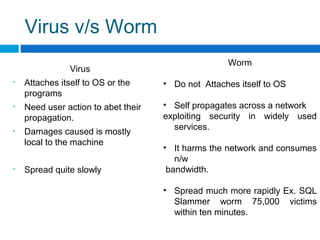
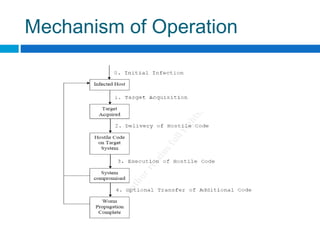
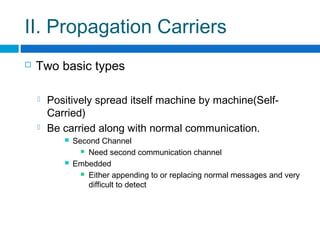
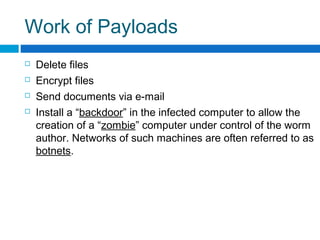
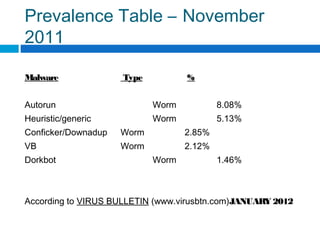
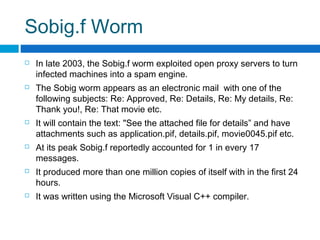
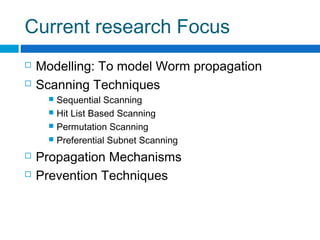
This document discusses computer worms, including how they work, types of worms, and examples of major worms. It defines worms as programs that replicate themselves across a network by exploiting security vulnerabilities. The document covers worm target discovery, propagation, activation methods, payloads, examples like Morris worm, Code Red, Nimda, SQL Slammer, and Sobig.f, as well as prevention techniques and current research focus areas.