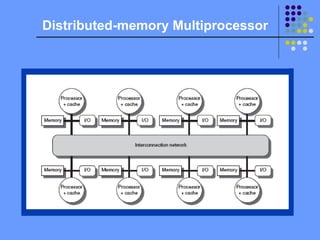
The document discusses multiprocessing and thread-level parallelism. It covers four categories of parallel architectures: SISD, SIMD, MISD, and MIMD. MIMDs offer flexibility as they can function as single-user multiprocessors, run many tasks simultaneously, or a combination. MIMDs also leverage existing processor designs through replication. Centralized shared-memory and distributed-memory multiprocessors are described along with communication architectures like distributed shared memory and message passing. Challenges with parallel processing include limited parallelism in programs and high latency of remote access.
![Taxonomy of Parallel Architectures Four Categories ( Flynn[1966] ): SISD: Single Instruction Stream, Single Data Stream SIMD: Single Instruction Stream, Multiple Data Stream MISD: Multiple Instruction Stream, Single Data Stream MIMD: Multiple Instruction Stream, Multiple Data Stream](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multicore11-1225470325248273-9/85/Computer-Architecture-A-quantitative-approach-Cap4-Section-1-3-320.jpg)