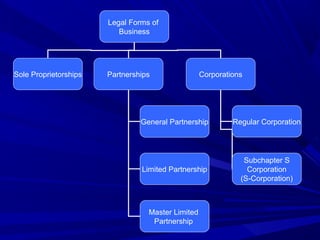
This document discusses different forms of business organization including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and franchising. Sole proprietorships are owned by one person while partnerships have two or more owners. Corporations are separate legal entities with owners called shareholders. Franchising involves a franchisor licensing their business model to franchisees.