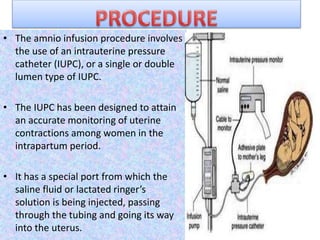
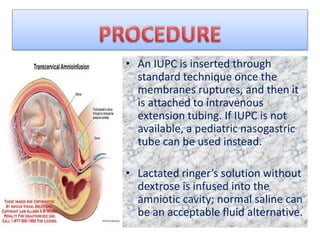
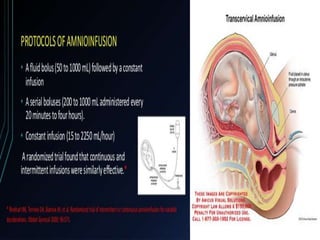
Amnioinfusion is a technique used during labor to instill isotonic fluid into the amniotic cavity to relieve umbilical cord compression and fetal distress. Indications for this procedure include fetal heart rate abnormalities and low Apgar scores, and it involves the use of an intrauterine pressure catheter for accurate monitoring. Nursing responsibilities include continuous monitoring of fetal heart tones and contractions, and discontinuing the infusion if certain complications arise.