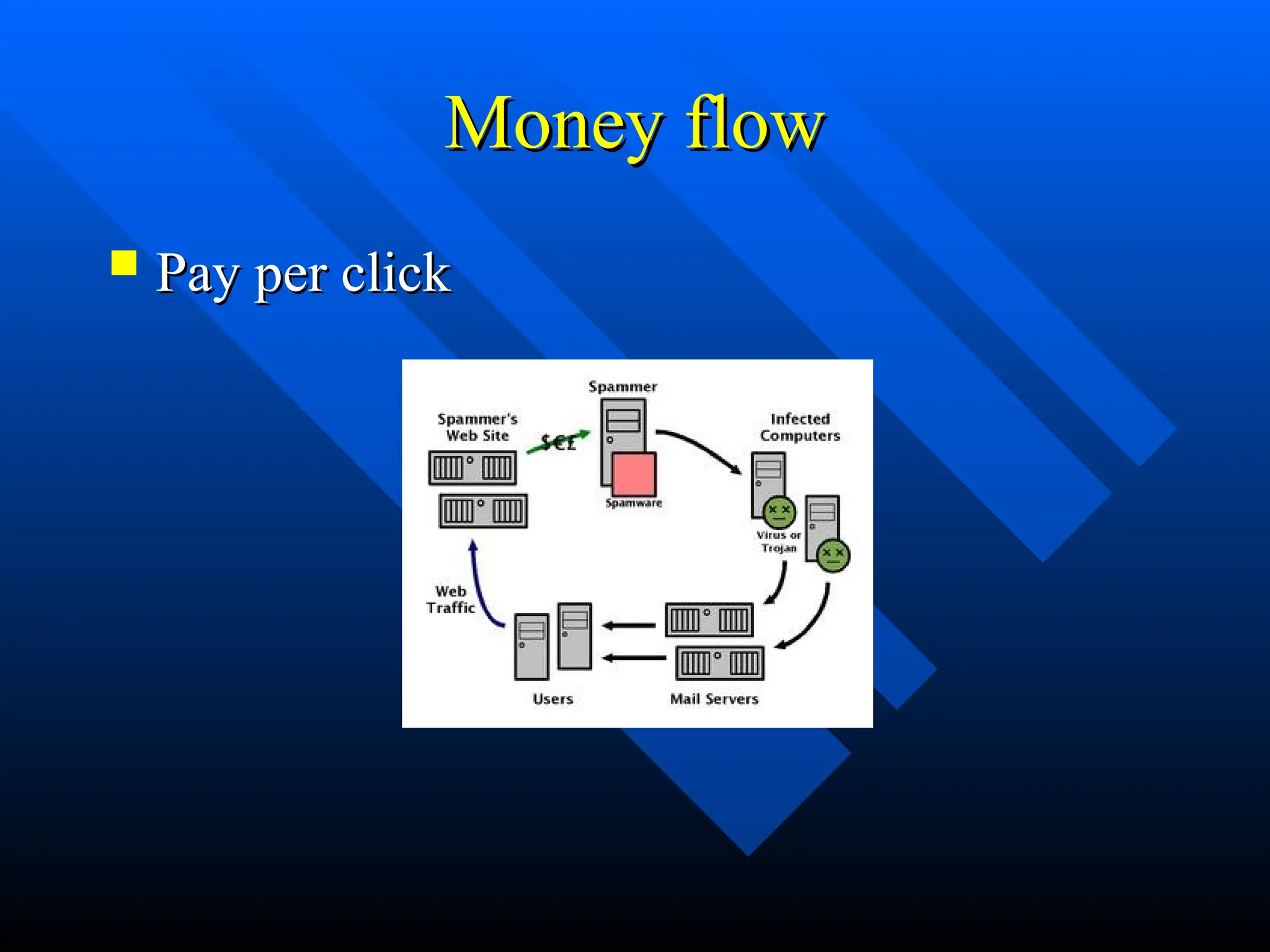
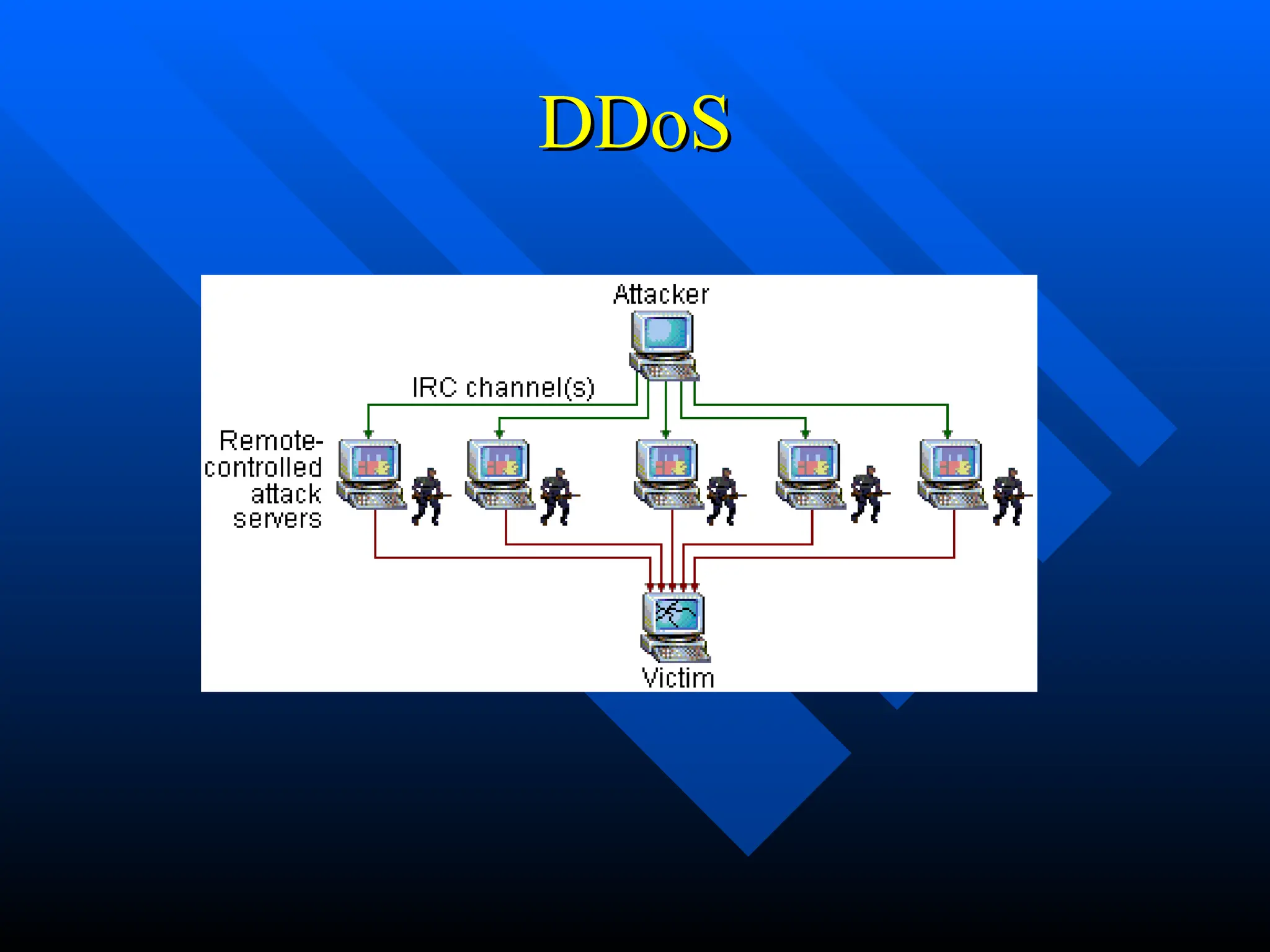
The document discusses computer viruses and worms, defining a virus as a software piece that executes through legitimate programs and spreads by inserting copies of itself into other code. It outlines the history of viruses from 1949 to notable incidents, including the Morris worm and the Mydoom virus, as well as various types of viruses such as email viruses and worms. The document concludes with prevention methods, including updates and anti-virus software.