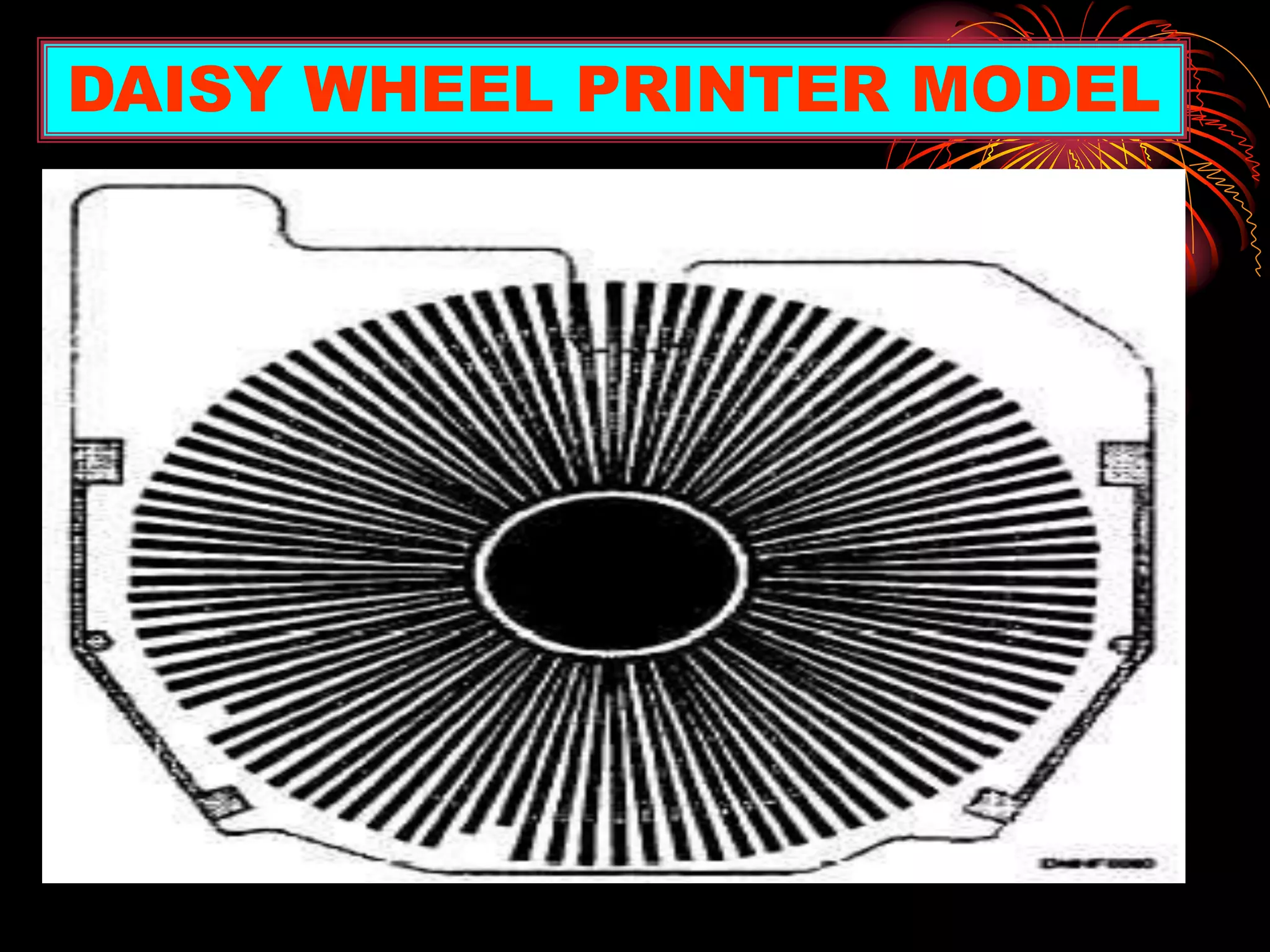
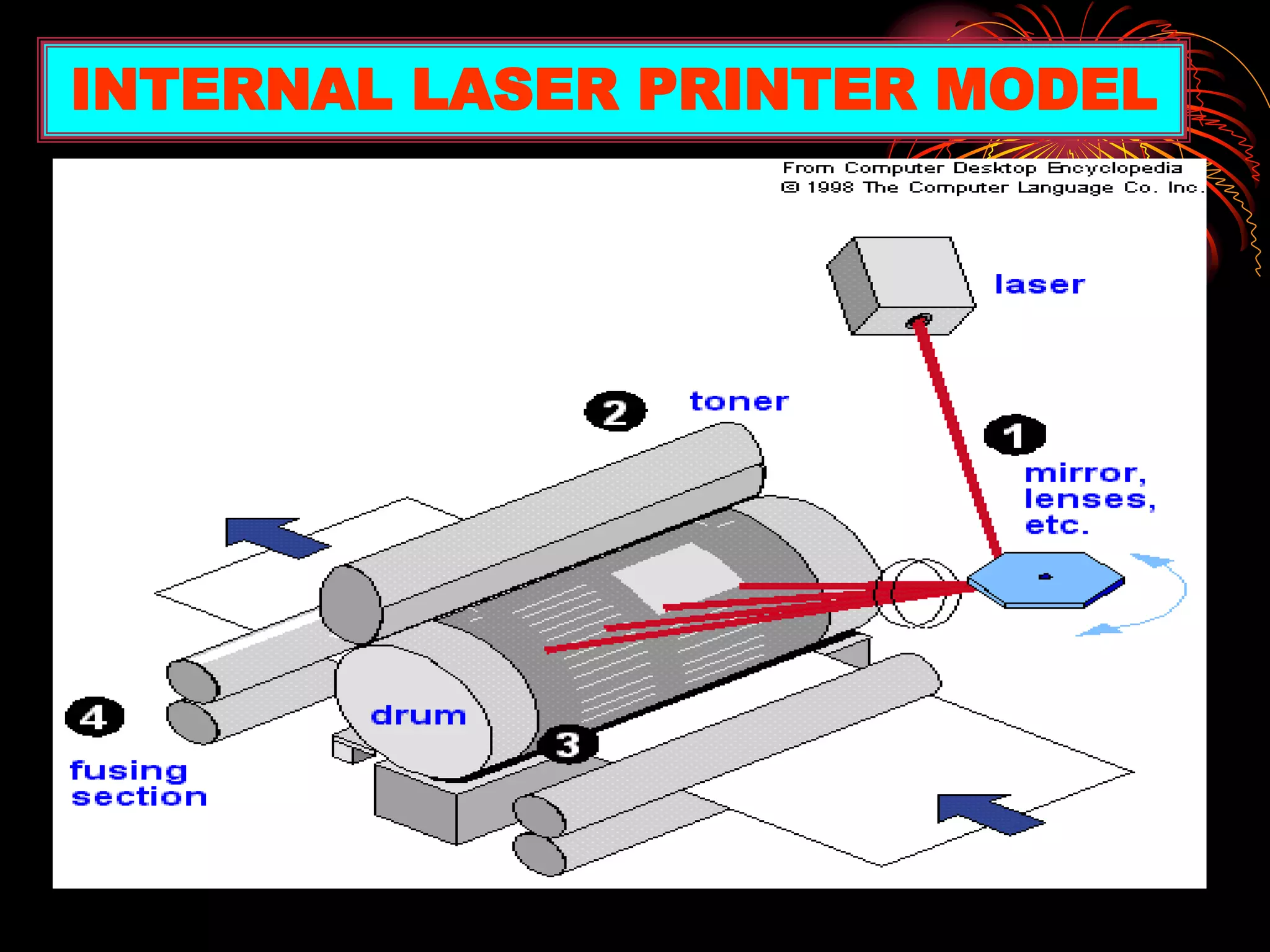
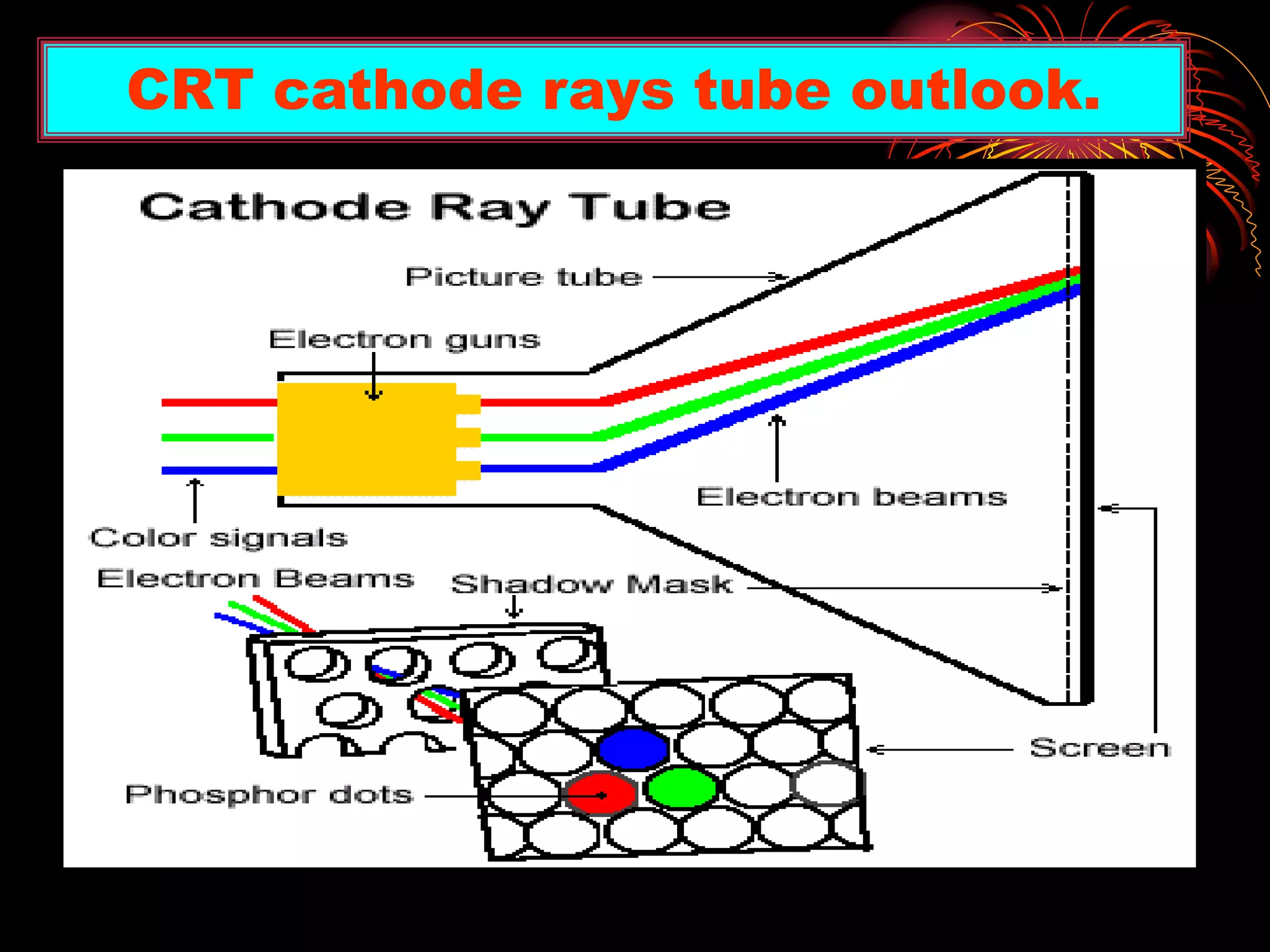
This document is a presentation summarizing various computer output devices. It discusses printers, including the history of printers from early impact printers to modern laser and inkjet printers. It also discusses monitors, including CRT, LCD, and other types of displays. Key details are provided on printer and monitor features like resolution, refresh rate, size, and dot pitch. The presentation was created for a class assignment and acknowledges the teacher and classmates for their support.