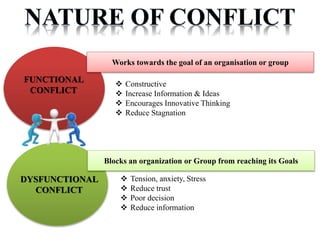
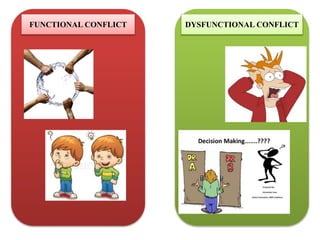
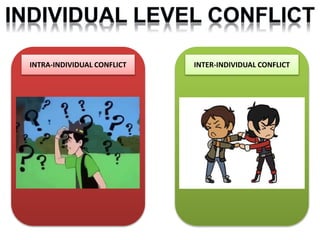
The document discusses the topic of conflict, beginning with definitions and views of conflict. It describes the nature, types, and levels of conflict including individual, group, organizational, and inter-organizational. The document outlines the relationship between organizational performance and conflict, distinguishing between functional and dysfunctional conflict. It provides examples of positive and negative impacts of conflict and discusses processes of conflict including latent, perceived, felt, and manifest conflict. Methods of conflict resolution are presented including communication, negotiation, mediation, arbitration, and legislation. Case studies on conflicts within organizations are also summarized.