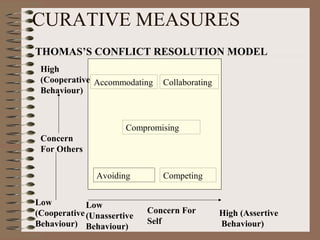
The document discusses the nature and causes of conflict at different levels. It defines conflict as a disagreement between two or more parties trying to achieve their own objectives. There are various views of conflict, including that it is natural but can be functional or dysfunctional. Conflict occurs at the individual, interpersonal, group and organizational levels due to factors like role incompatibility, personal differences and scarce resources. Both preventive and curative measures are needed to manage conflict constructively.