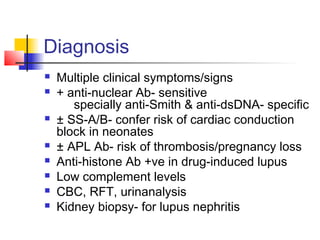
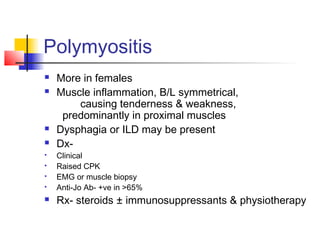
This document discusses several connective tissue diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, Sjogren syndrome, polymyositis, and Sharp syndrome. Systemic lupus erythematosus is a multisystem autoimmune disease most common in young females, with symptoms involving multiple organ systems. Scleroderma involves skin fibrosis and internal organ involvement. Sjogren syndrome causes dryness from immune damage to exocrine glands. Polymyositis features muscle inflammation. Sharp syndrome is an overlap syndrome combining features of systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren syndrome, scleroderma, and polymyositis.