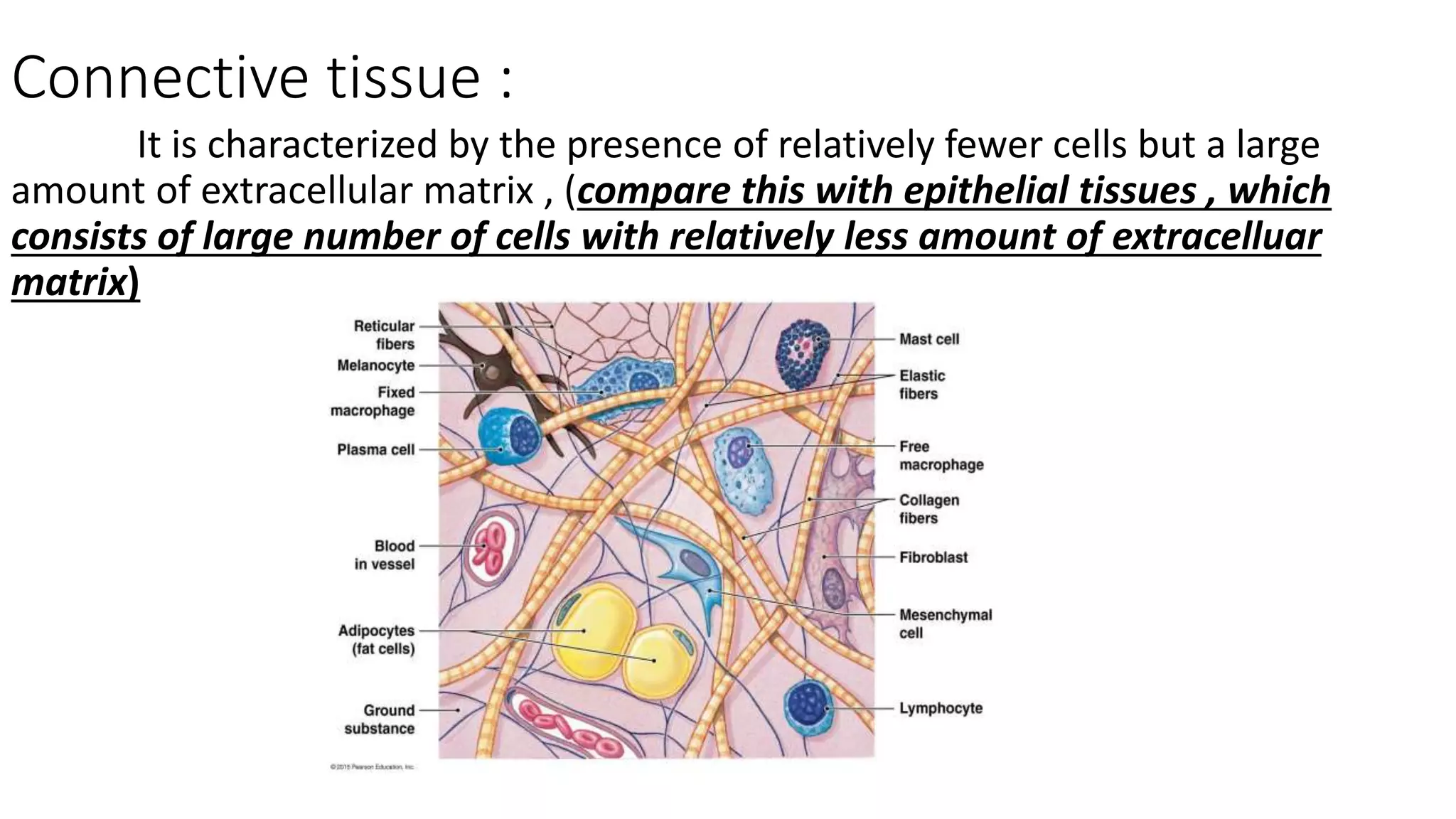
Connective tissue is characterized by fewer cells but a large amount of extracellular matrix. It has several functions including structural support, exchange mediation, defense and protection, and fat storage. There are different types of connective tissue including embryonic connective tissue (mesenchymal and mucoid), connective tissue proper (loose and dense connective tissue), and specialized connective tissue (cartilage, bone, blood, reticular, and adipose tissue). Connective tissue contains fibers such as collagen, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers as well as ground substance and various cell types including fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells, plasma cells, and leukocytes that carry out important roles.