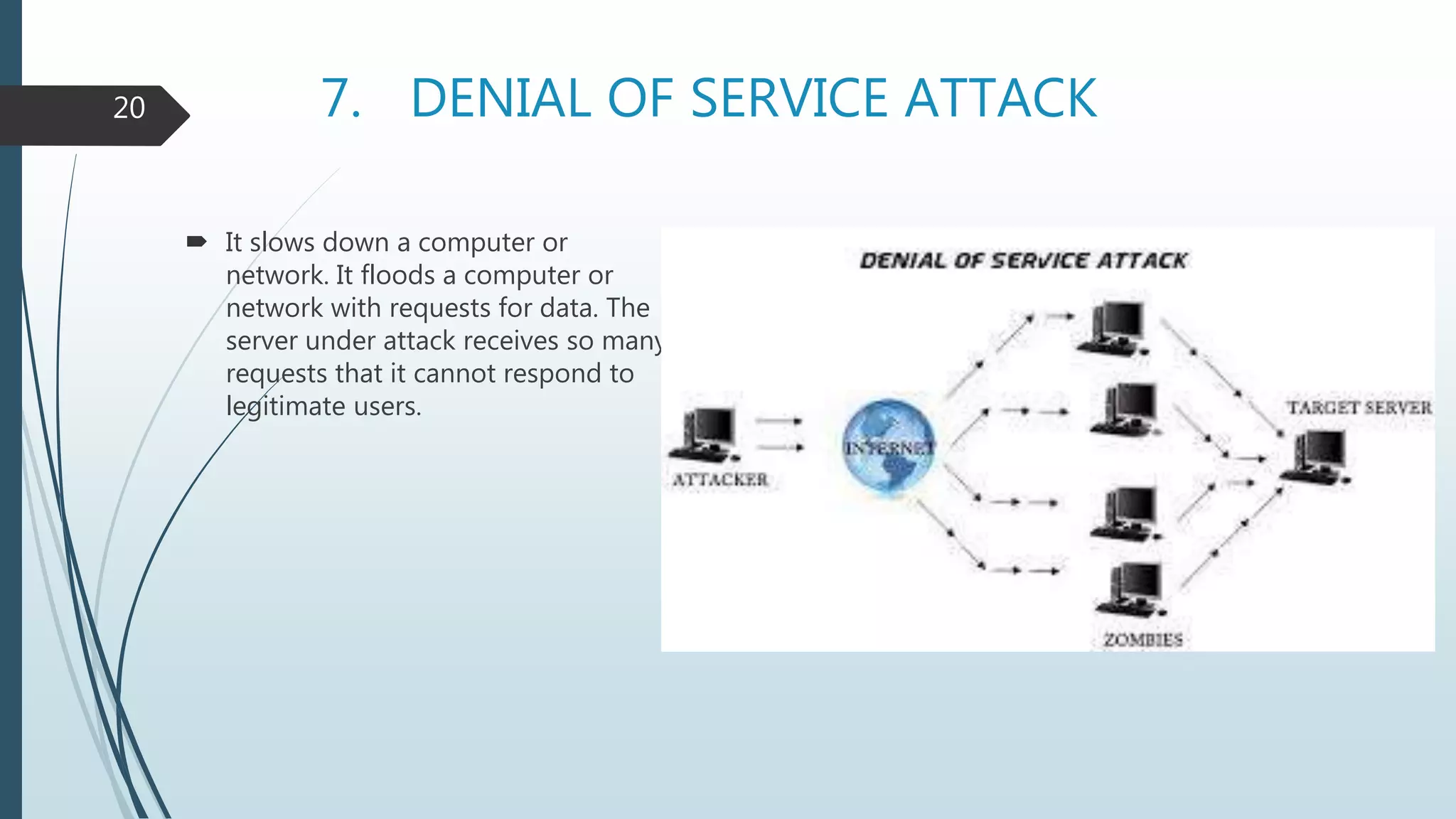
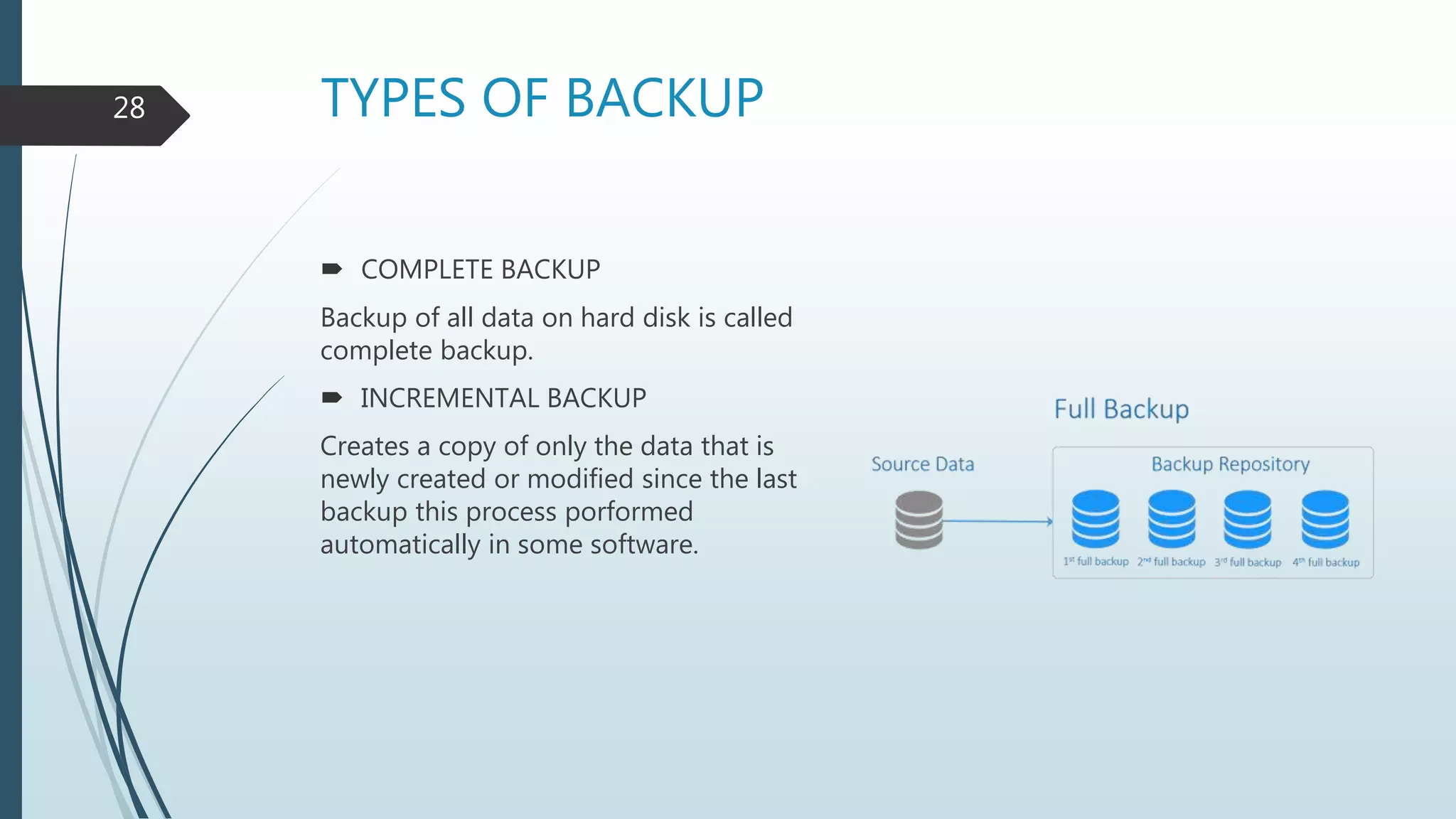
The document discusses computer security, detailing cybercrime, types of computer criminals, and methods employed by them. It emphasizes the importance of computer security, potential disasters from security violations, threats, and various protective measures such as firewalls and data backups. Additionally, it explains the nature and risks associated with computer viruses and the necessity for preventive measures to safeguard data and hardware.