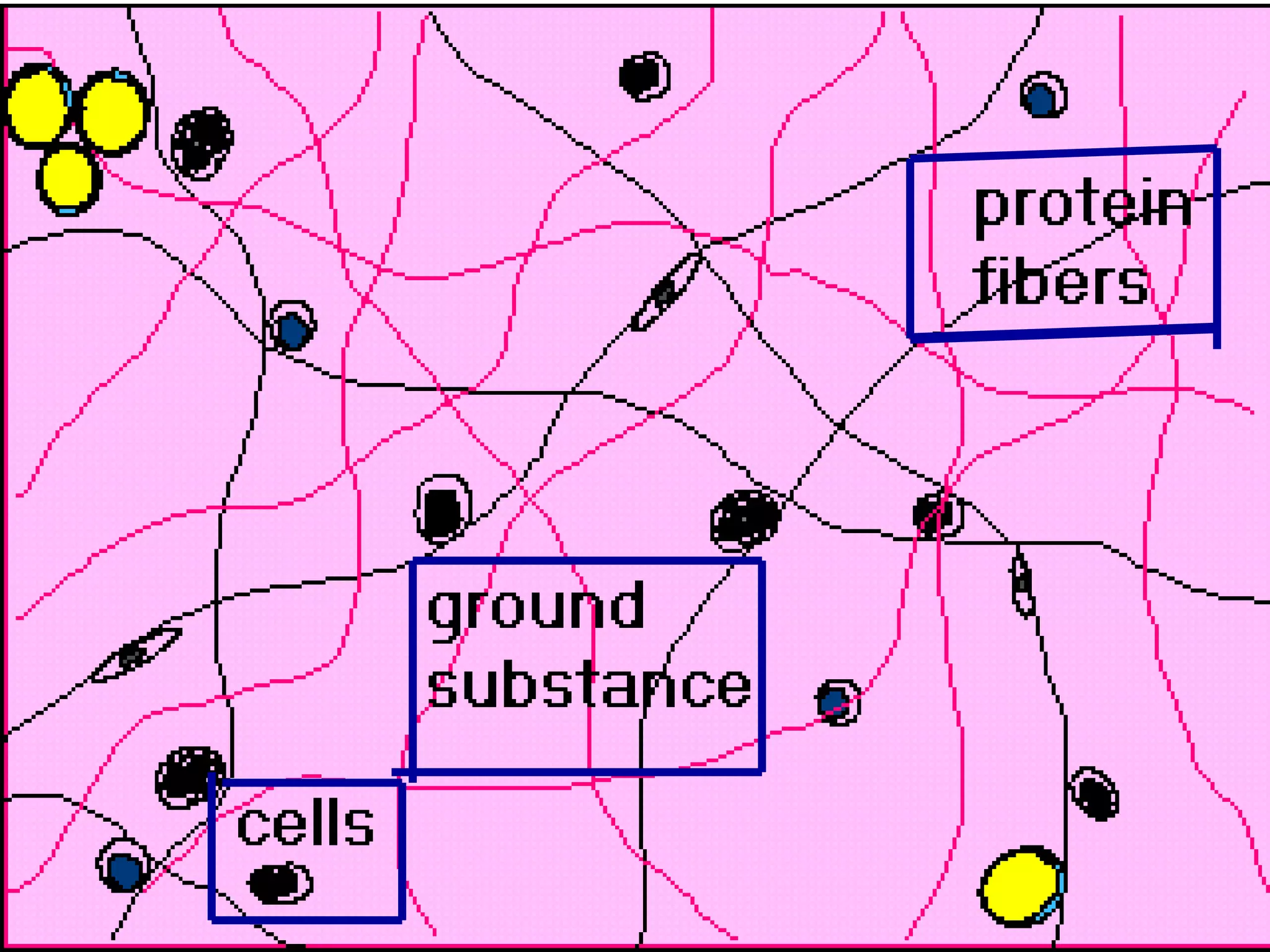
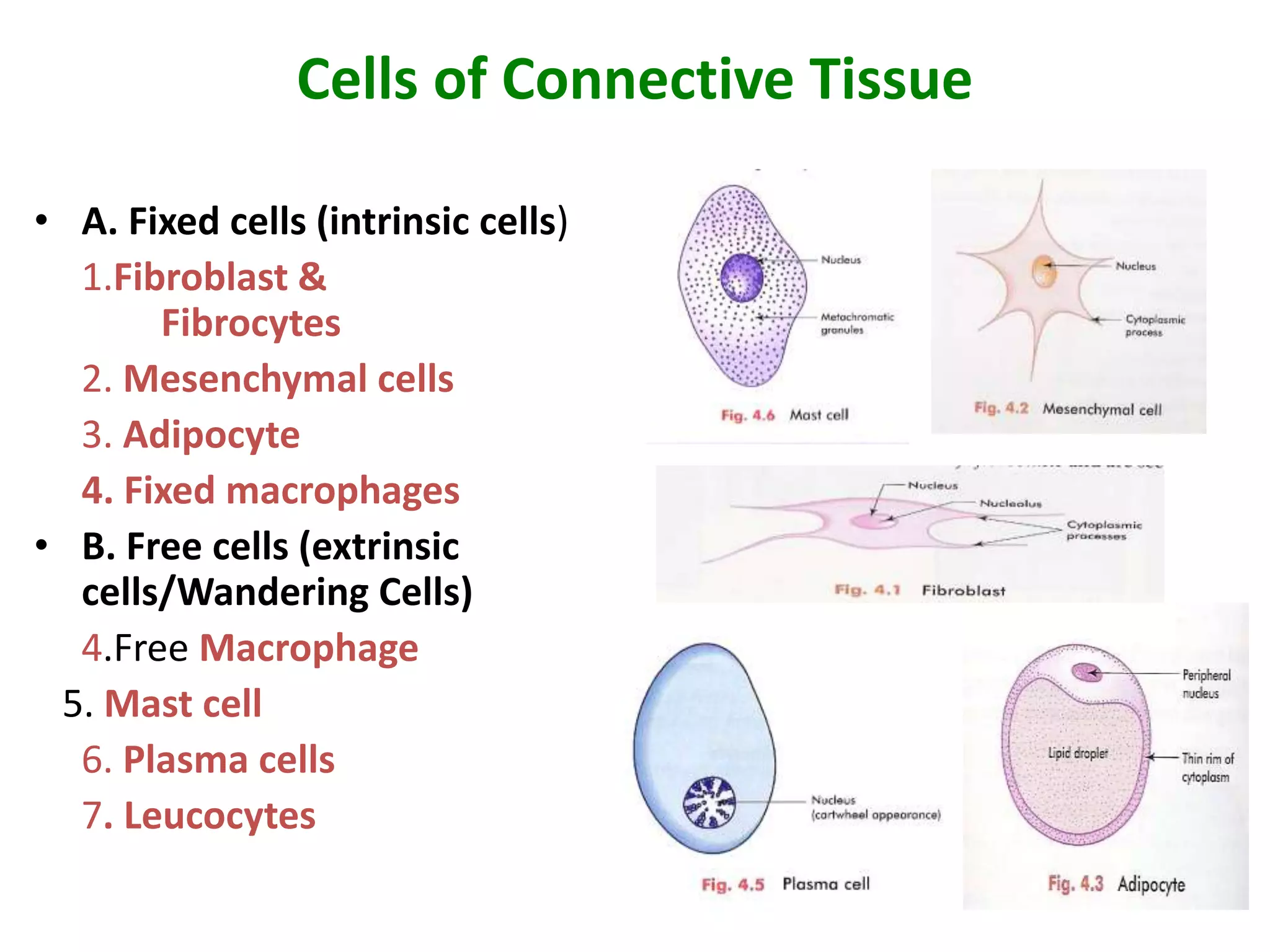
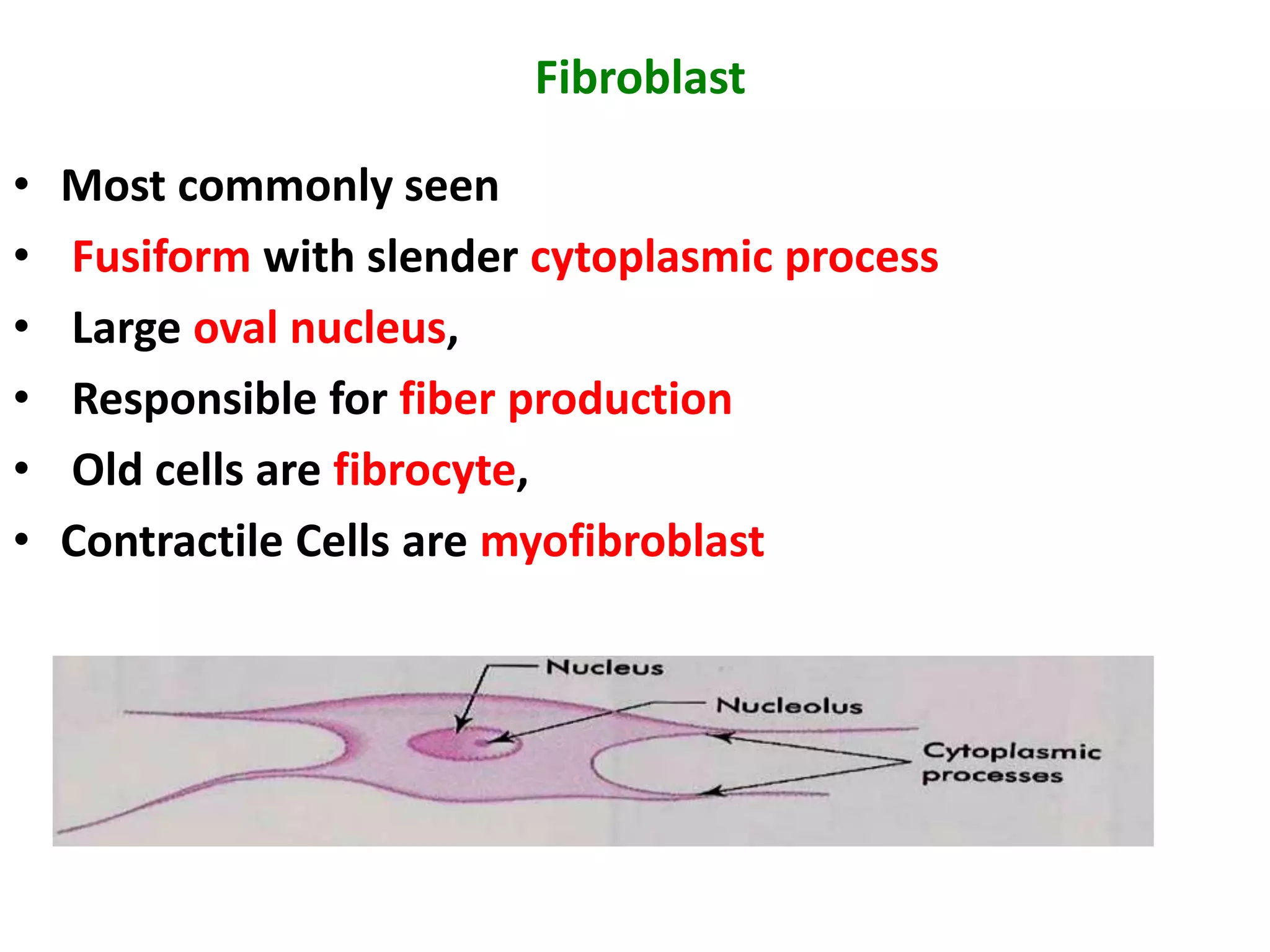
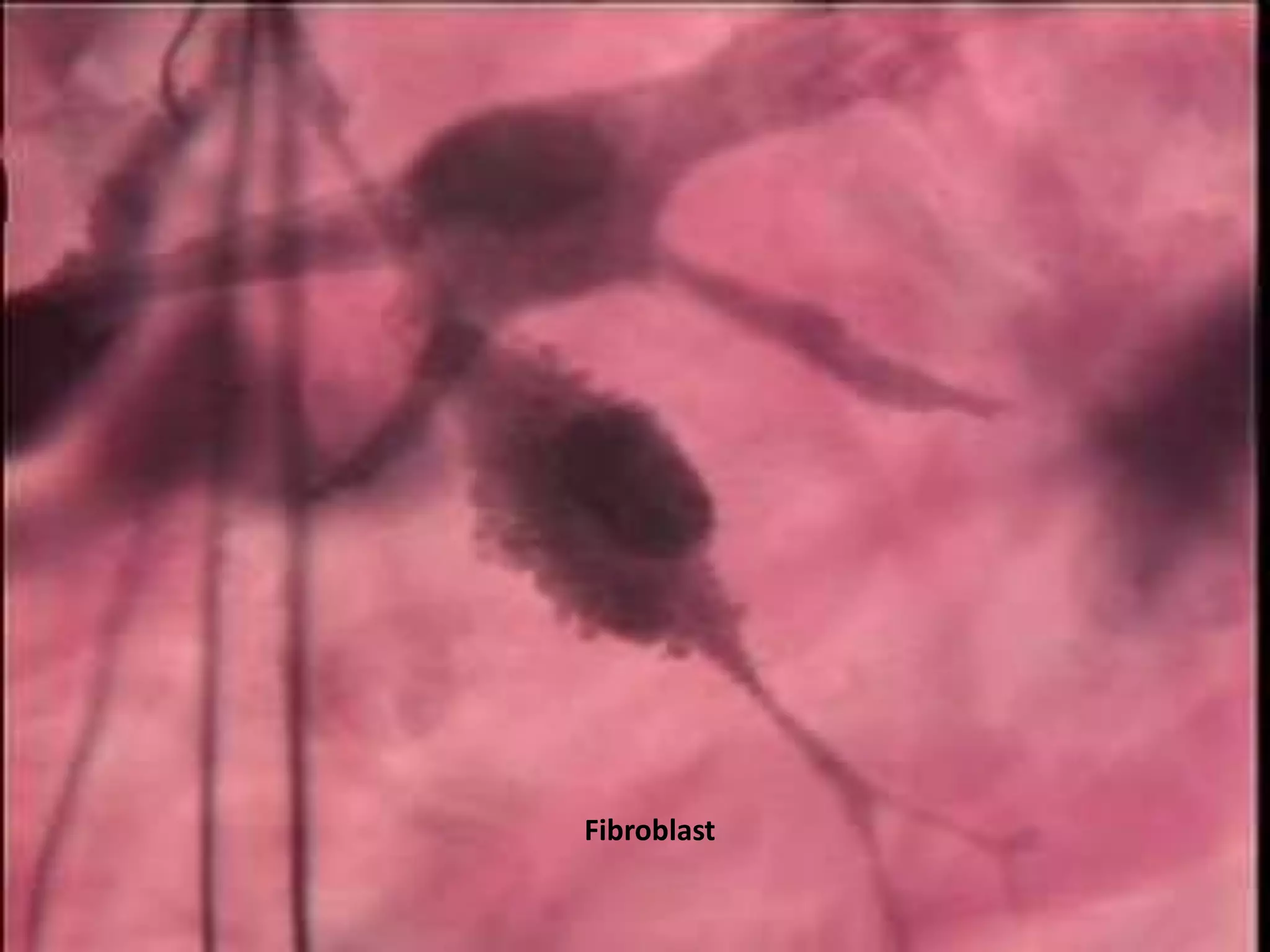
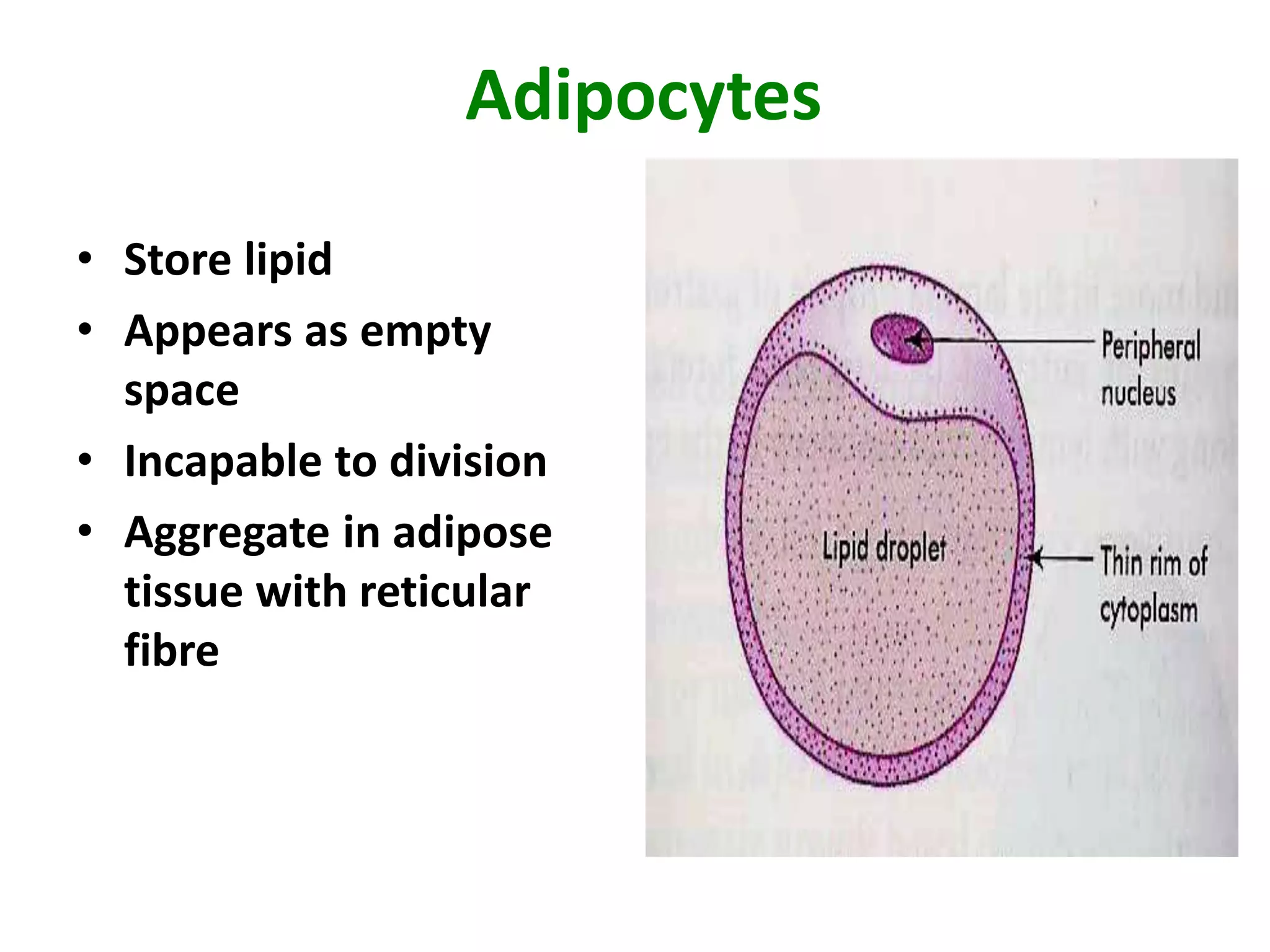
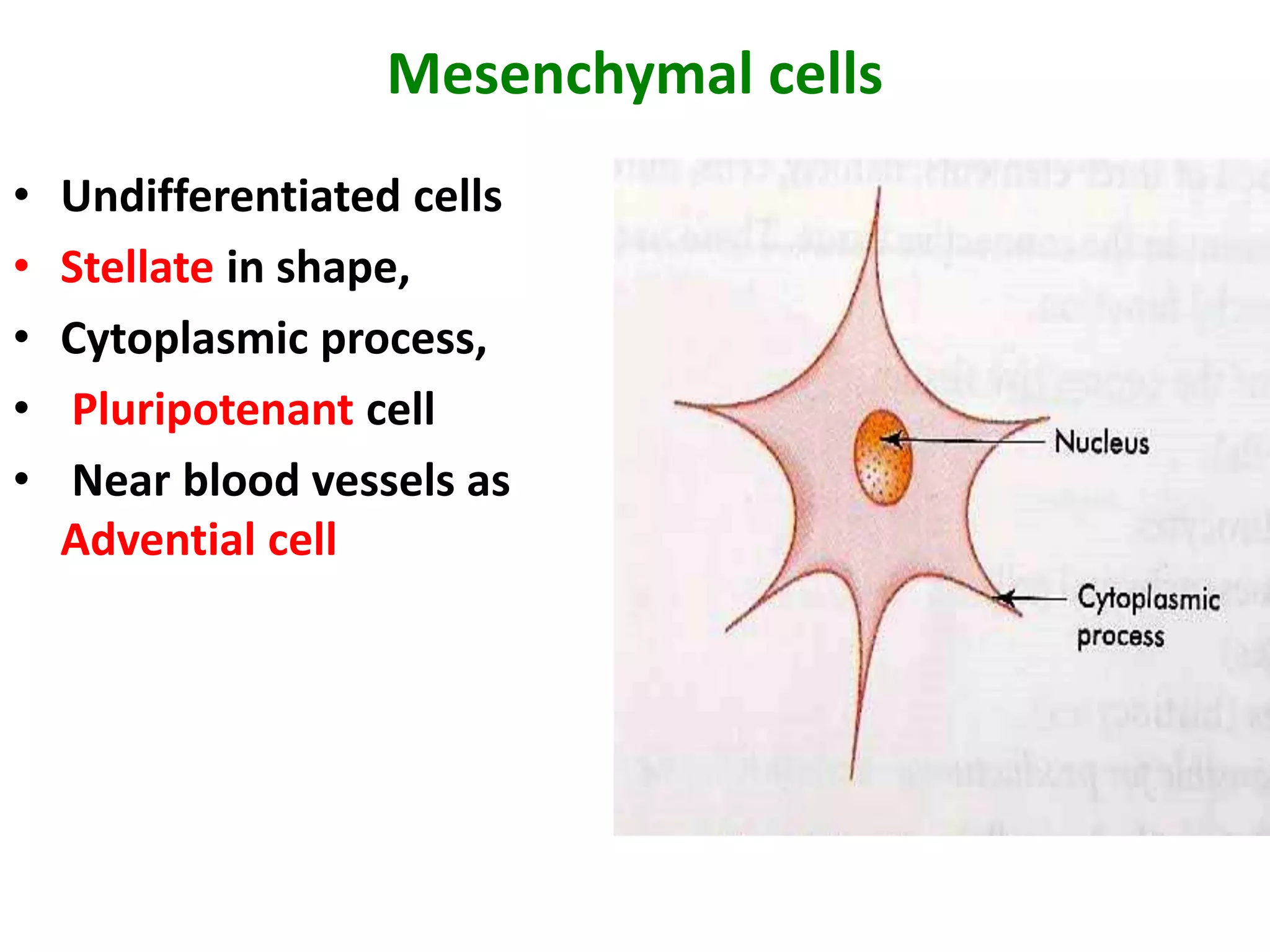
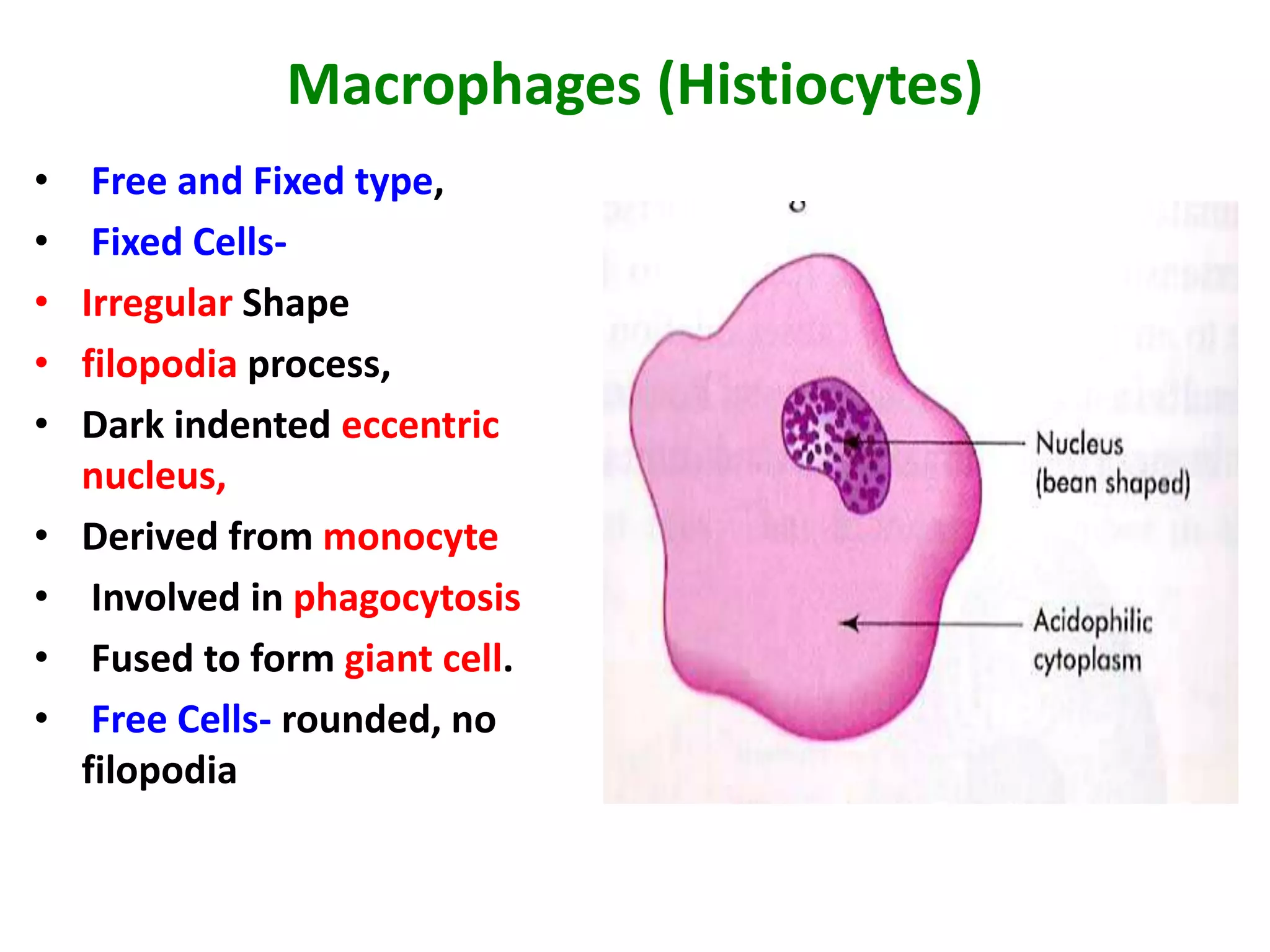
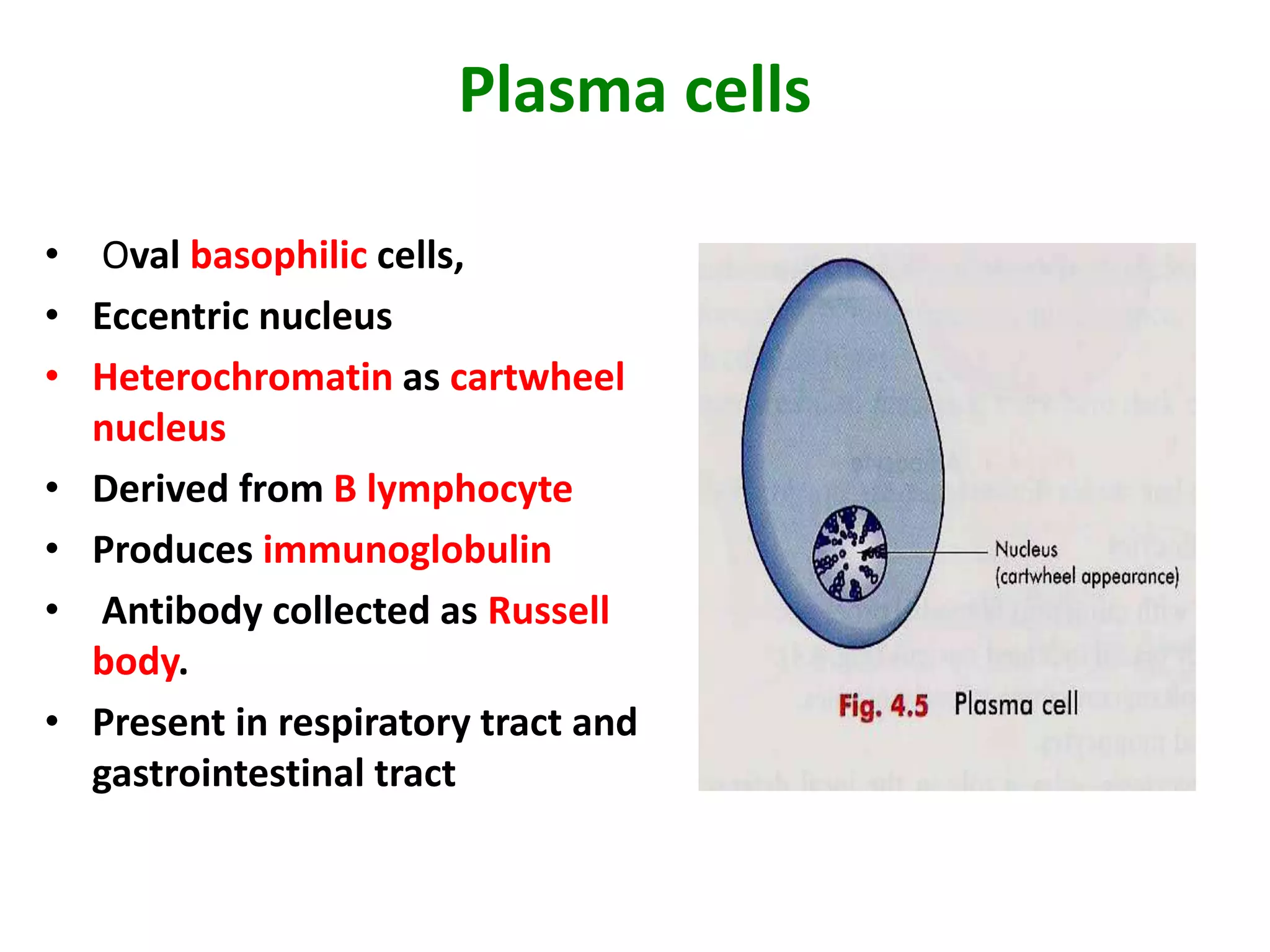
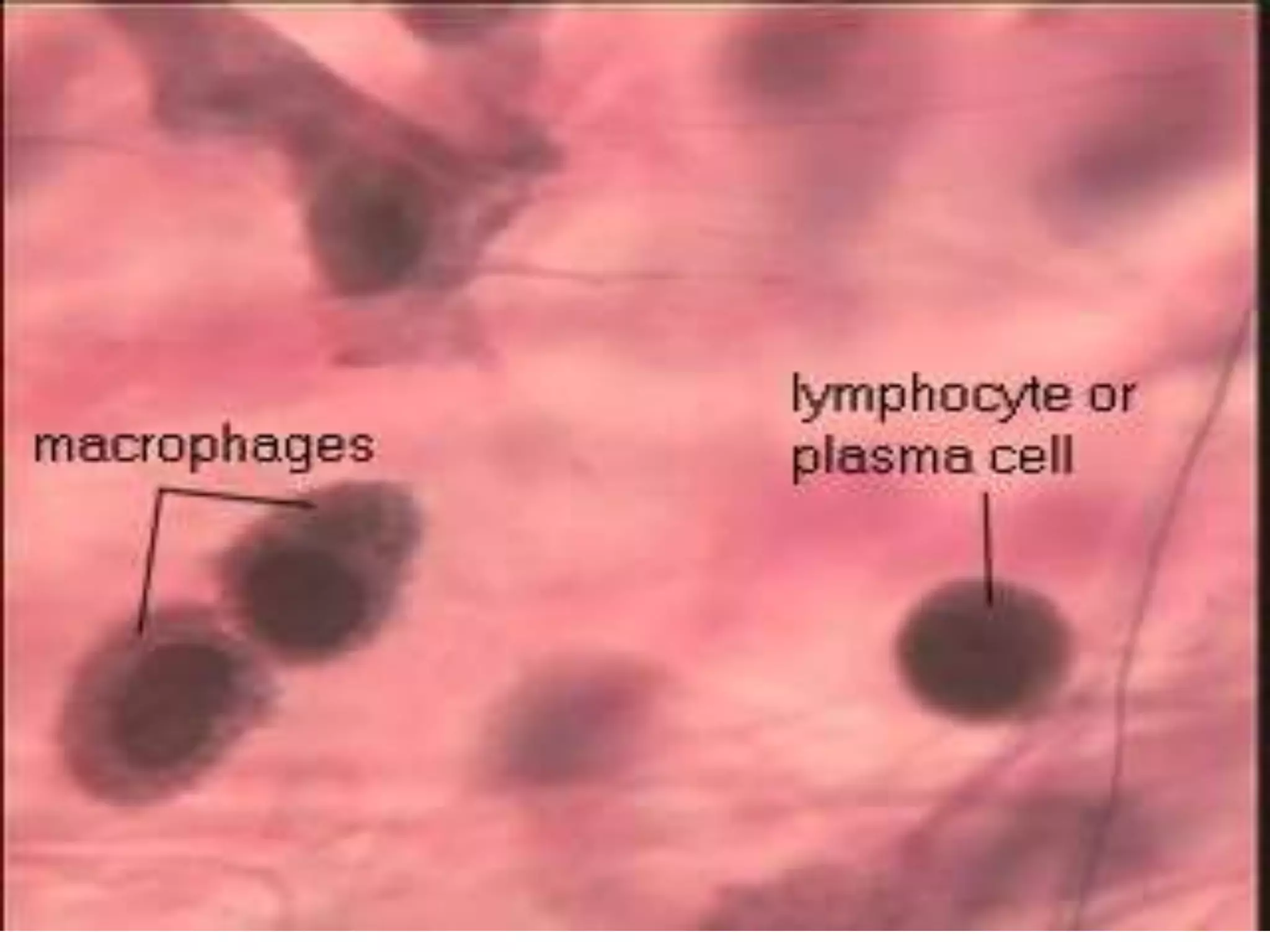
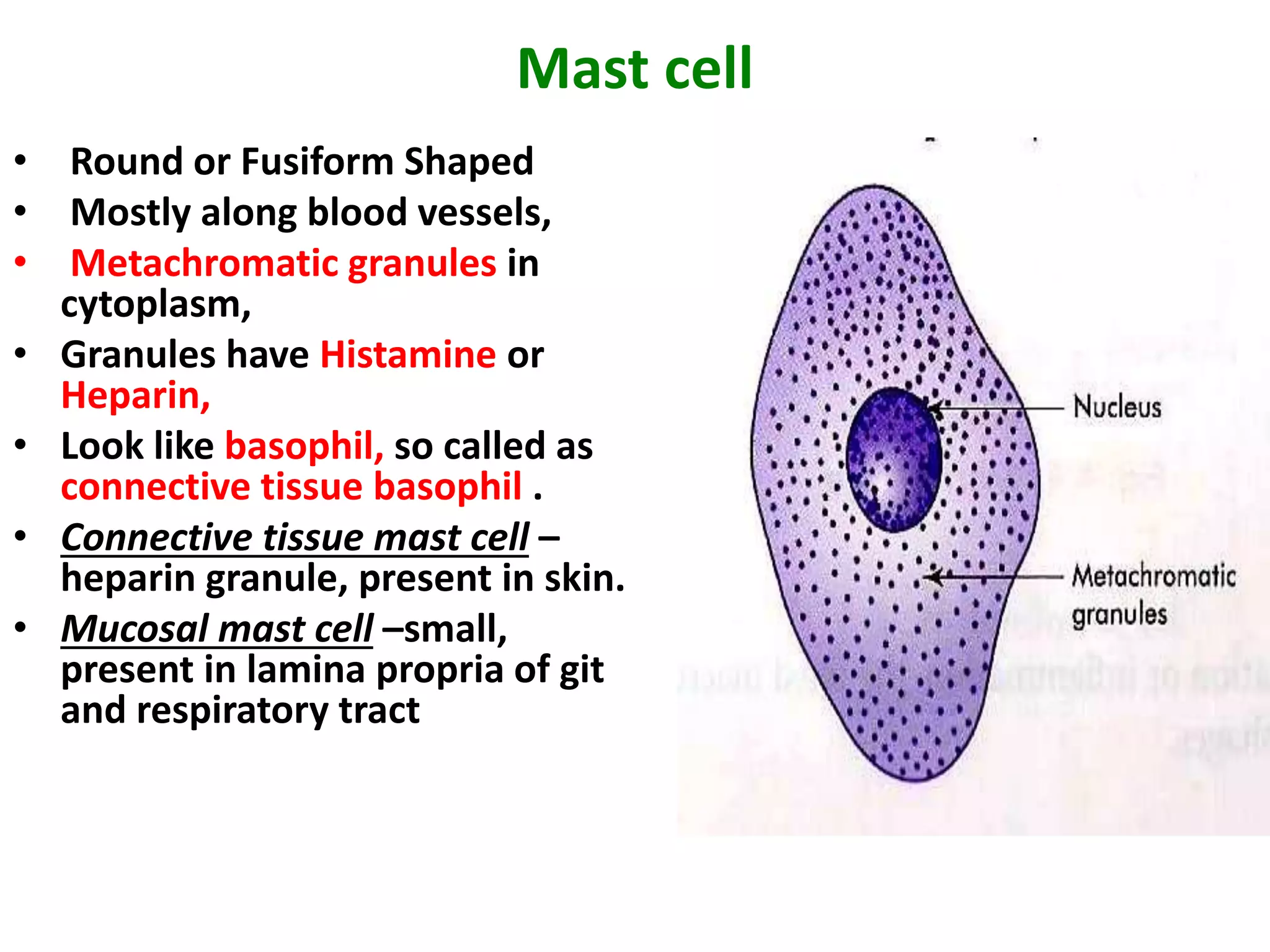
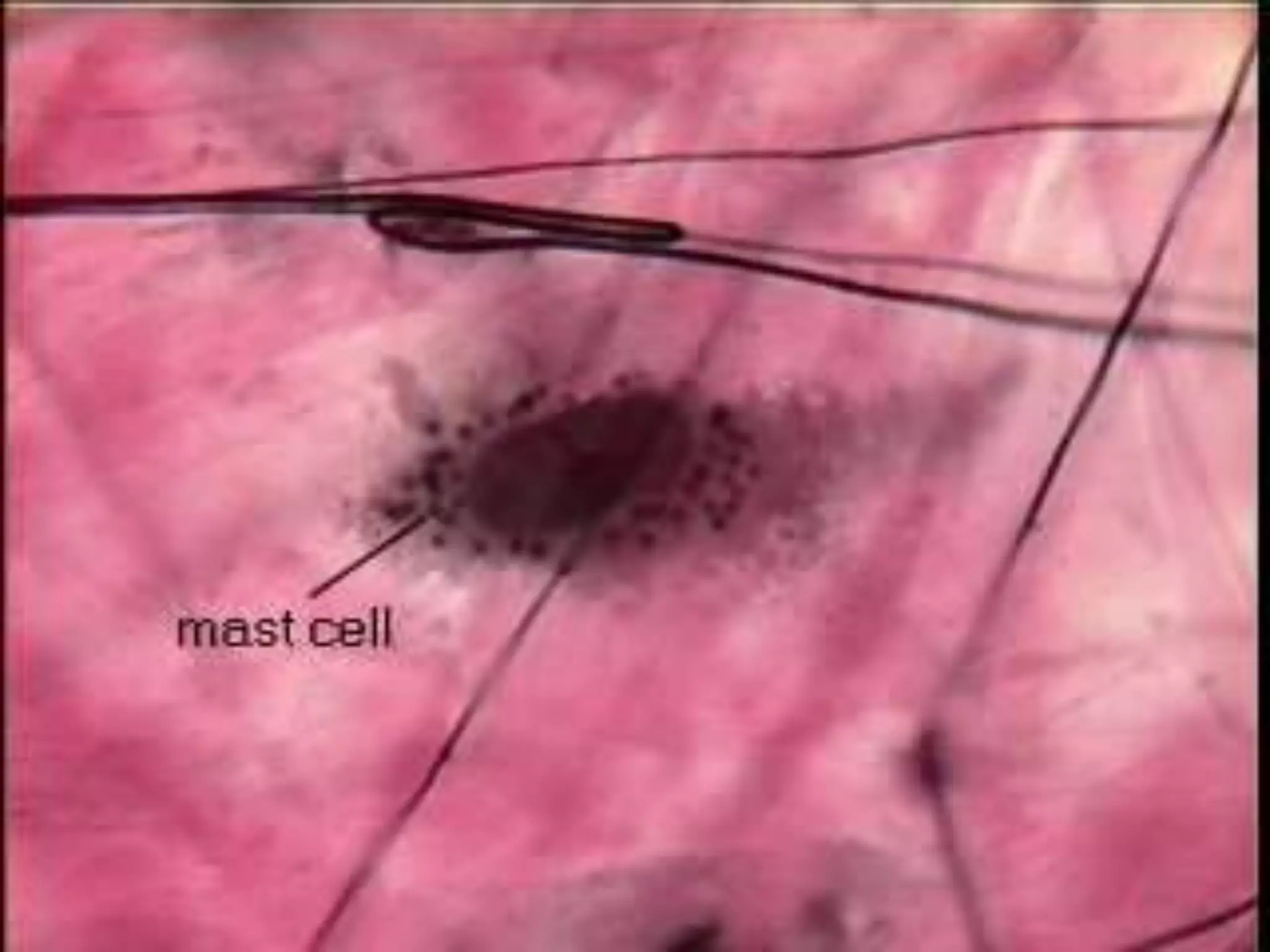
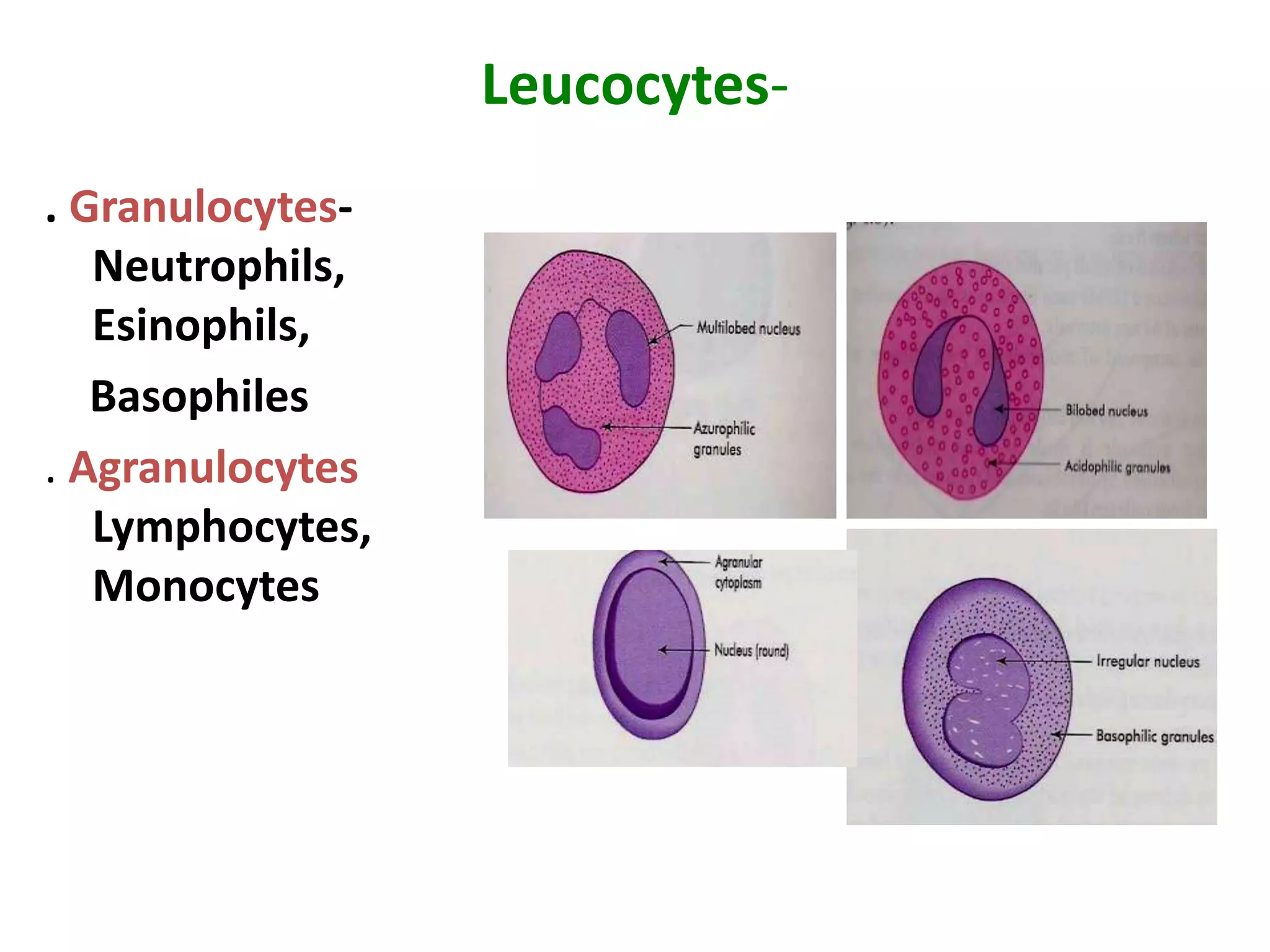
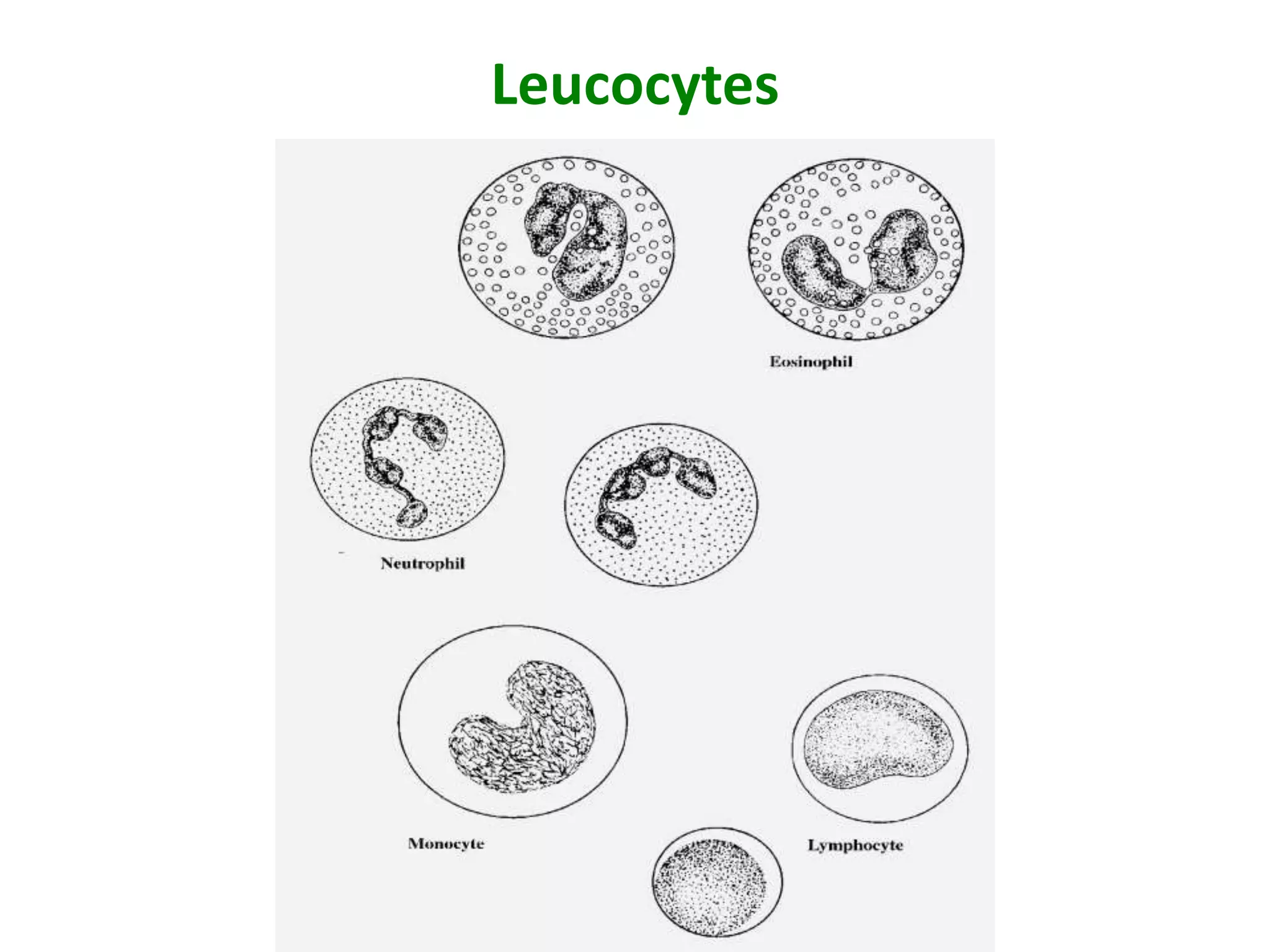
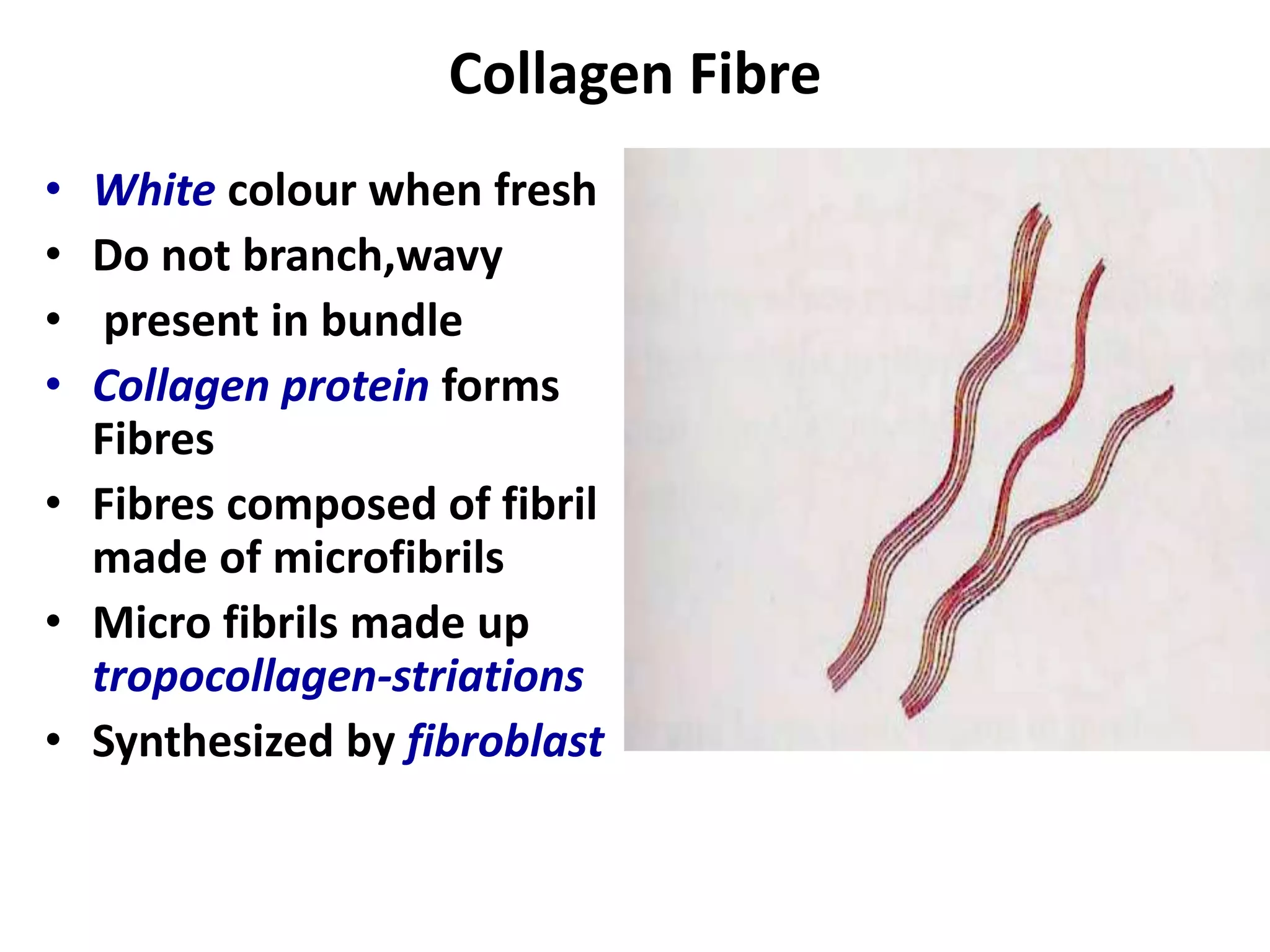
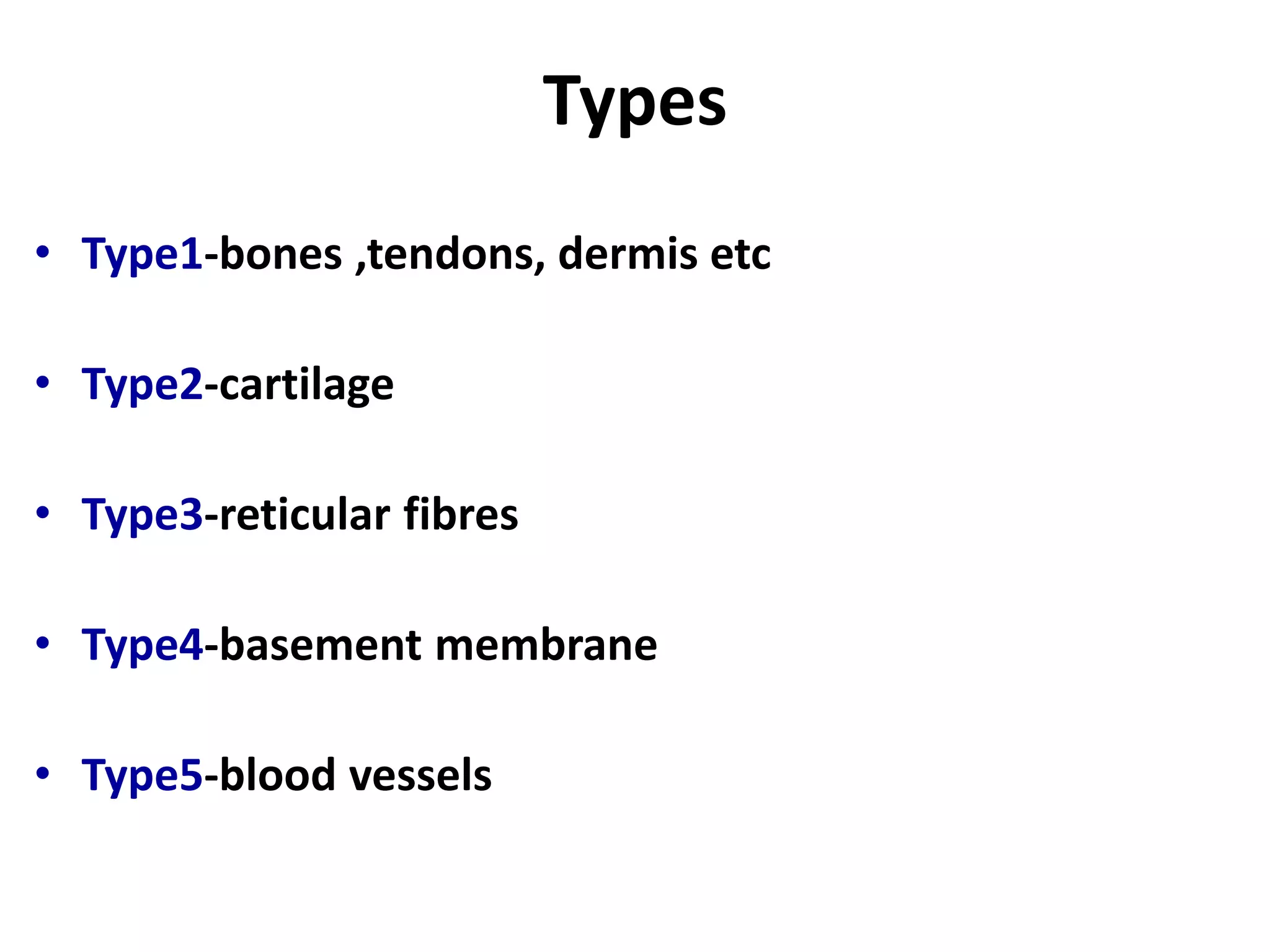
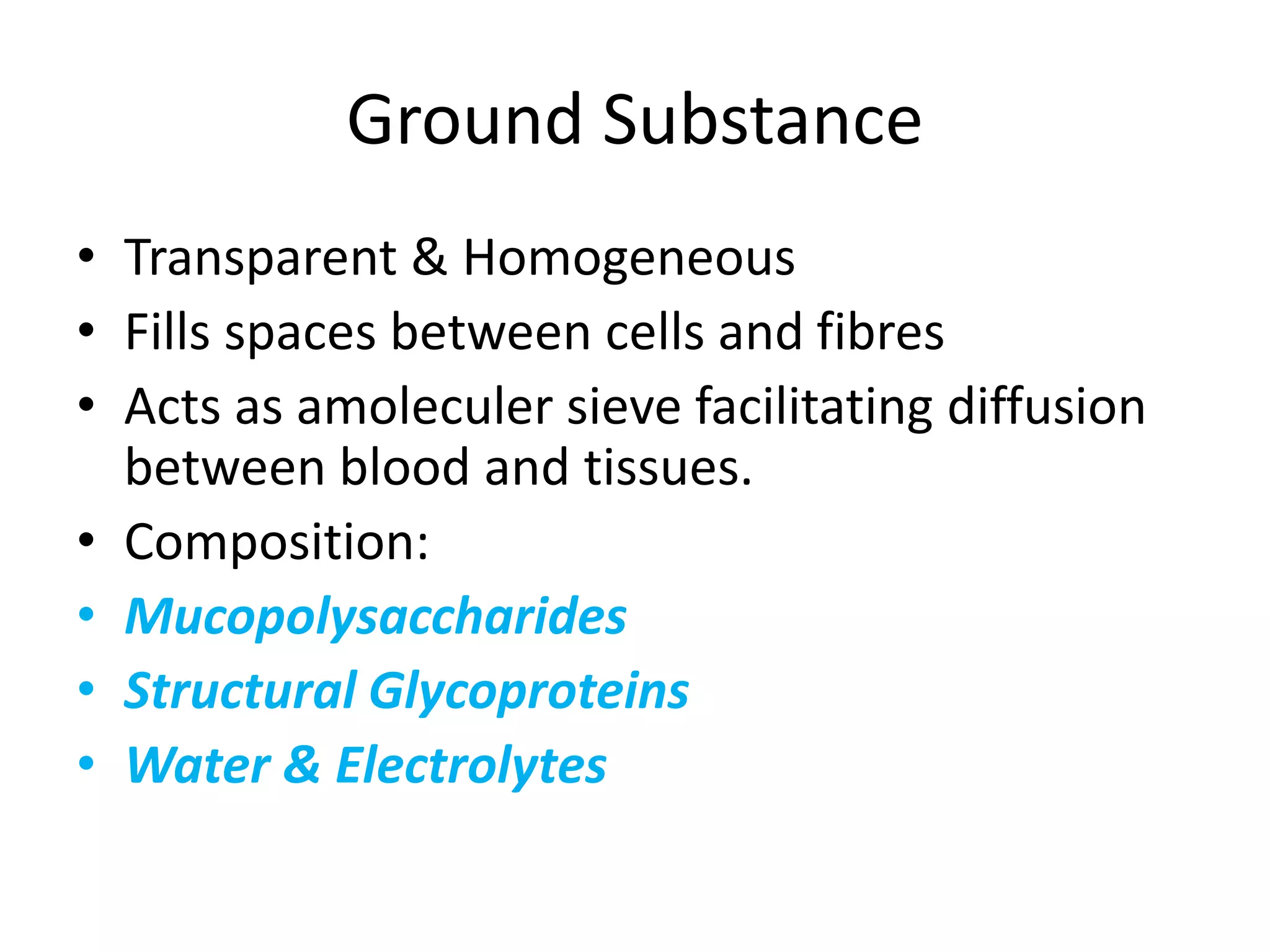
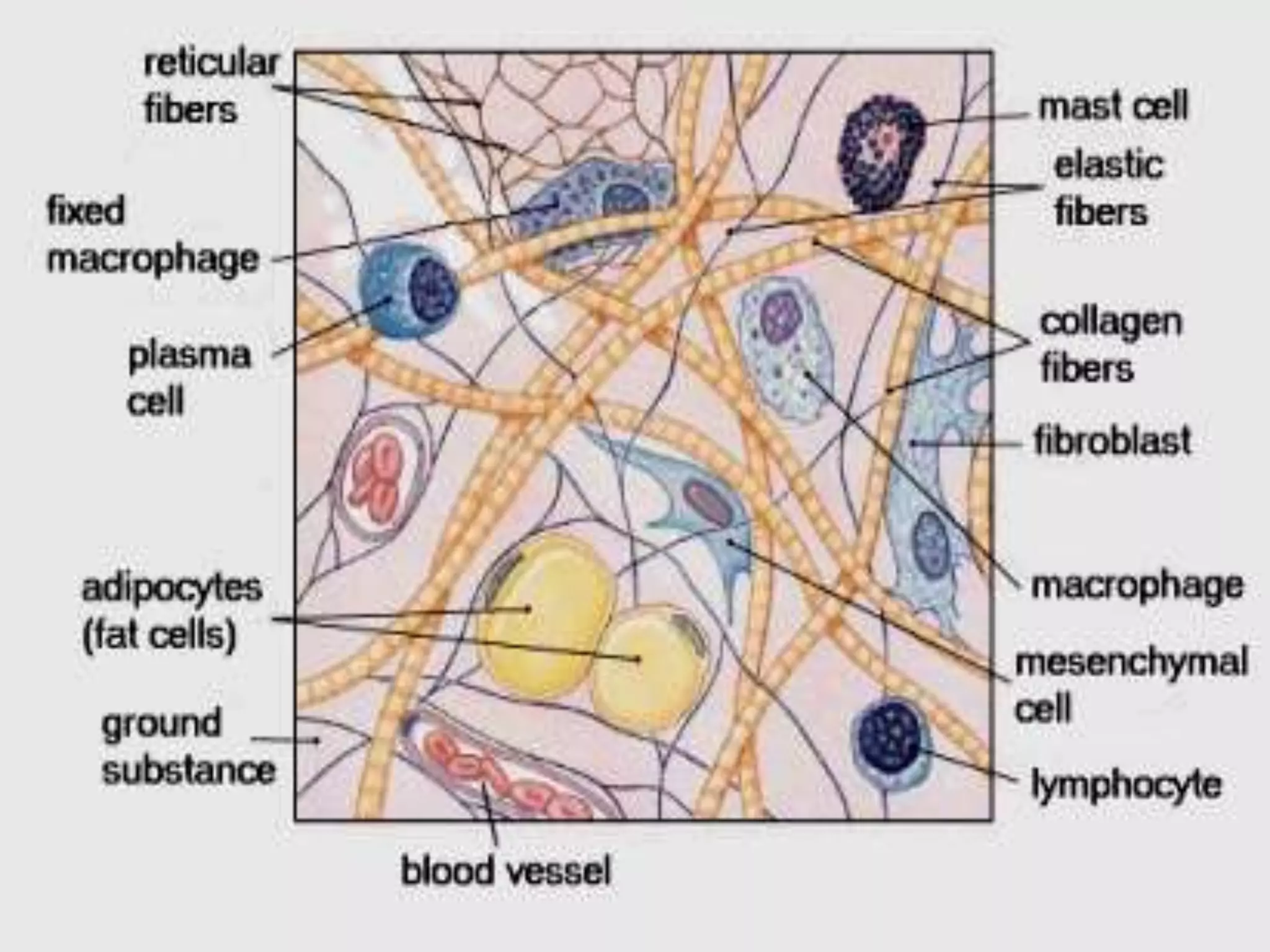
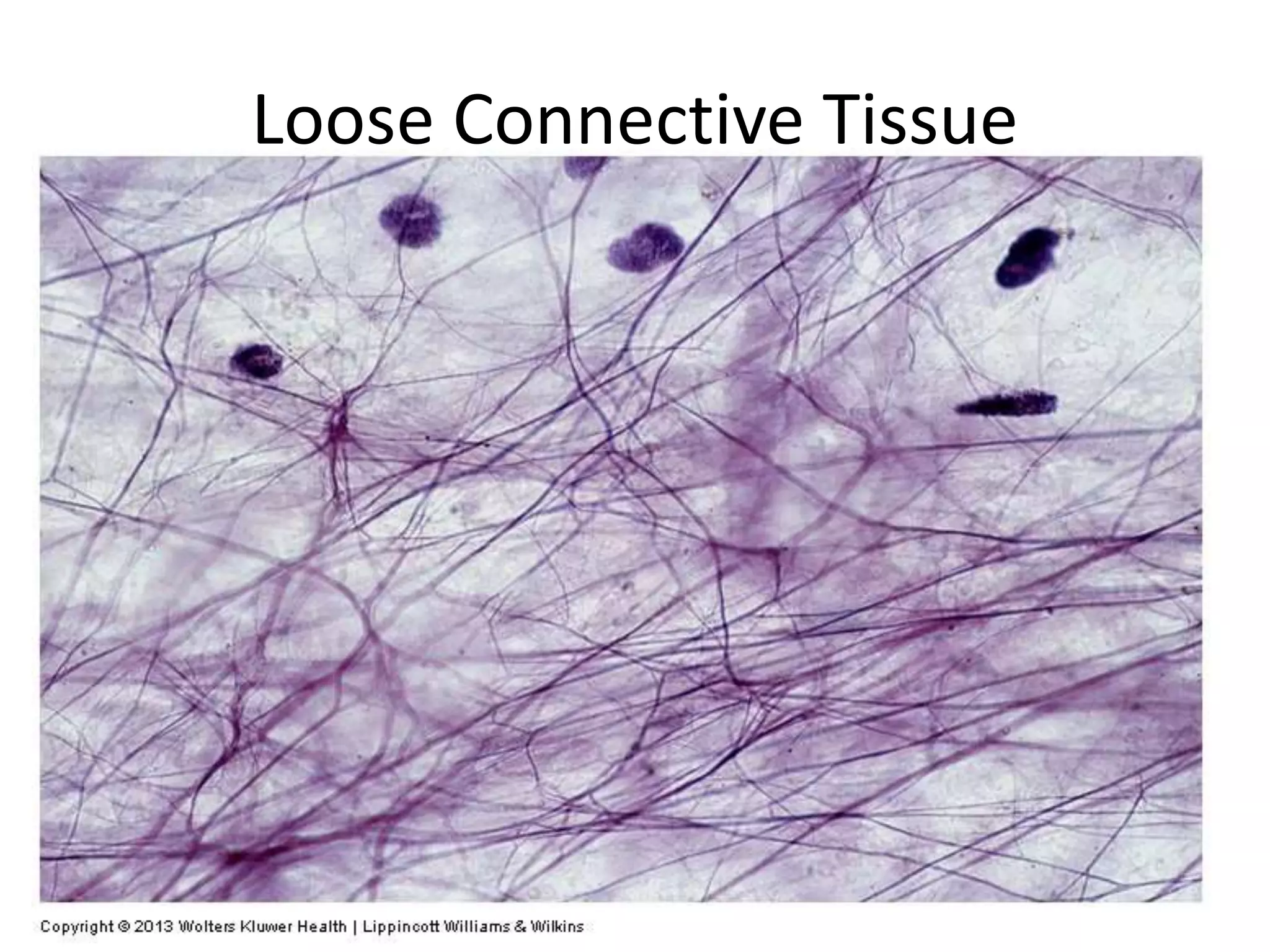
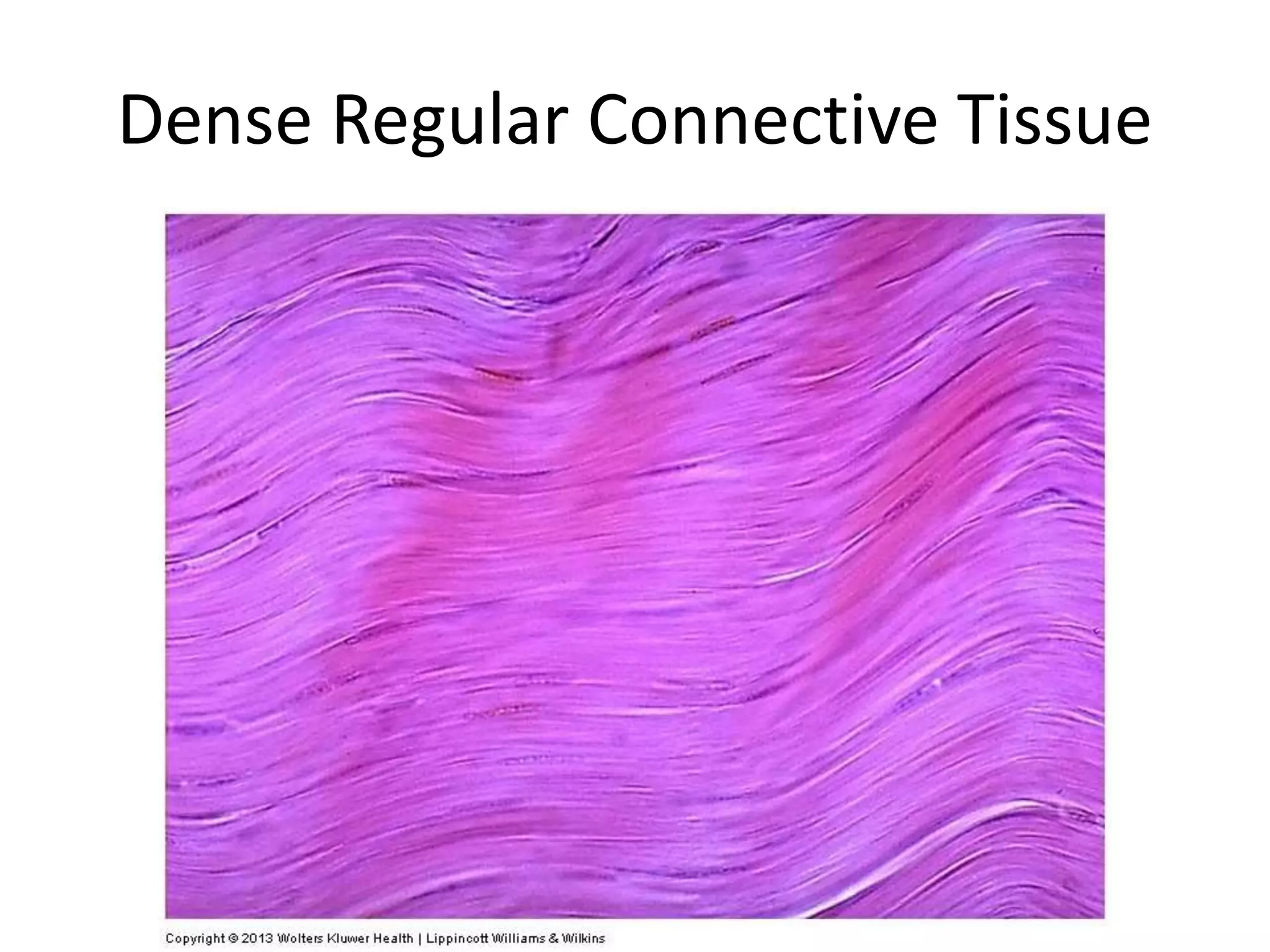
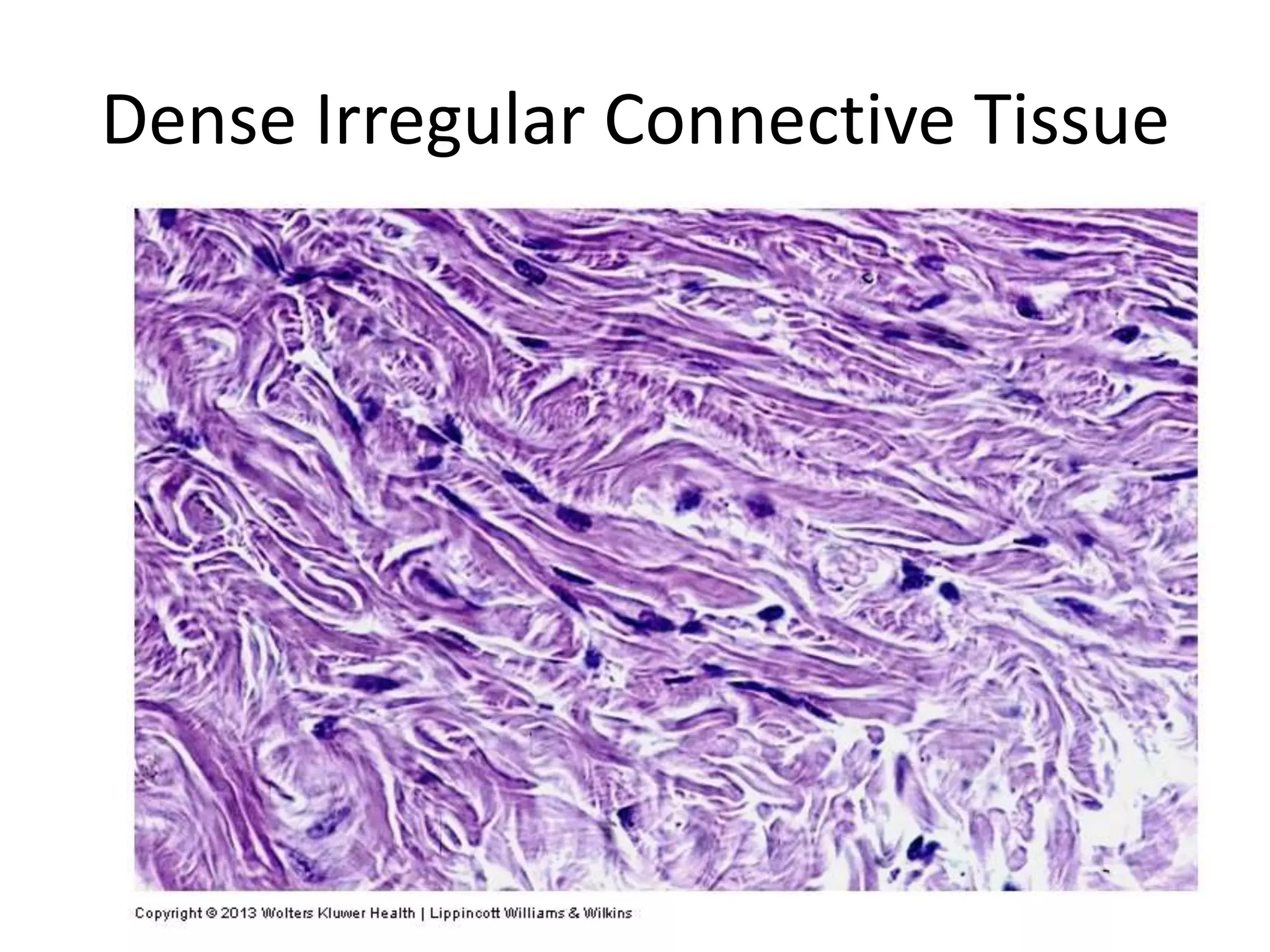
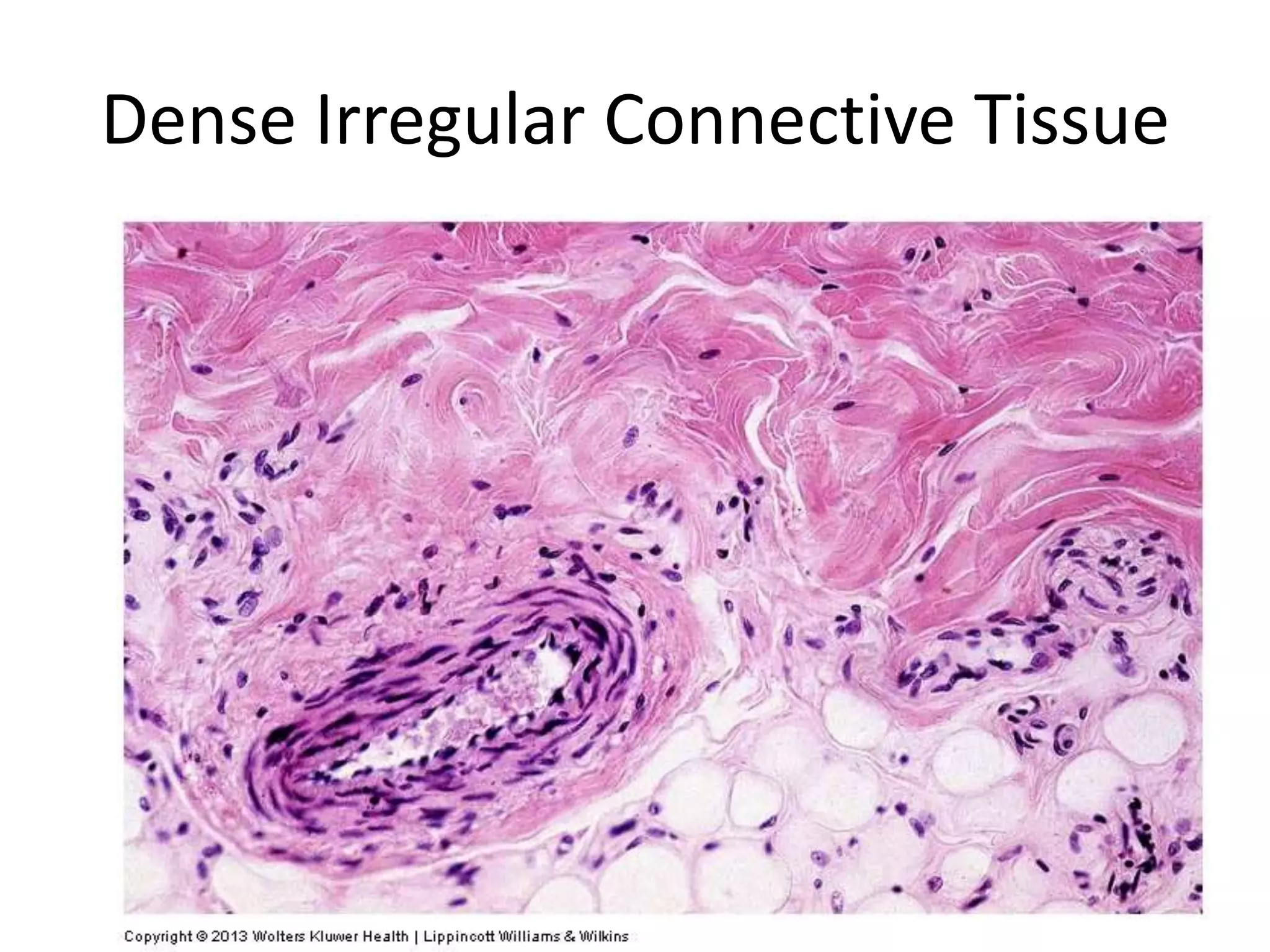
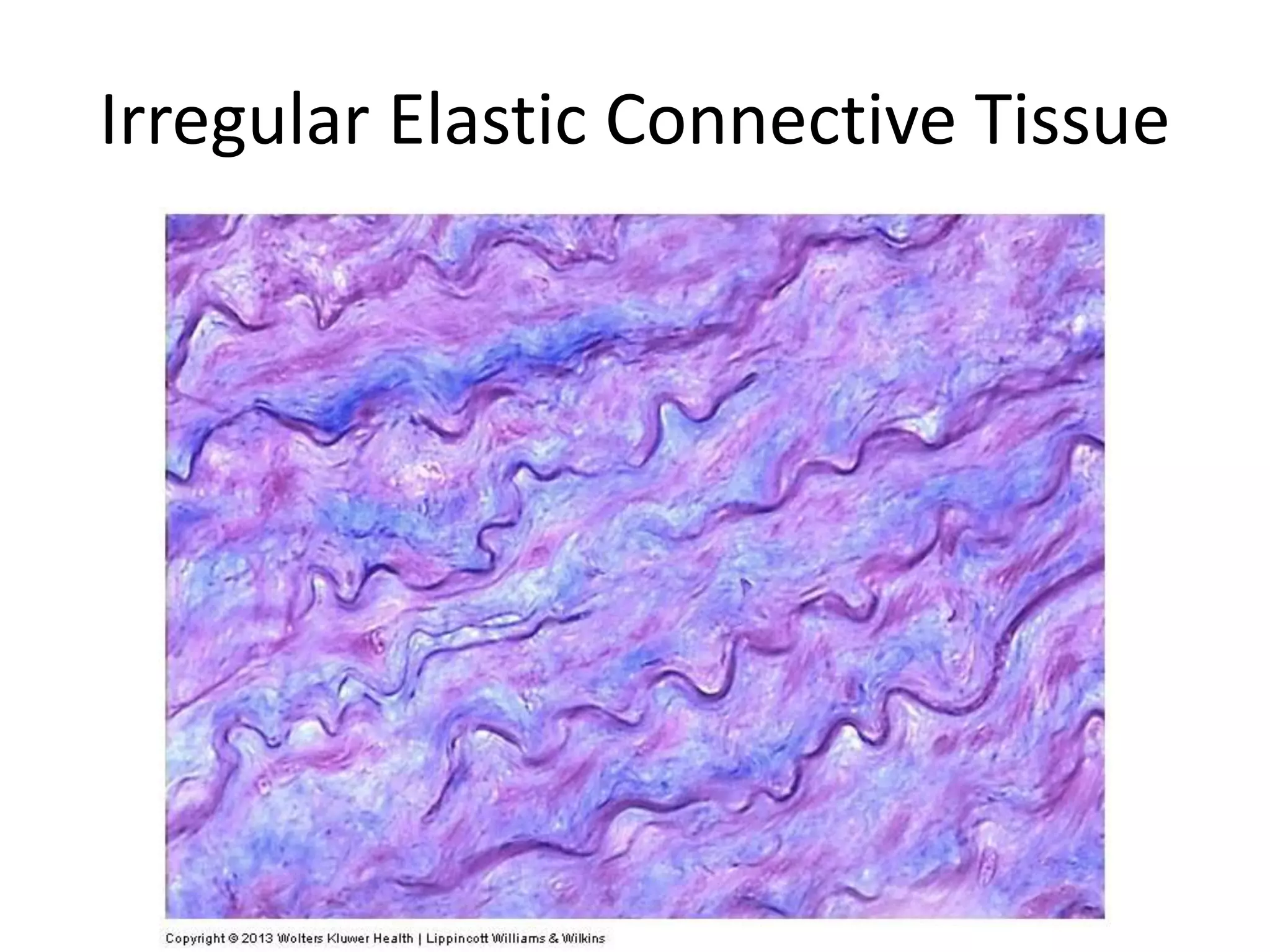
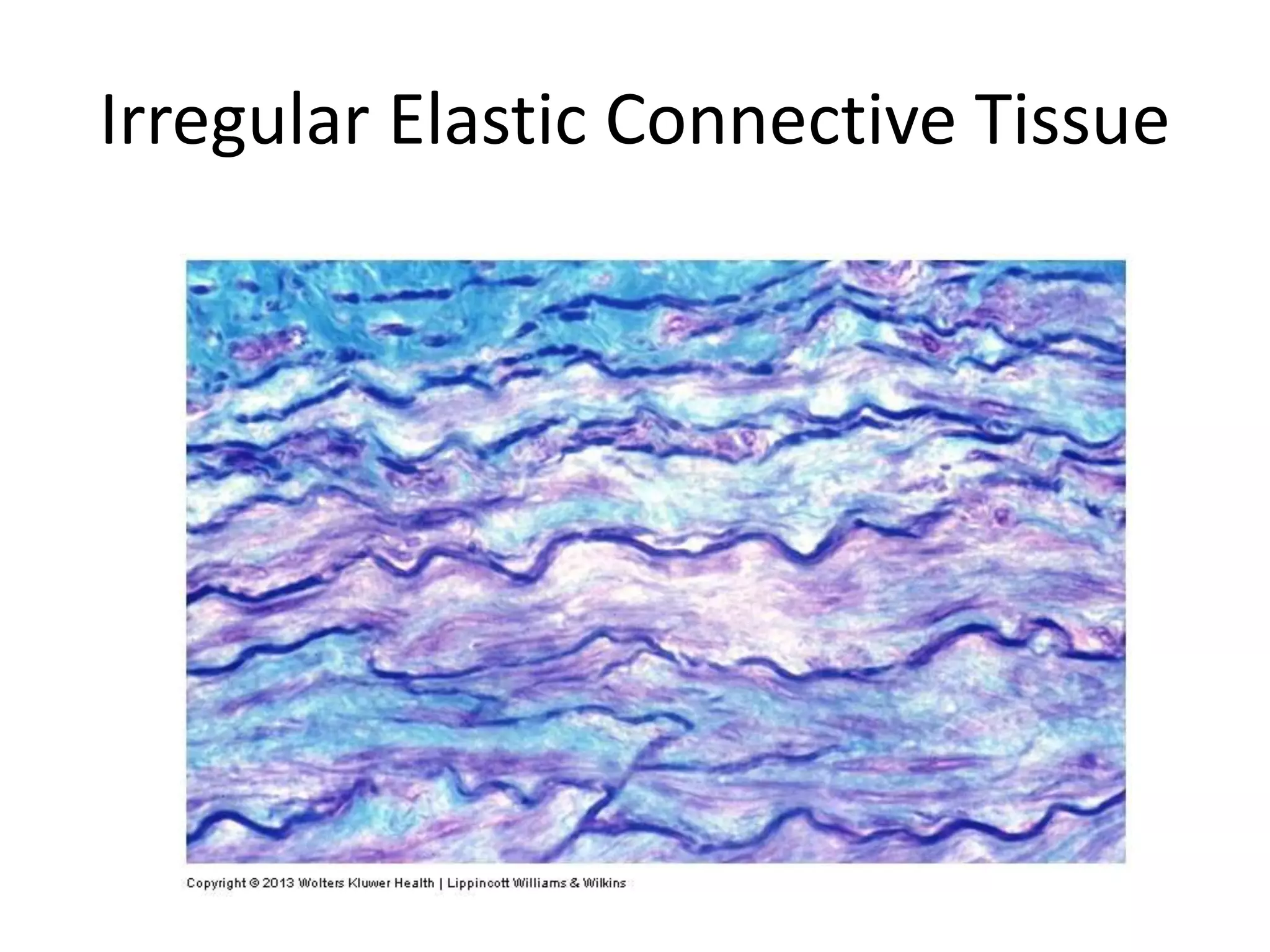
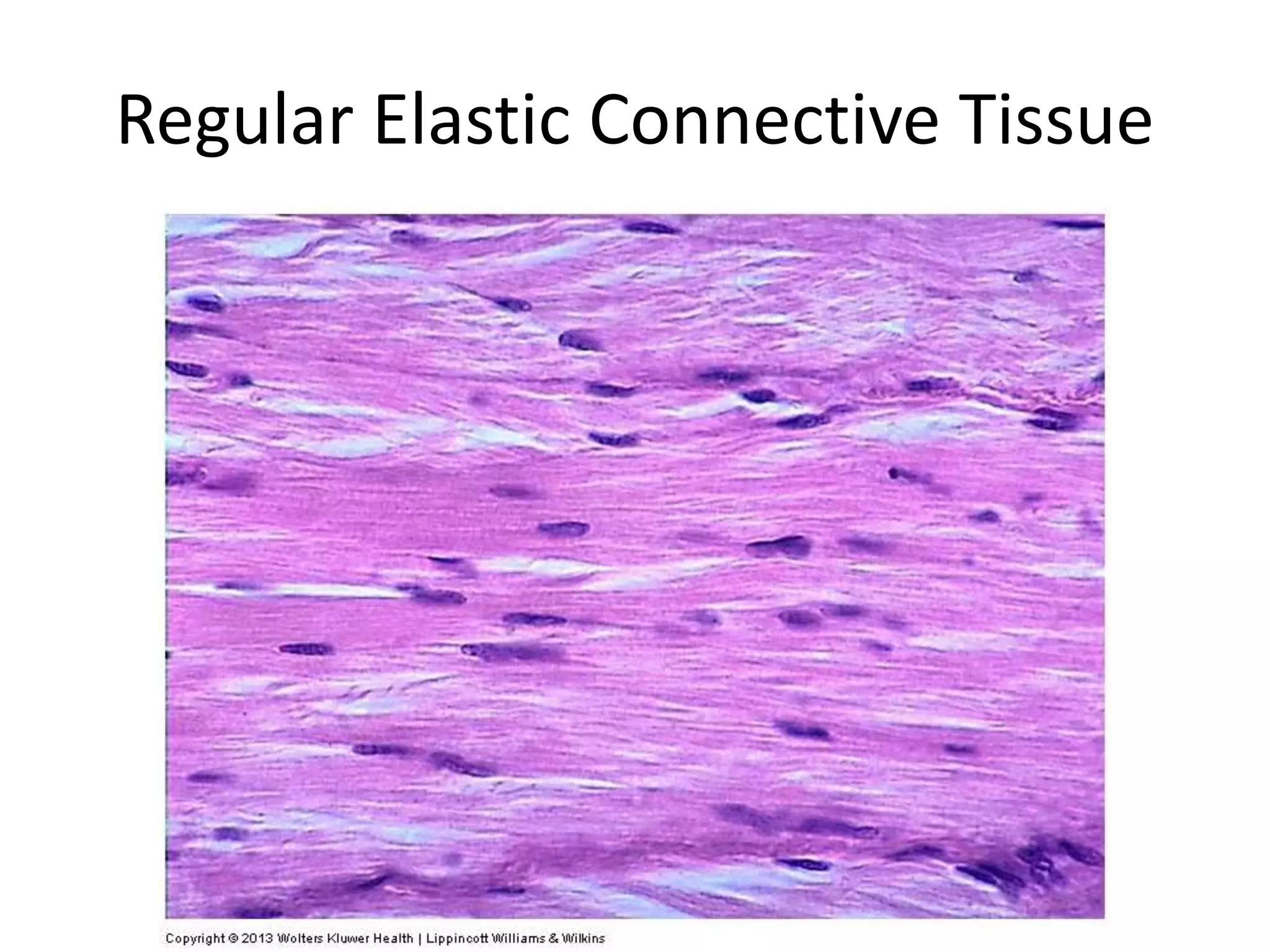
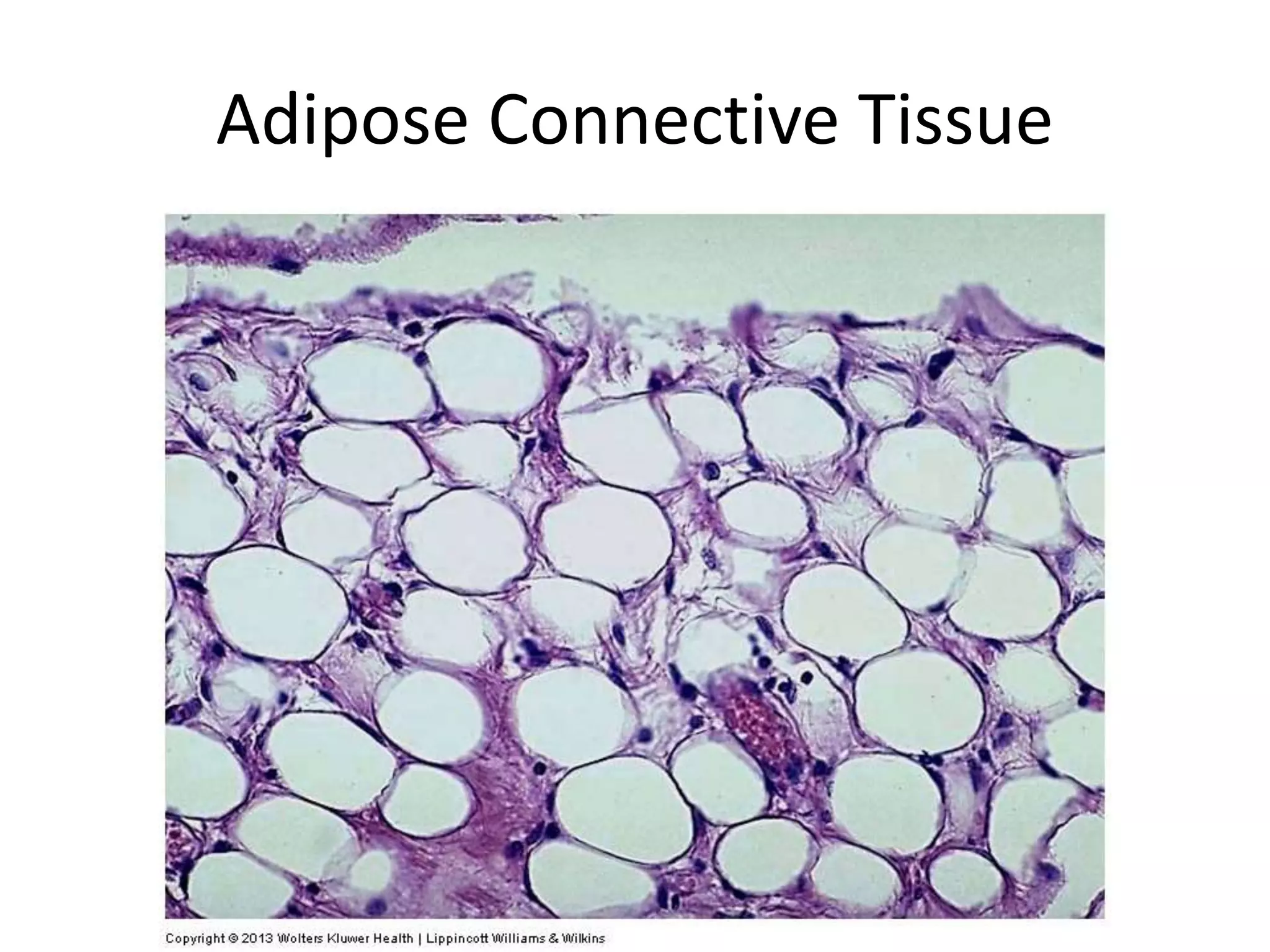
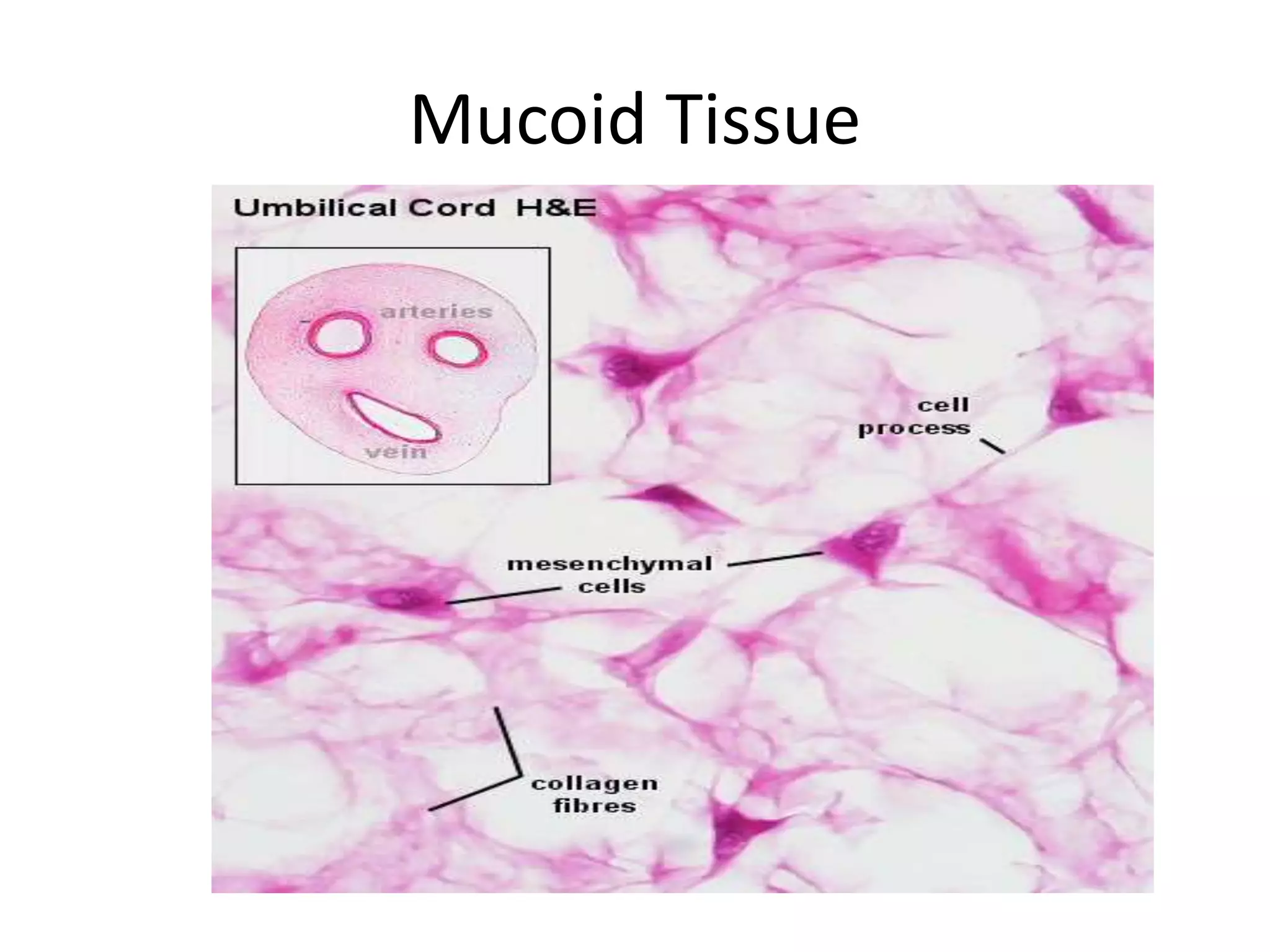
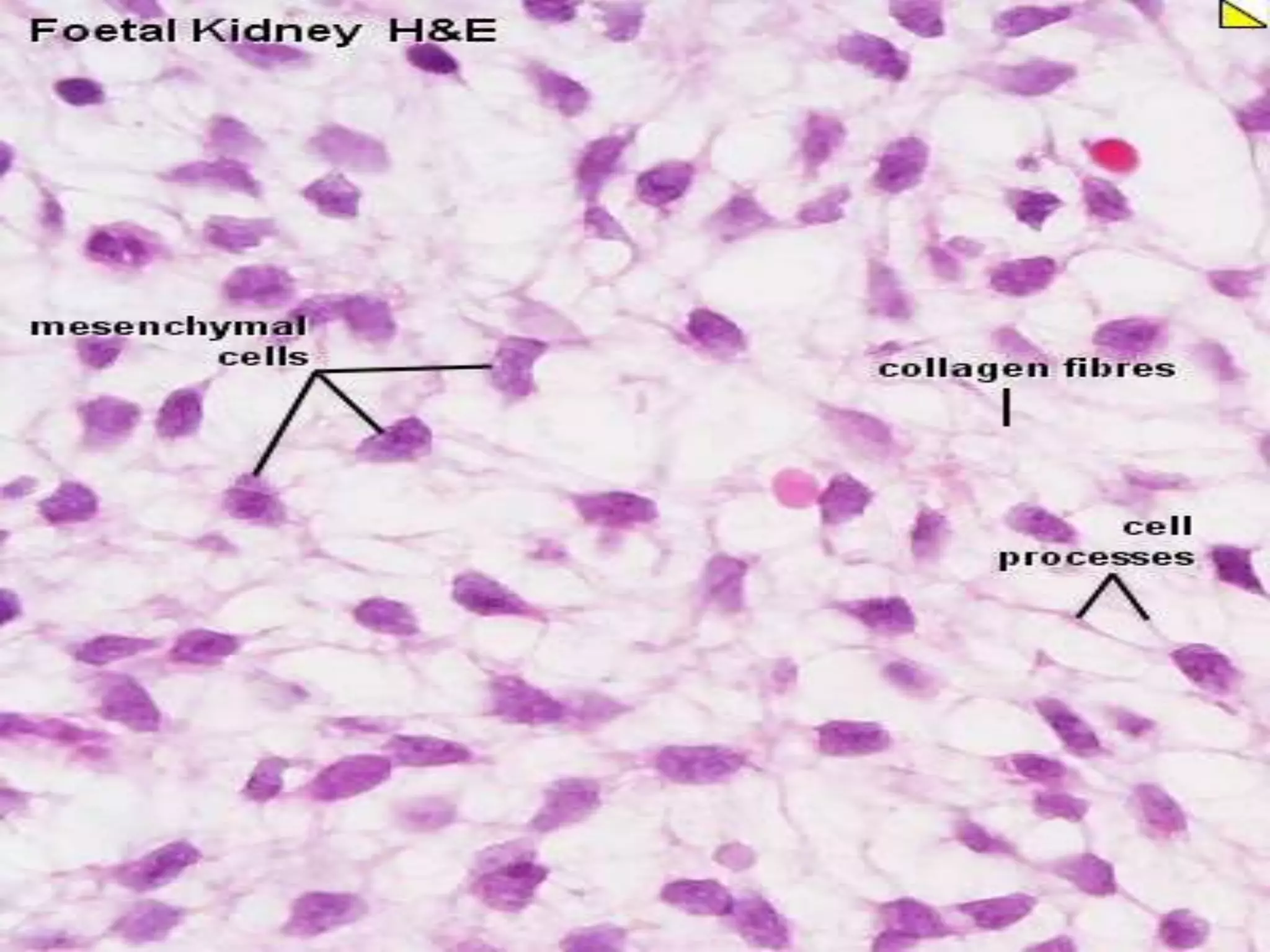
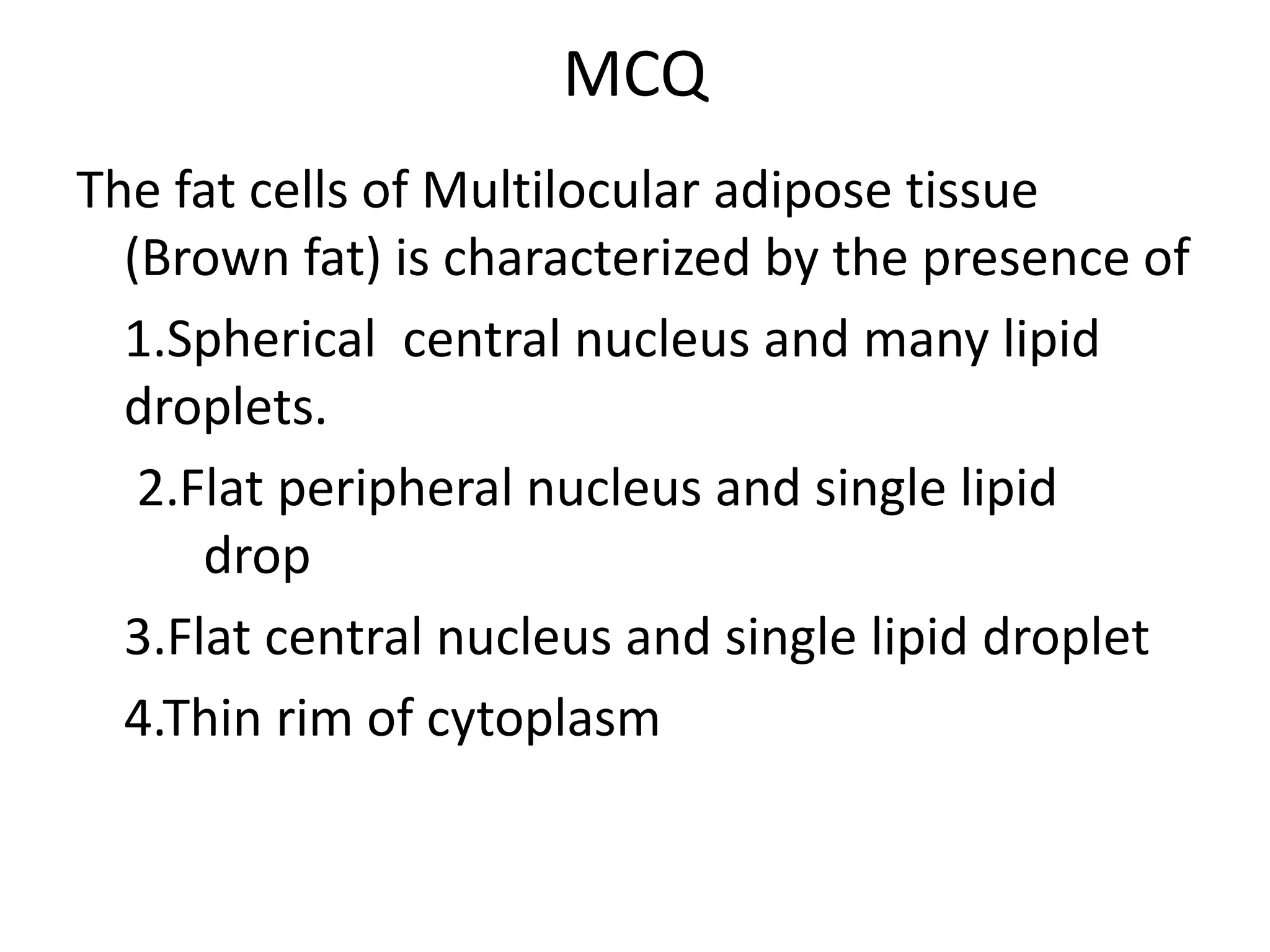
Connective tissue provides structural and metabolic support throughout the body. It connects other tissues and fills spaces. Connective tissue consists of cells and an extracellular matrix containing fibers and ground substance. The main cell types are fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, plasma cells, and mast cells. Fibers include collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers. Ground substance is made of mucopolysaccharides and structural glycoproteins in a water and electrolyte-rich base. Connective tissue includes loose connective tissue, dense regular and irregular connective tissue, adipose tissue, and special types like elastic, reticular, and mucoid tissue.