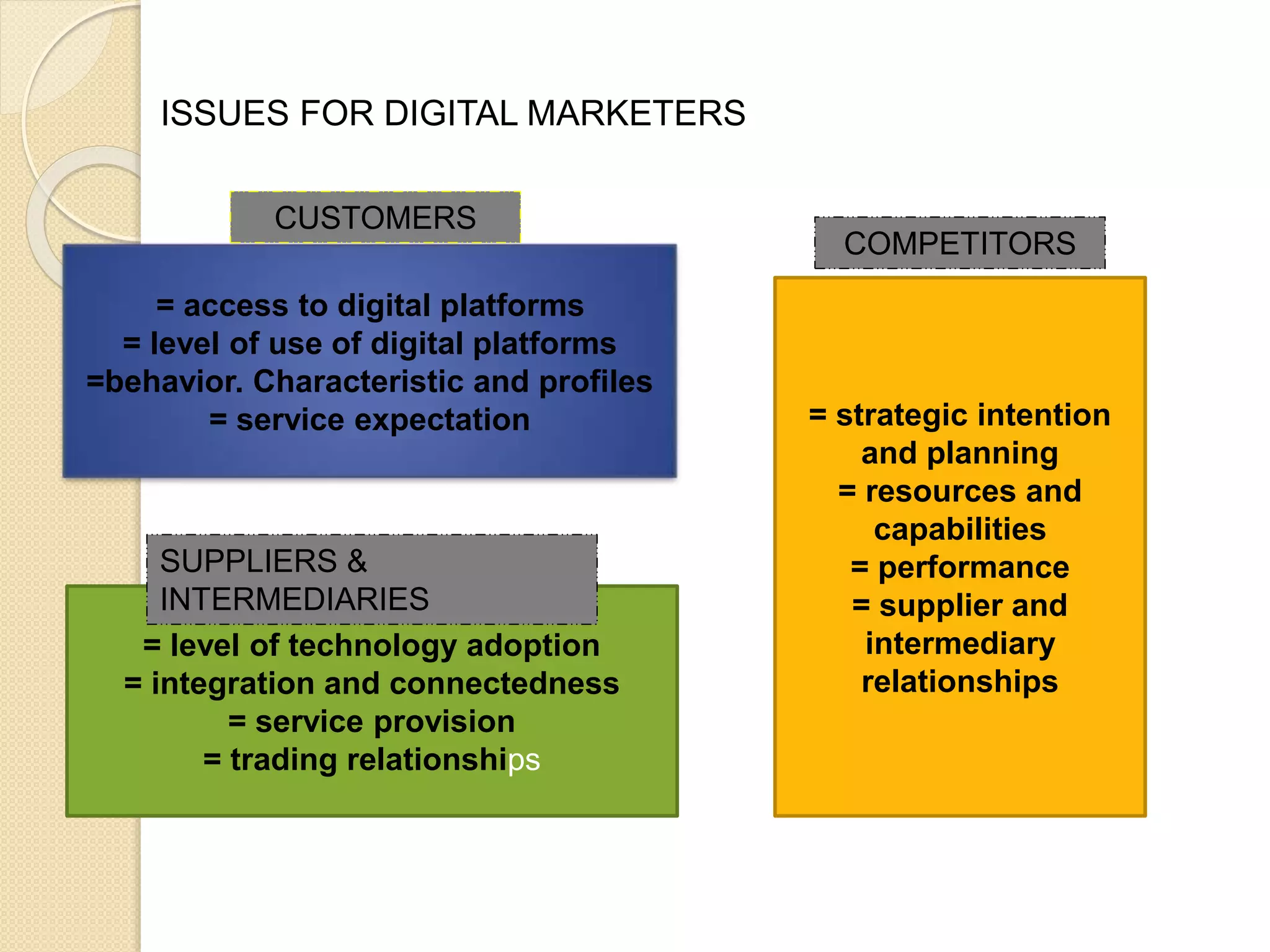
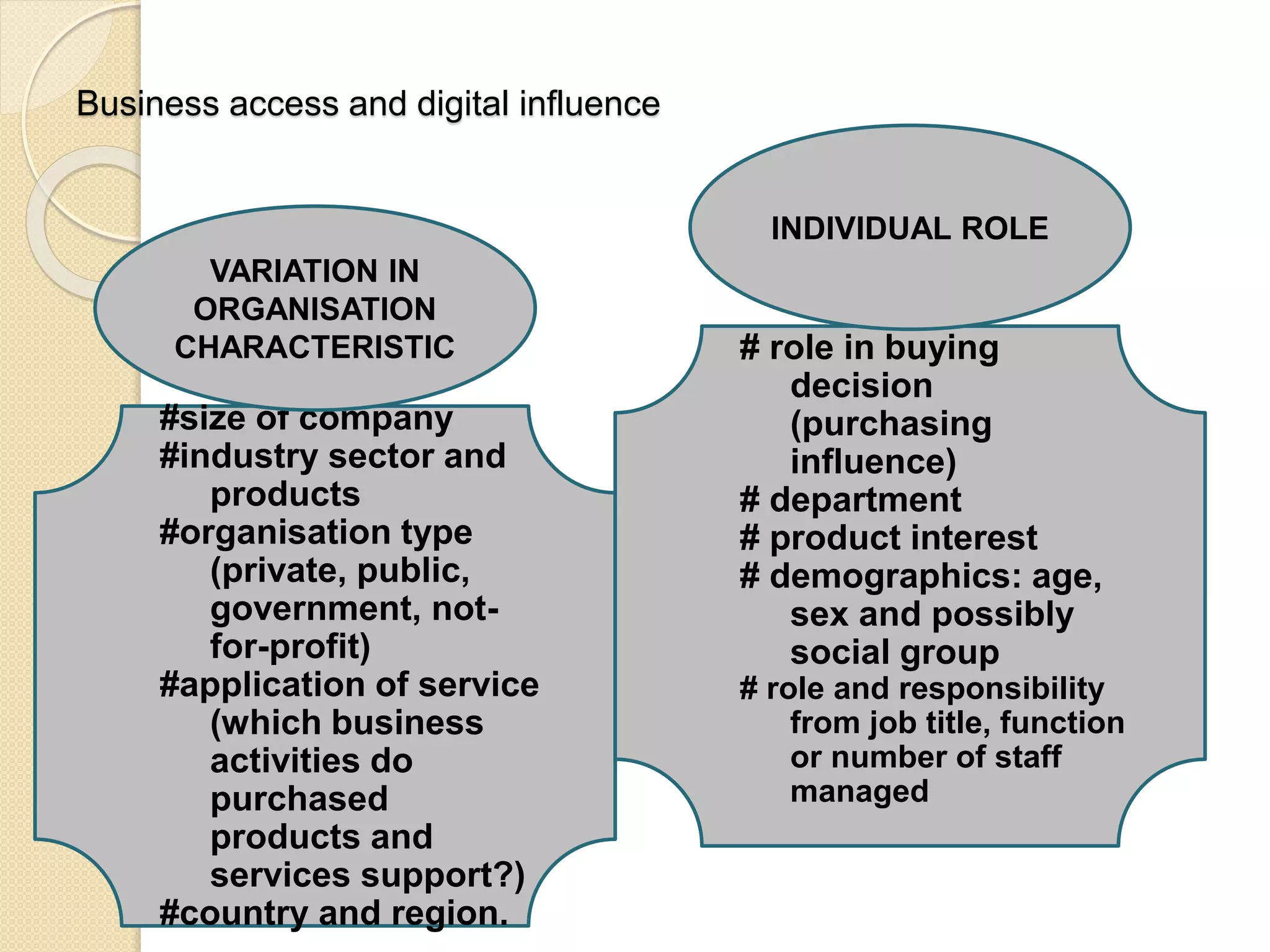
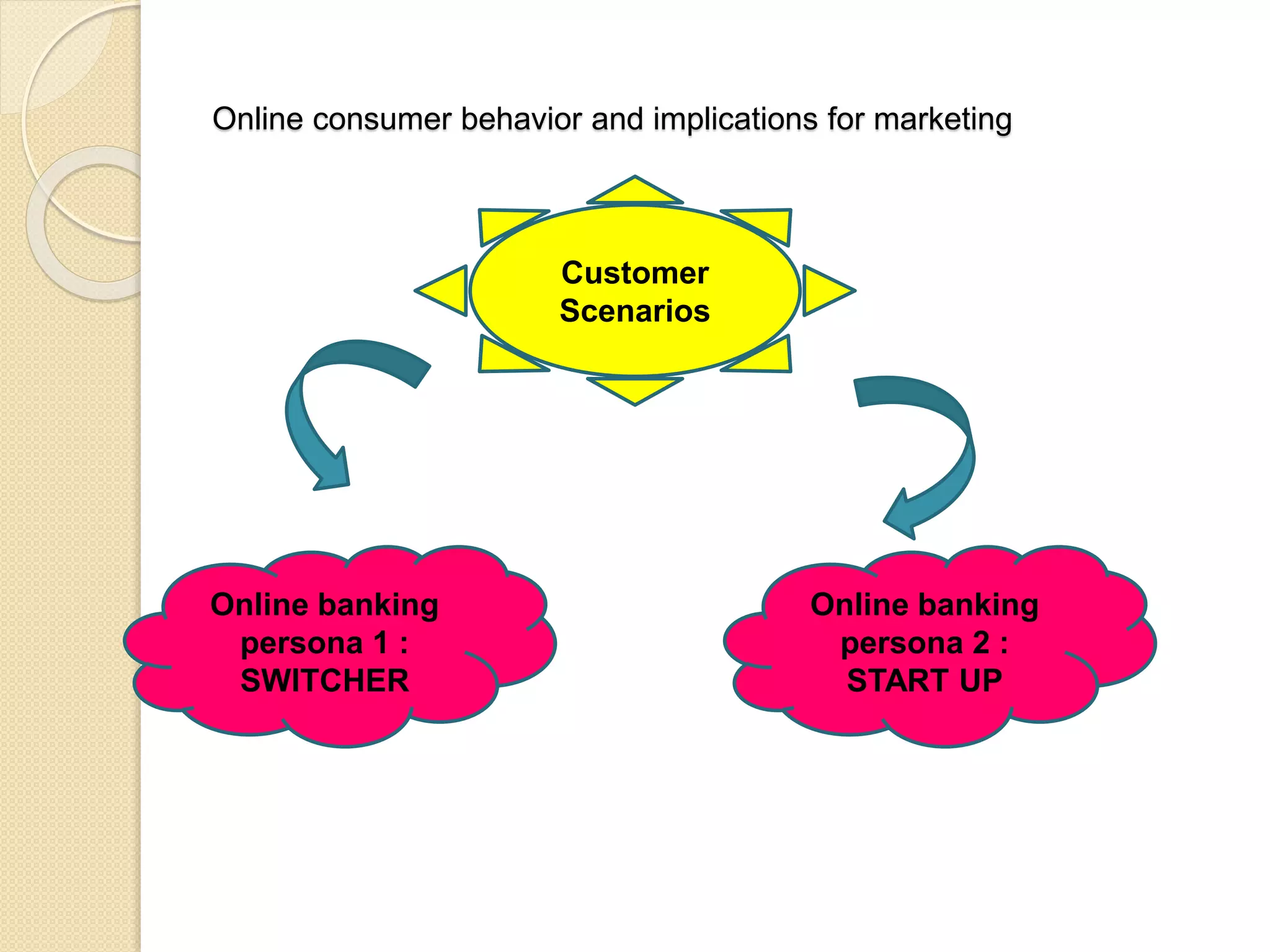
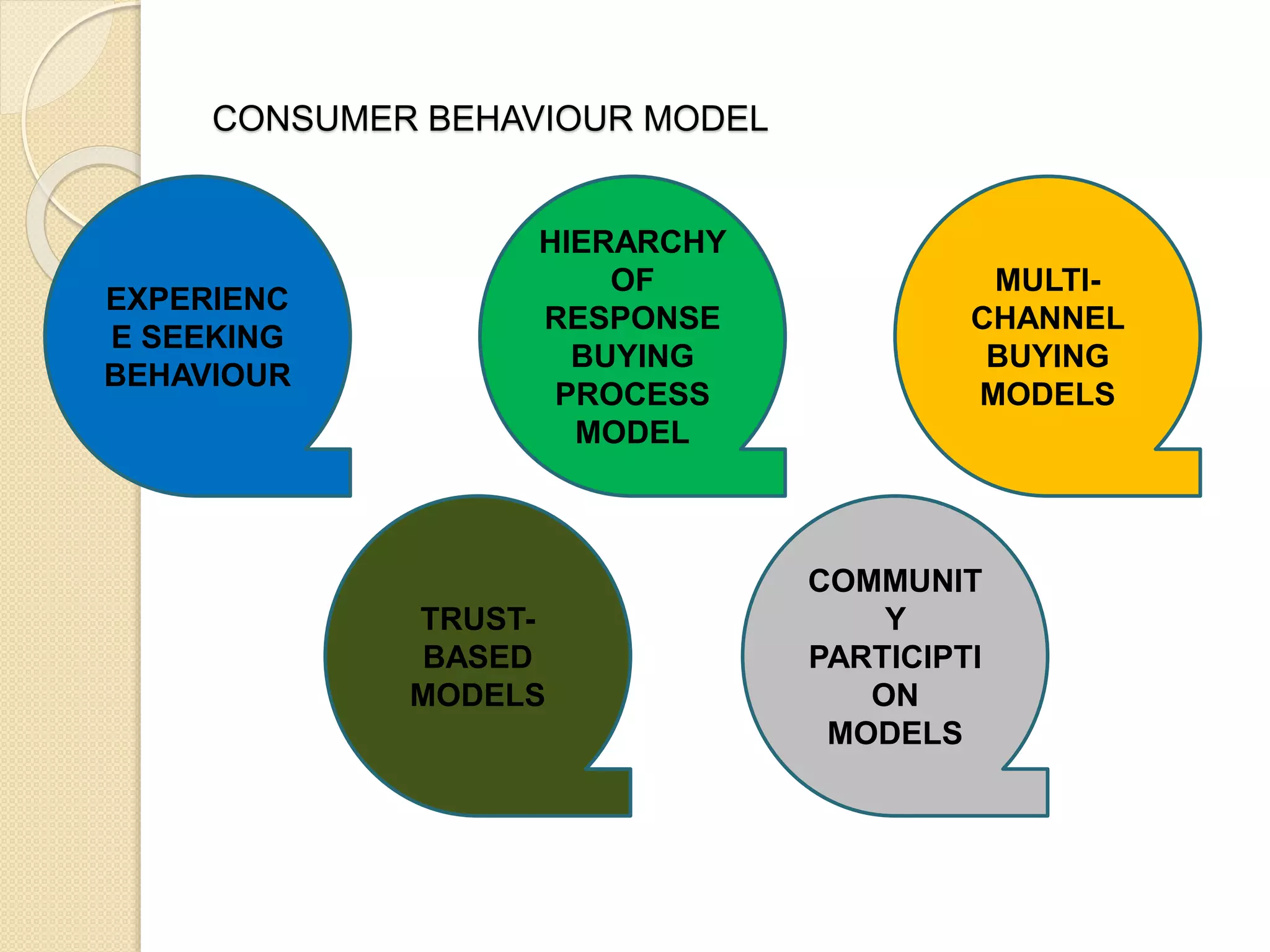
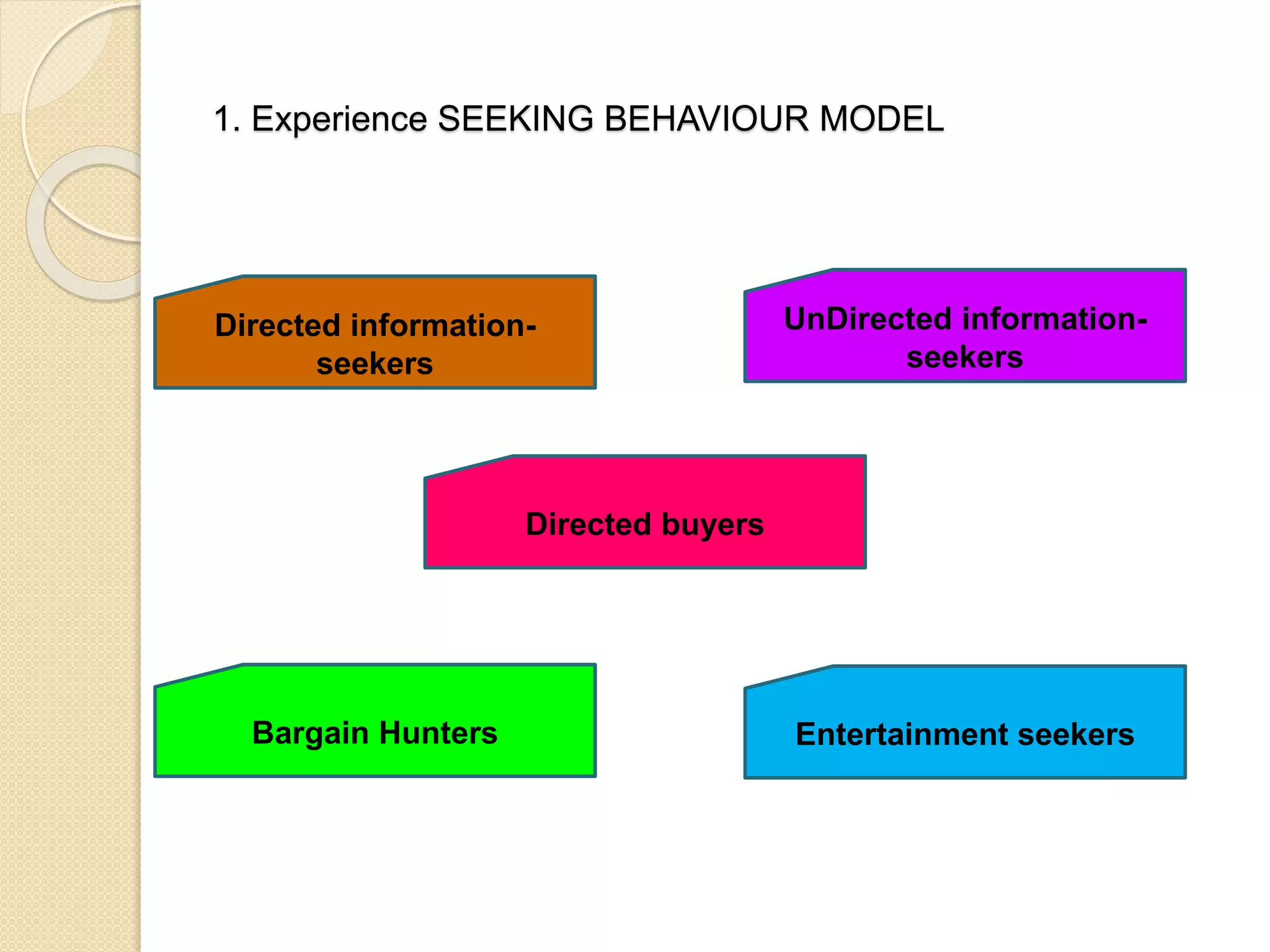
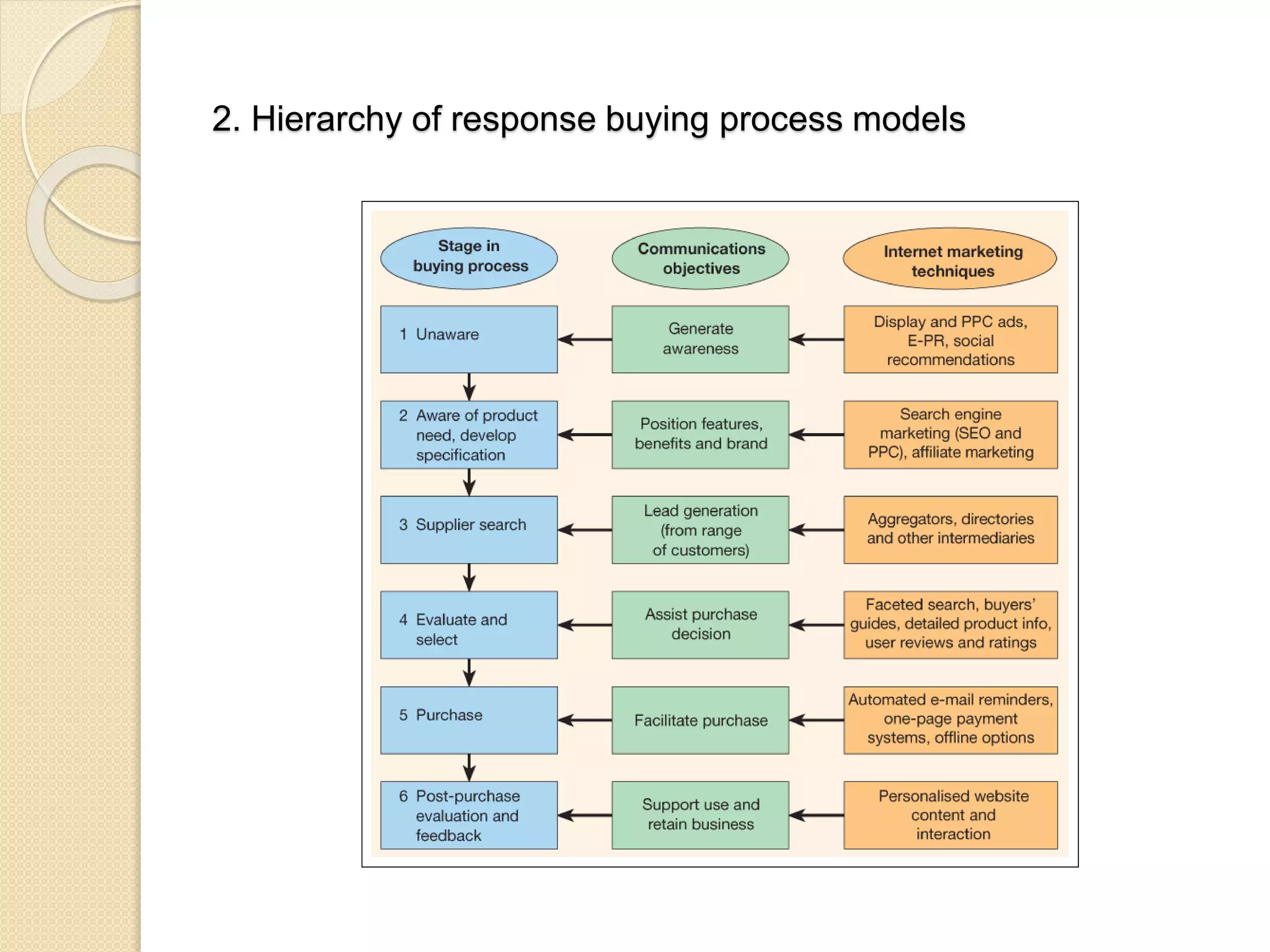
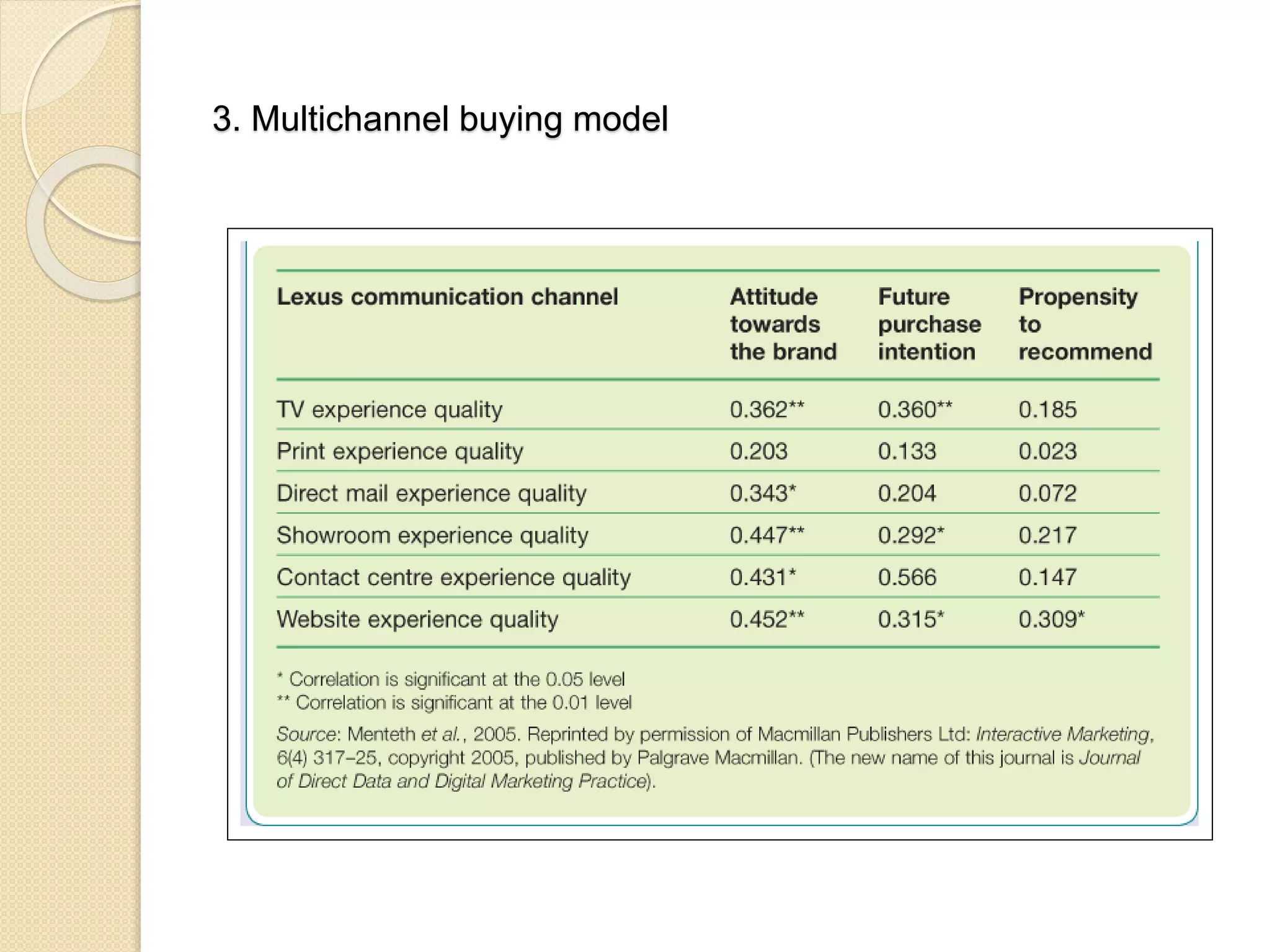
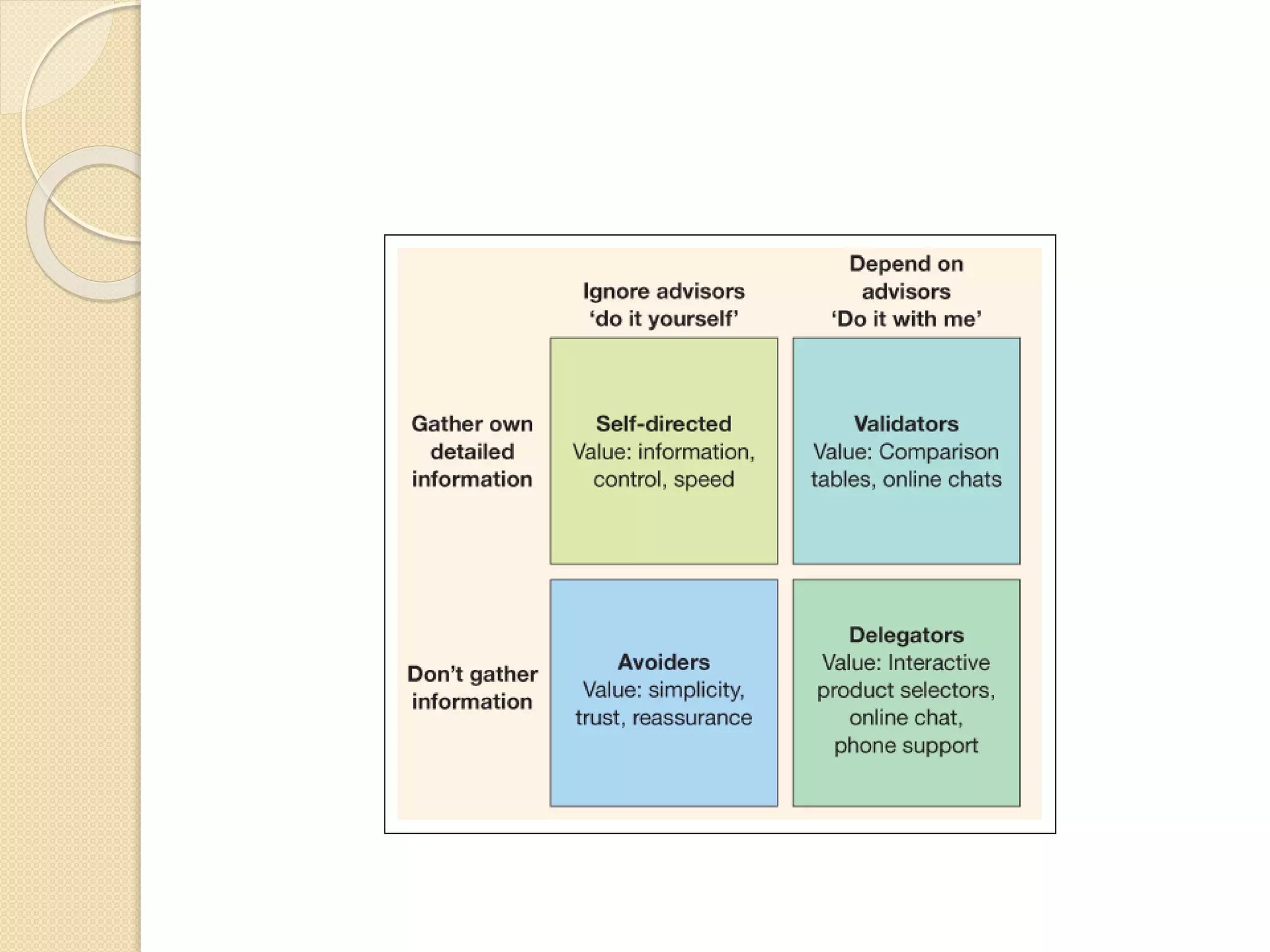
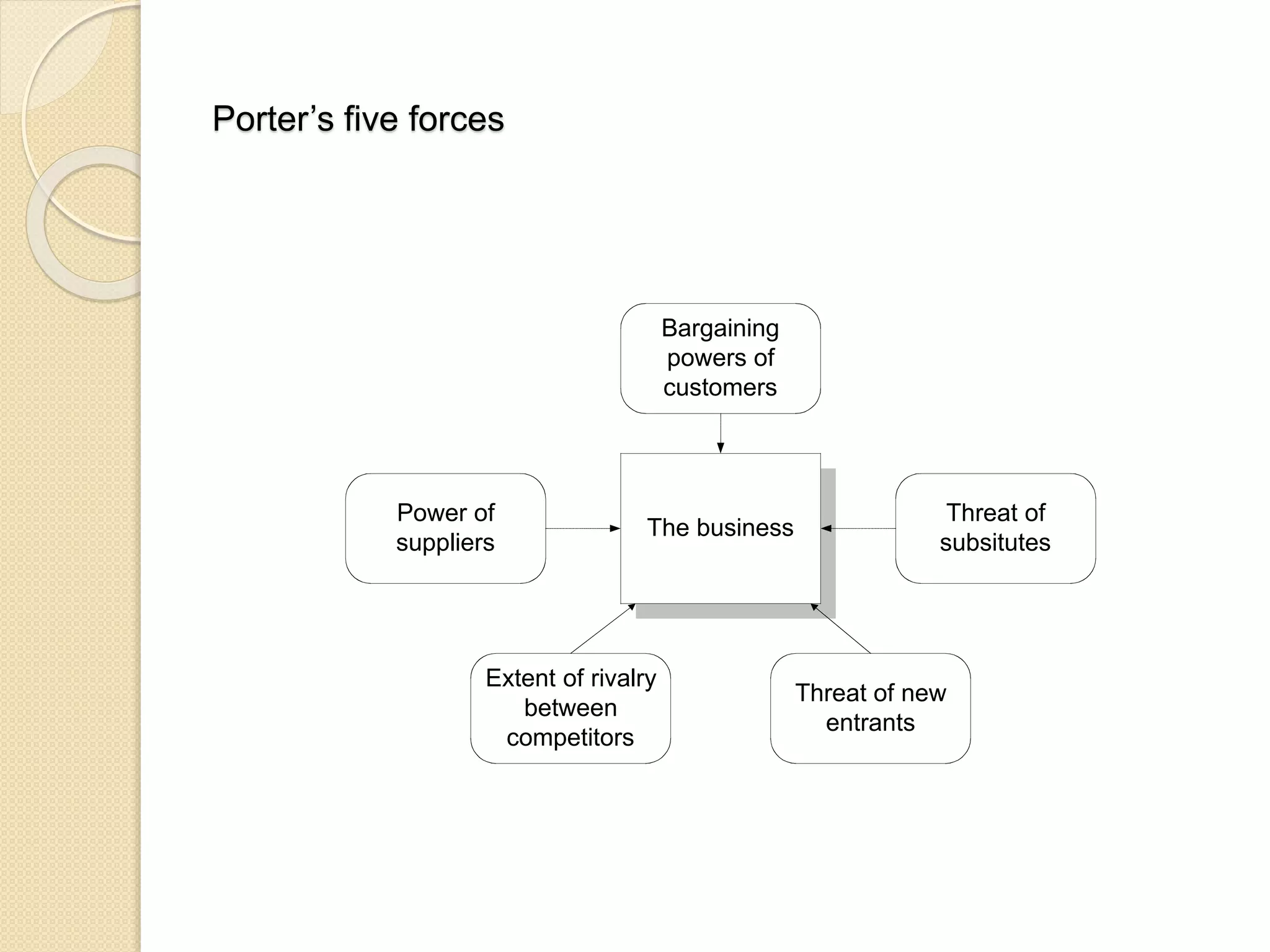
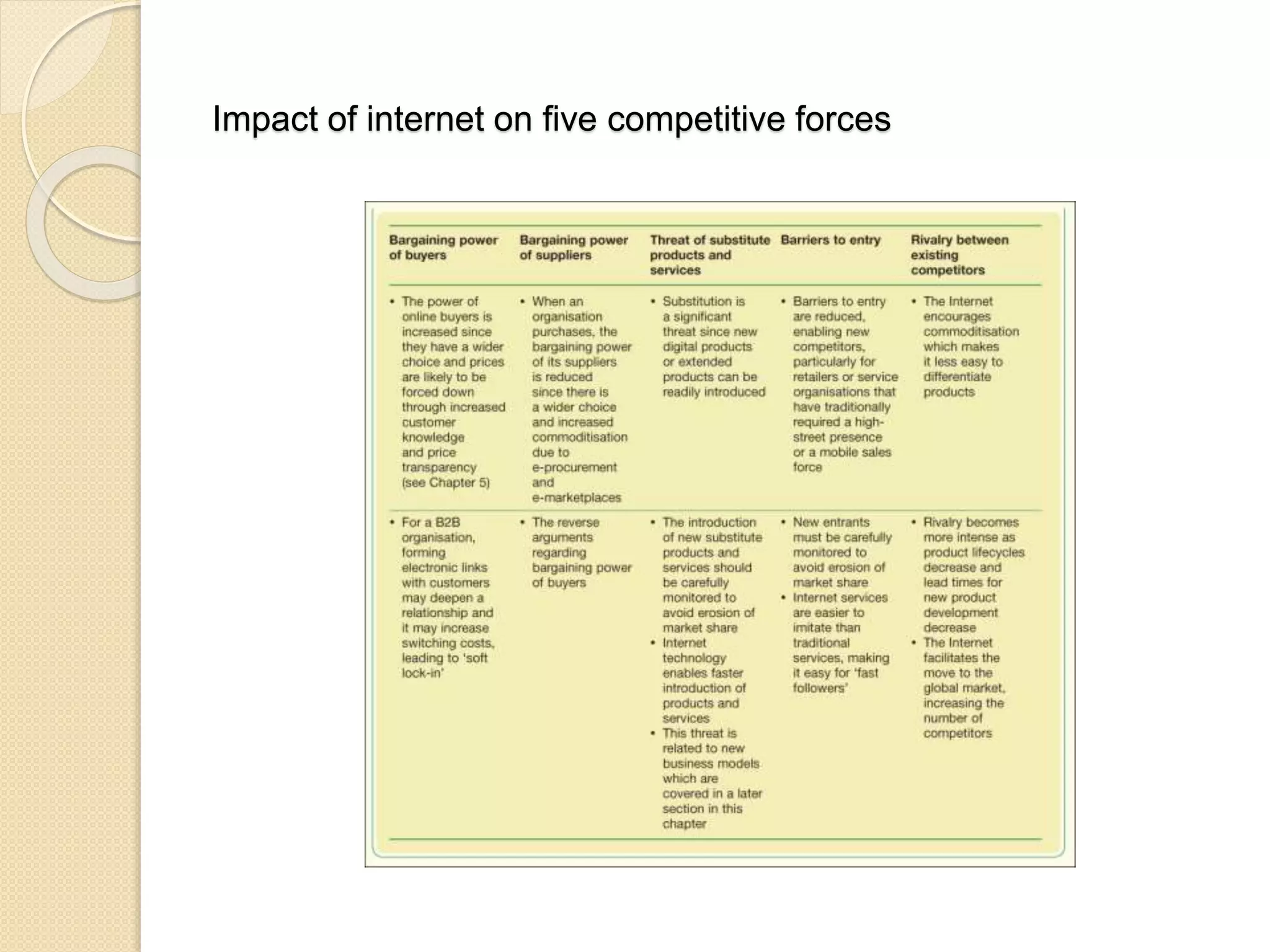
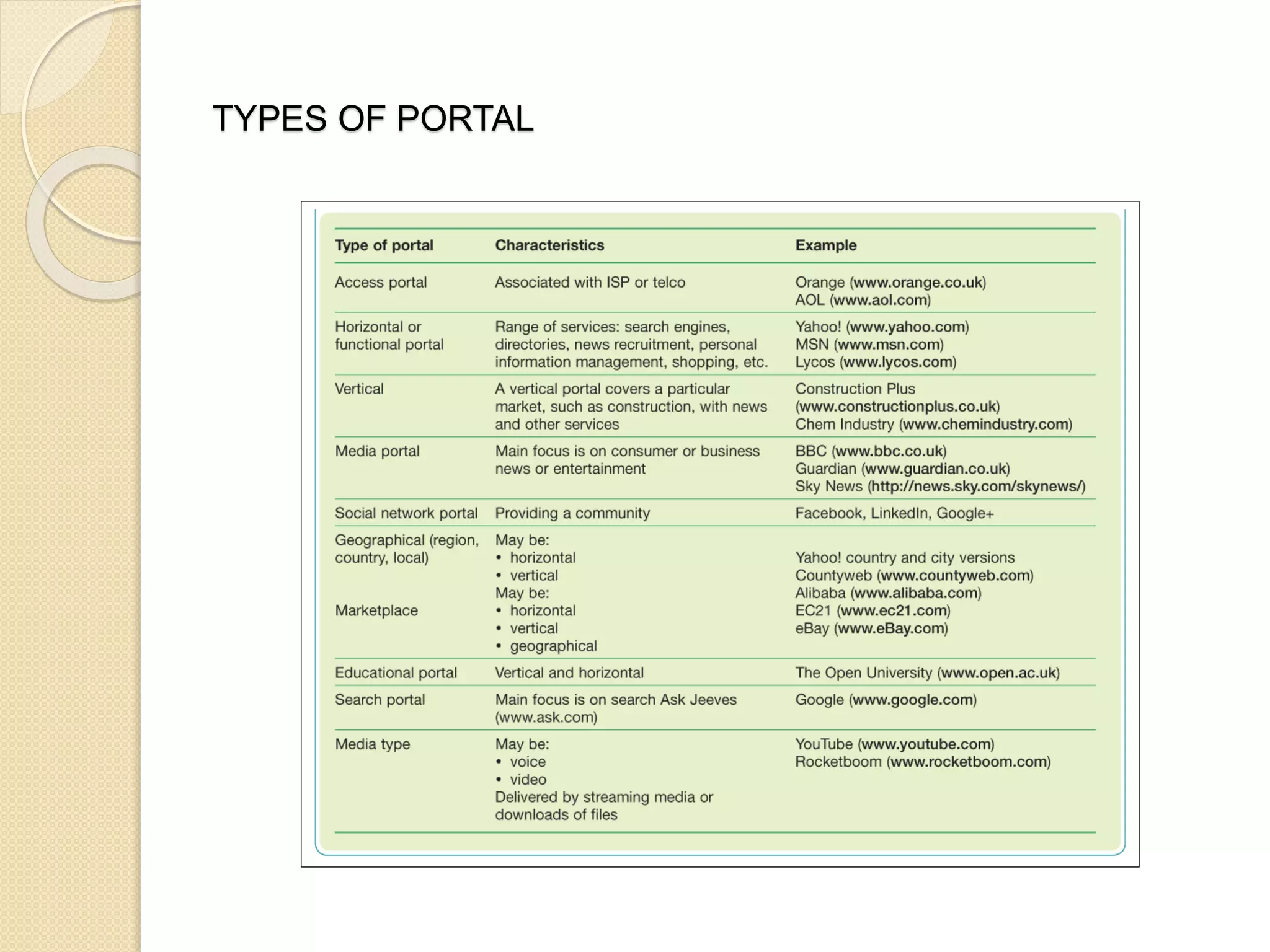
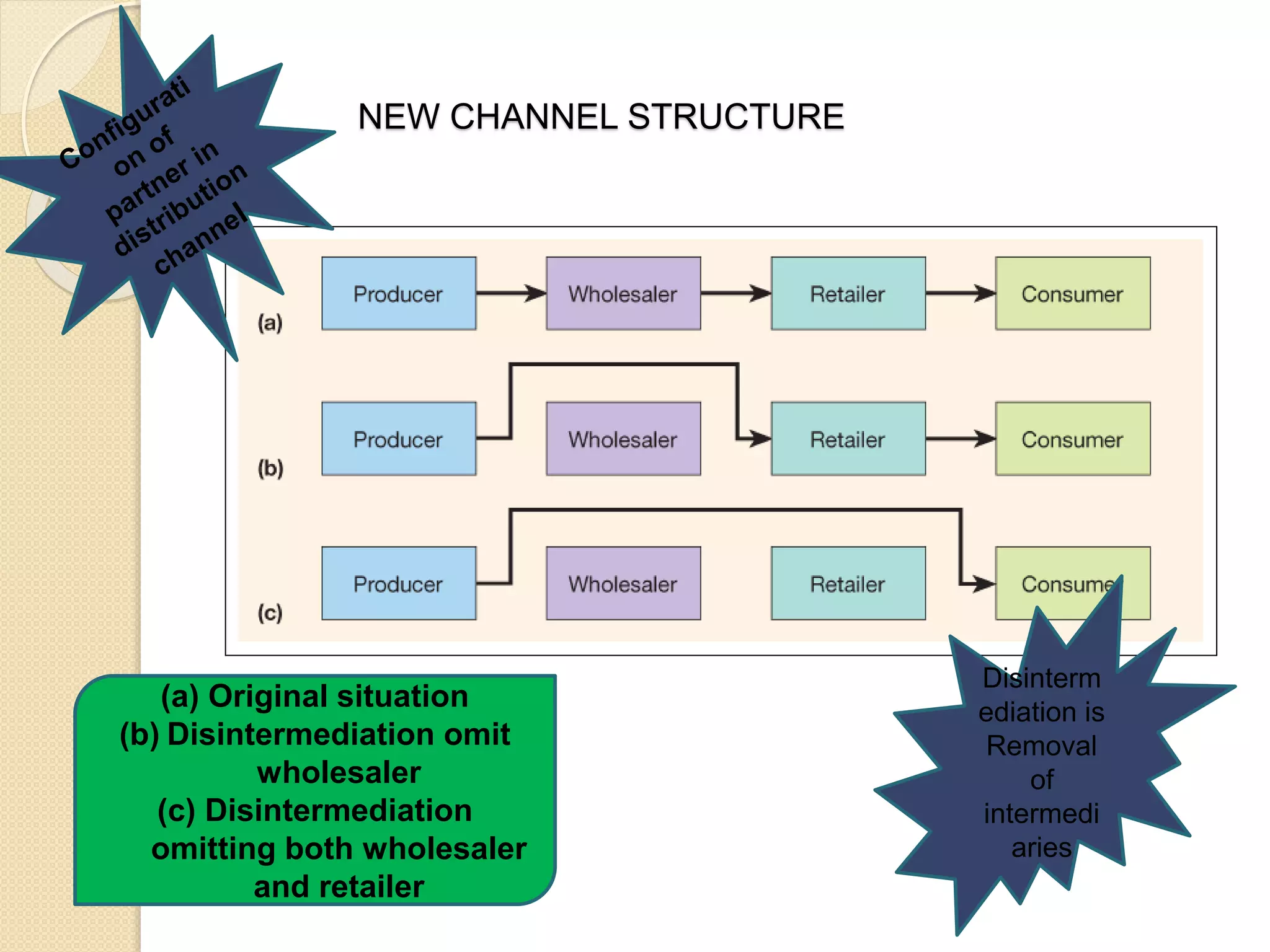
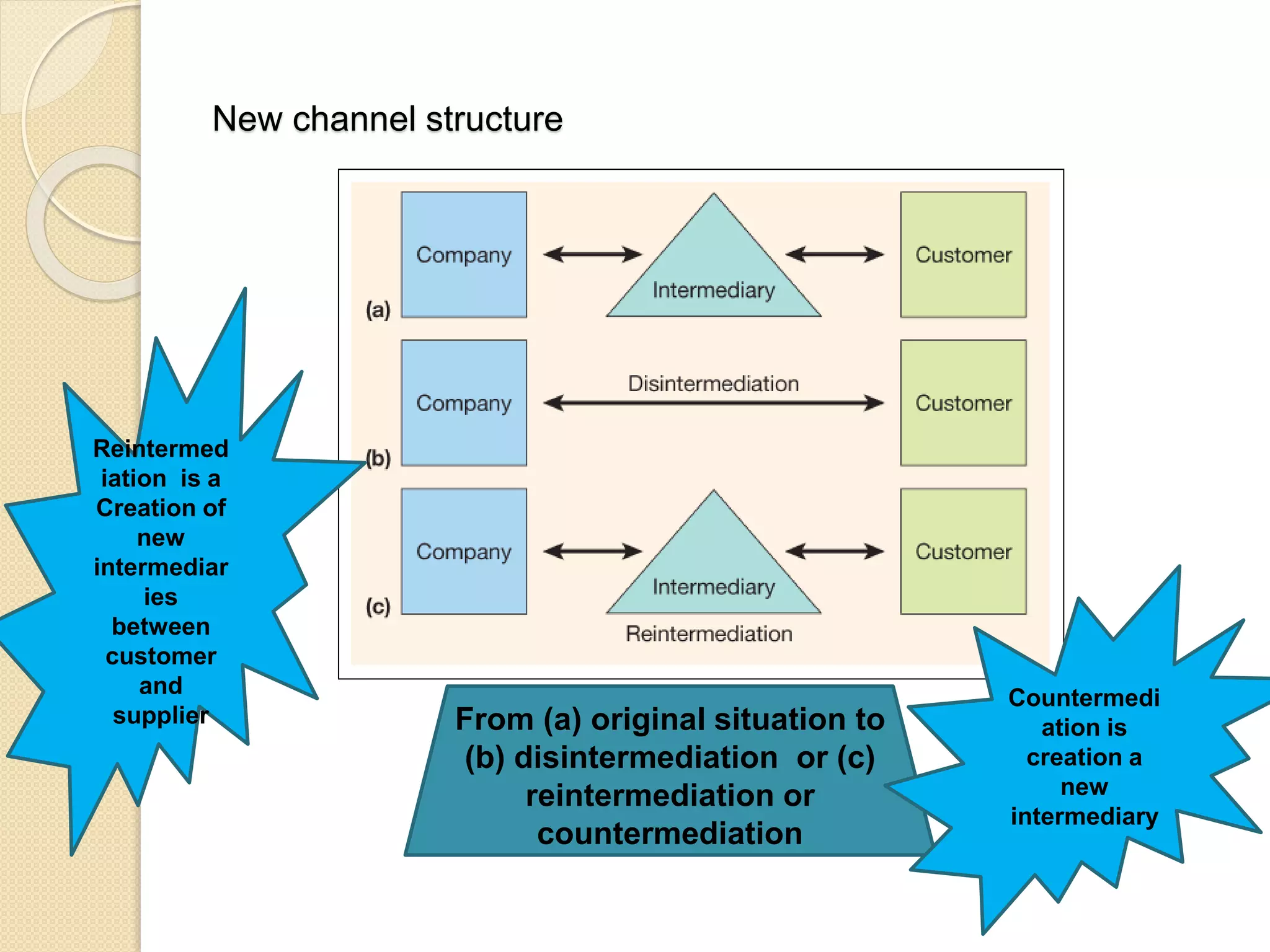
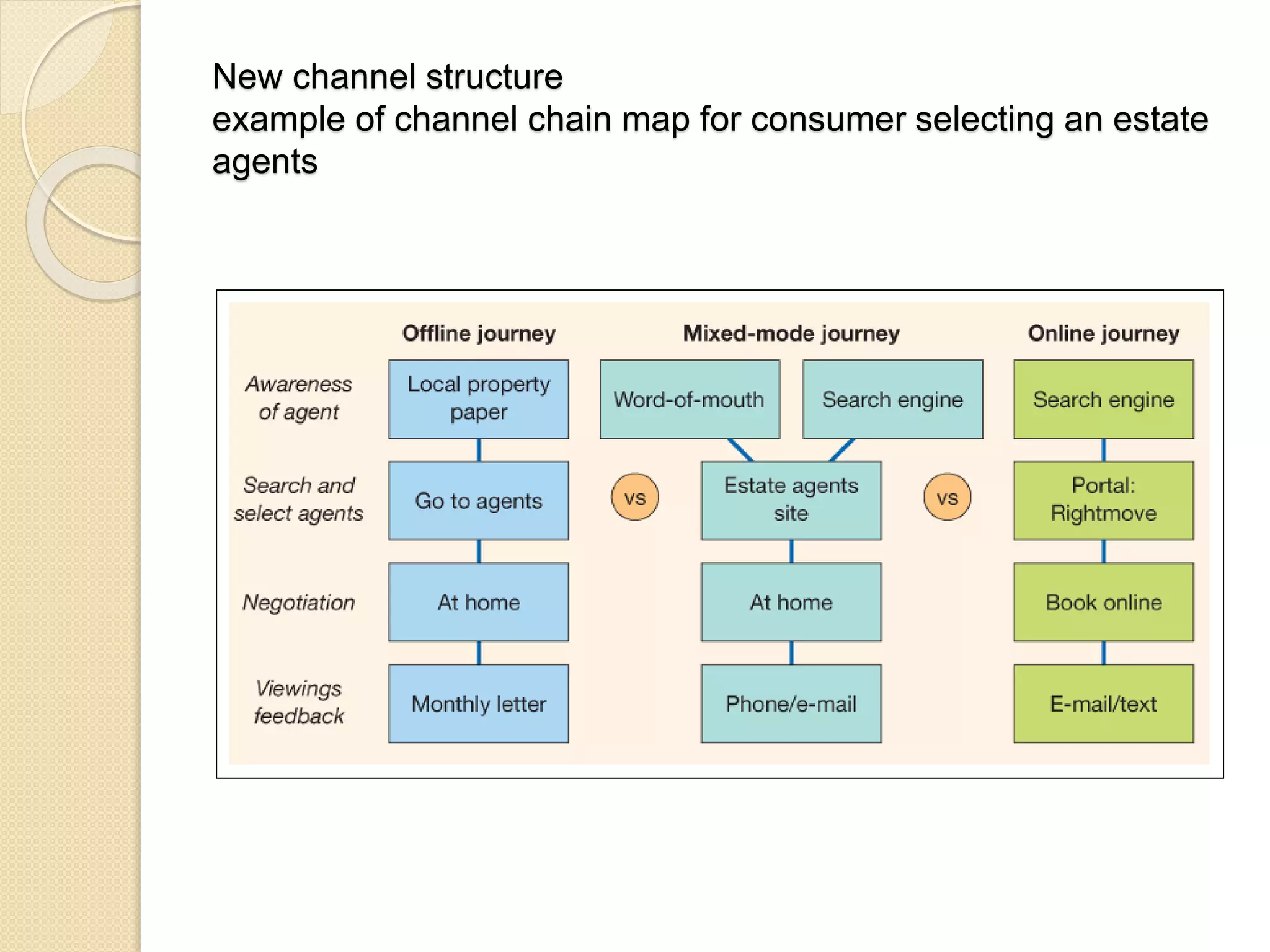
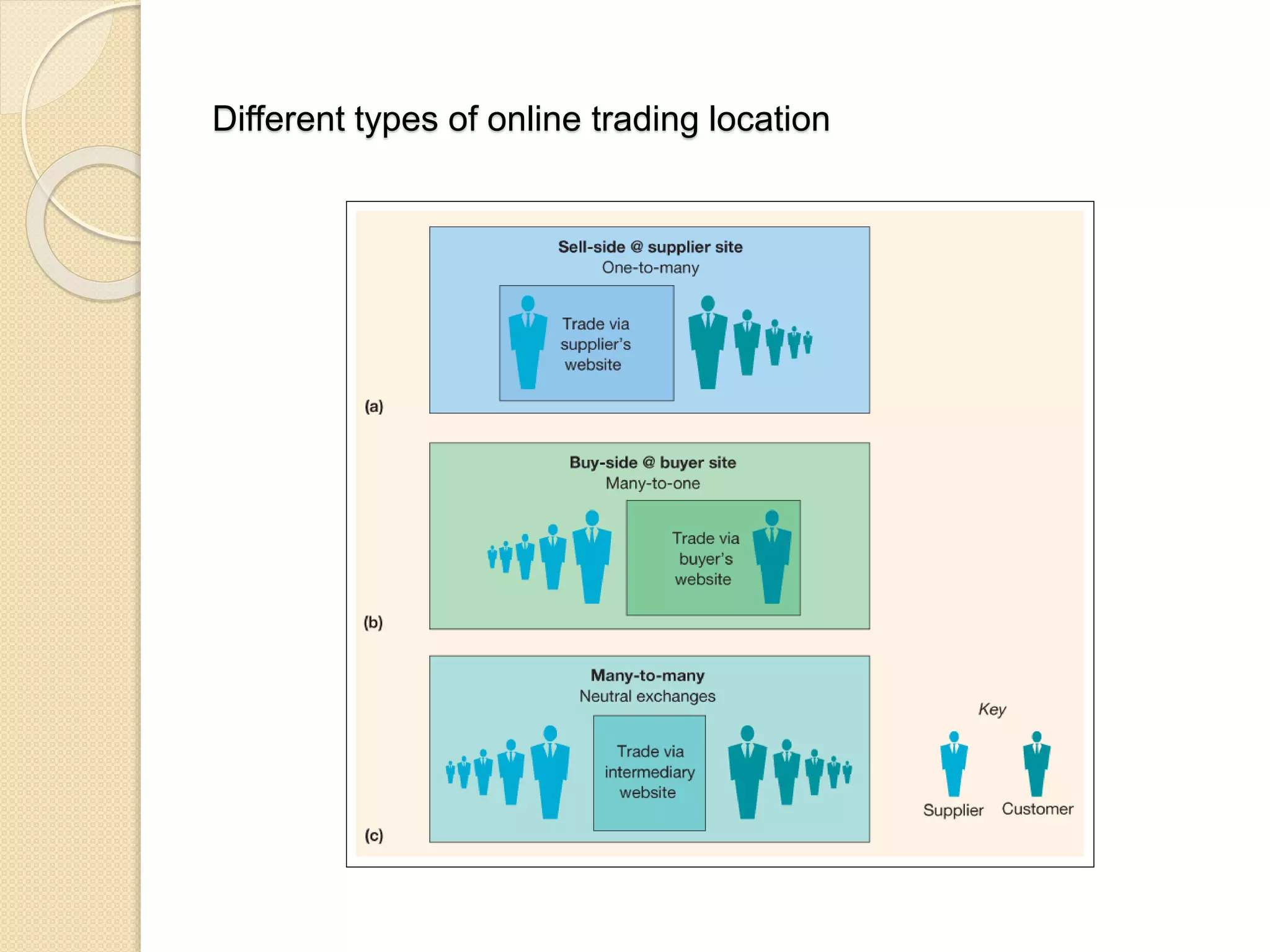
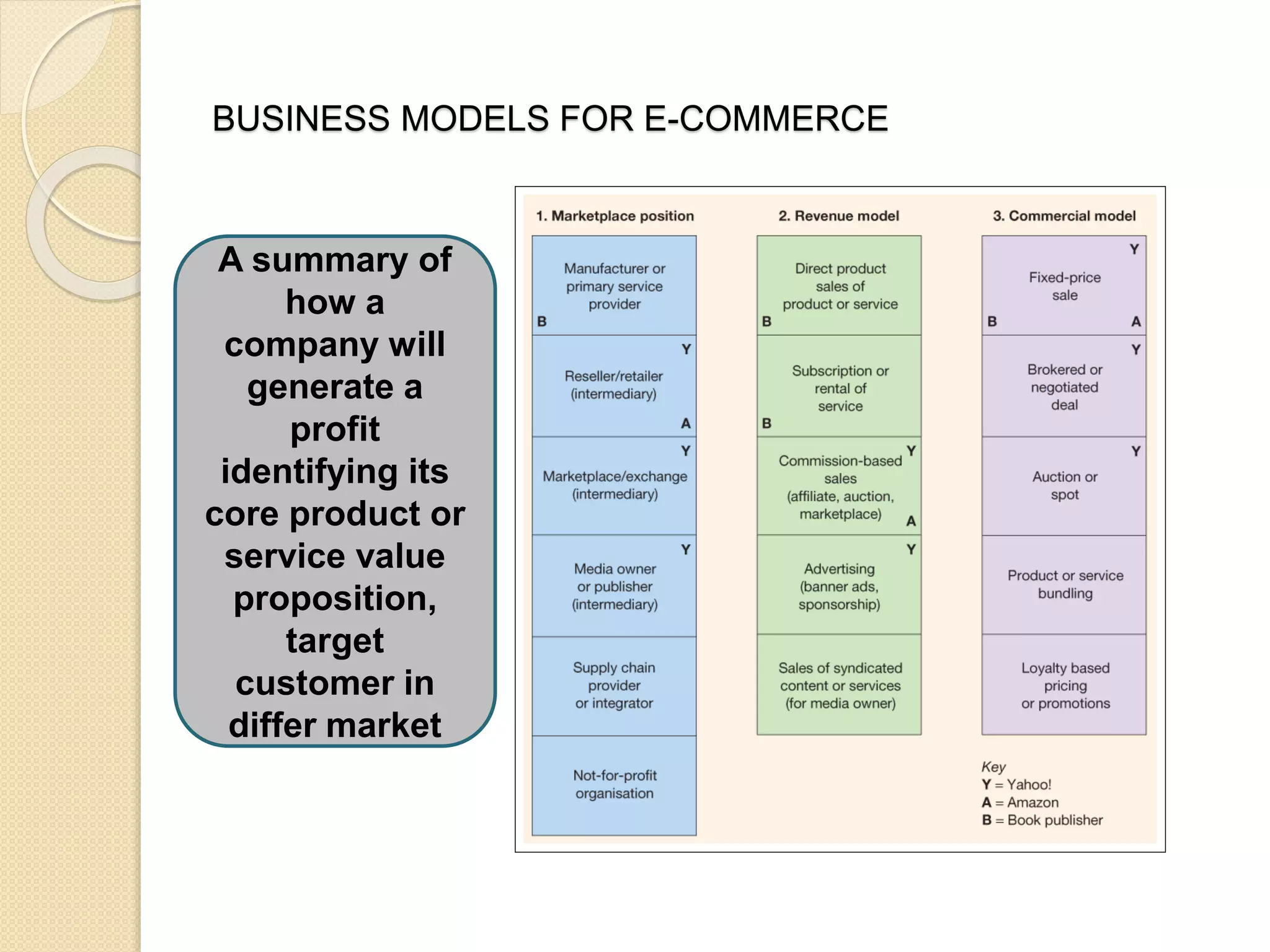
This document discusses the micro-environment of online marketplaces and its implications for digital marketing strategy. It defines the micro-environment as the actors and their interactions that influence how an organization responds in its marketplace. It also examines how customers, competitors, suppliers, and intermediaries shape the immediate trading environment and issues organizations should consider regarding these groups in their digital marketing. The document also explores various models of online consumer behavior and the impact of the internet on traditional marketing channels.