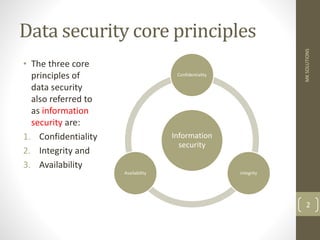
There are three core principles of data security: confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Confidentiality means that sensitive data should not be accessed by unauthorized individuals. Integrity refers to ensuring data is not modified without permission. Availability means information must be accessible on demand. Data security controls aim to protect data from threats like unauthorized access, alteration, and destruction. Common threats include malware, hacking, and data loss from system failures. Organizations implement measures like encryption, firewalls, and monitoring to prevent threats and ensure the security of their data and IT systems.