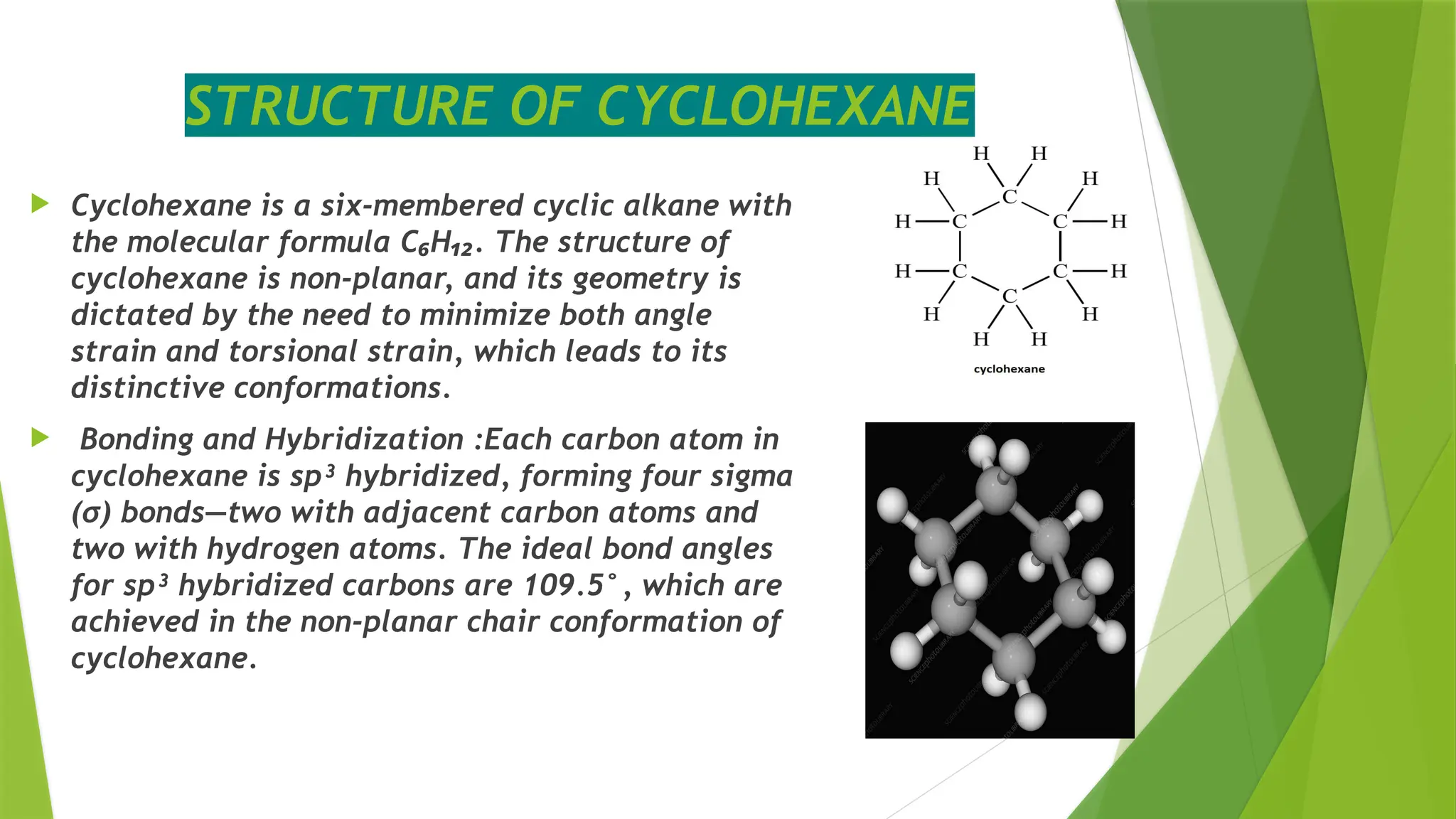
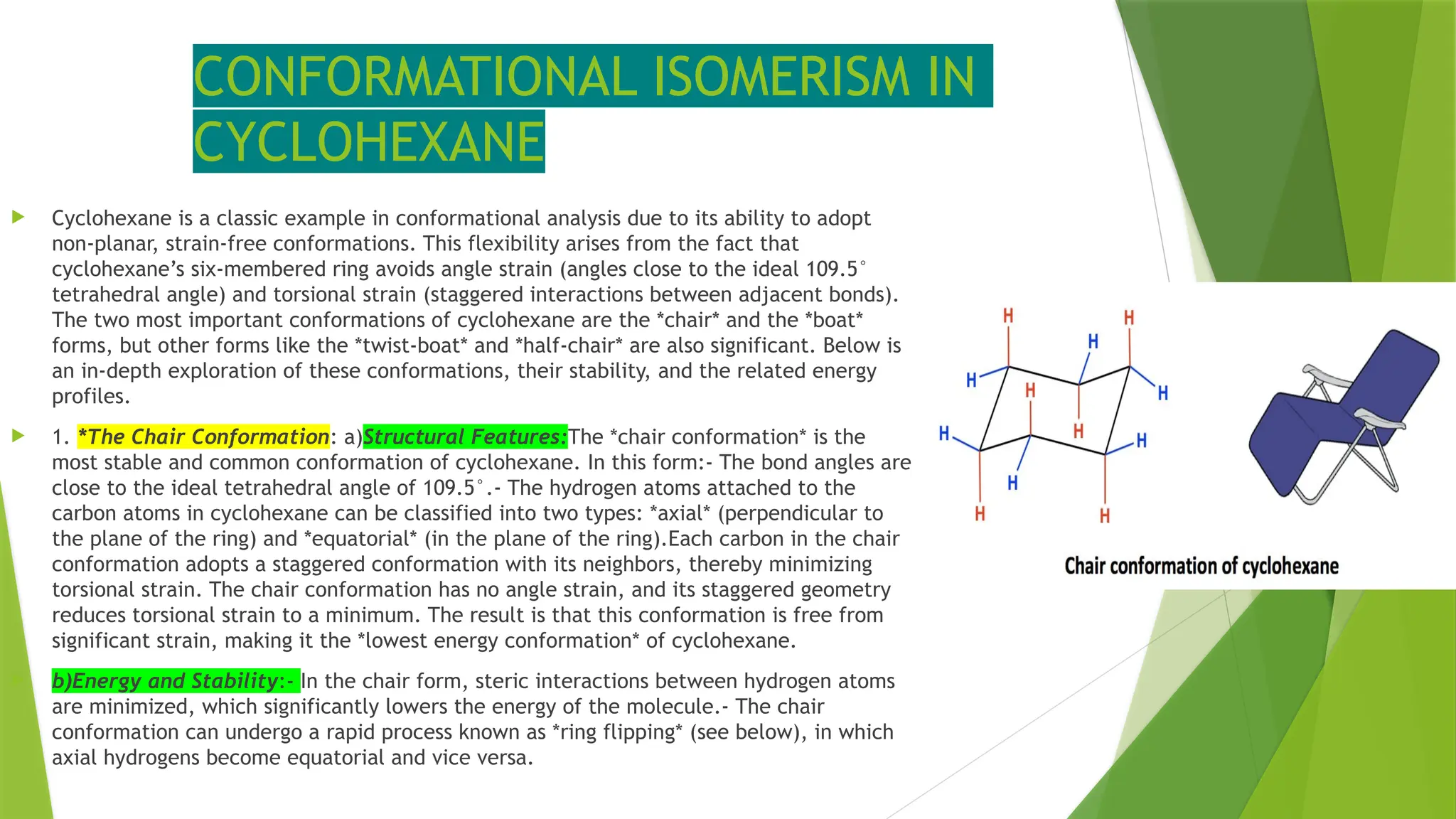
The document discusses conformational isomerism in cyclohexane, including its structure, distinct conformations (chair, boat, twist-boat, and half-chair), and stability considerations. It explains how cyclohexane minimizes torsional and angle strain through its flexible conformations, affecting stability and reactivity, particularly in the presence of substituents. Additionally, it covers the effects of substituent positions on steric interactions and provides insights into the stability hierarchy of cyclohexane conformers.