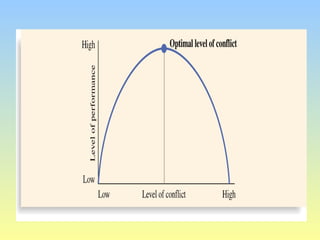
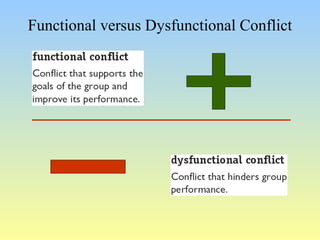
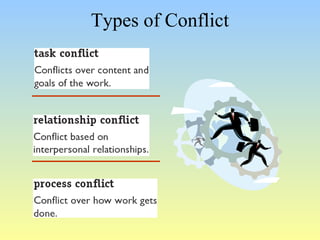
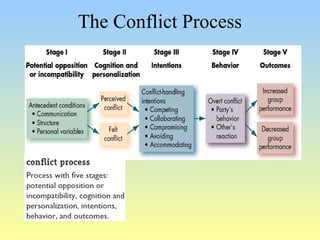
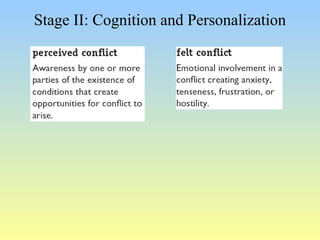
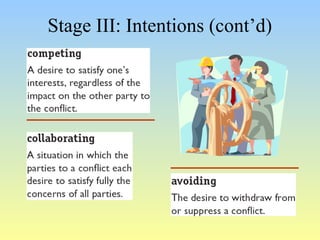
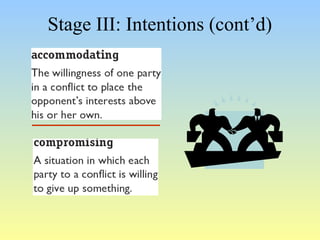
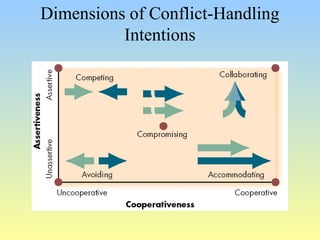
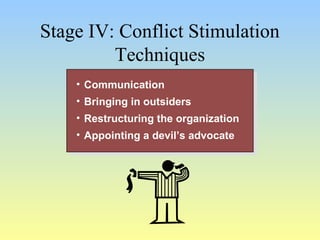
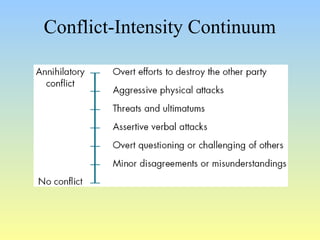
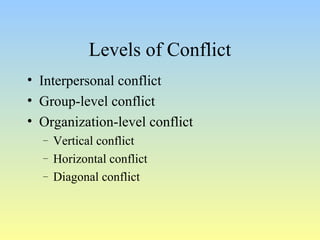
This document discusses organizational conflict at various levels. It defines organizational conflict as goal-directed behavior being blocked by another person or group. Causes of conflict include poor communication and lack of openness. Conflict can be functional, releasing tension and stimulating change, or dysfunctional, causing high turnover and distrust. The stages of conflict are potential opposition, cognition/personalization, intentions, behavior, and outcomes. Conflict resolution techniques include problem-solving, compromise, and altering structures/people. Conflict occurs at interpersonal, group, and organizational levels within and between departments.