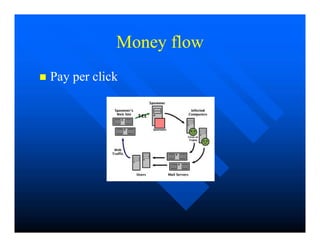
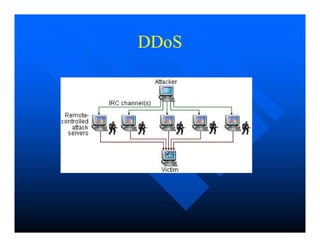
Computer viruses and worms replicate themselves by inserting copies into other programs or documents. Viruses are pieces of code that piggyback on other programs, while worms are self-contained and use network vulnerabilities to spread. Notable examples include the Morris worm of 1988, which was the first to gain widespread attention, and the MyDoom virus of 2004, which caused major internet disruptions through distributed denial of service attacks. Prevention methods against viruses, worms, and other malware include software updates, antivirus programs, and more secure operating systems.