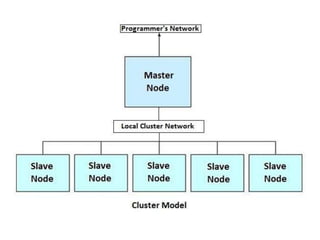
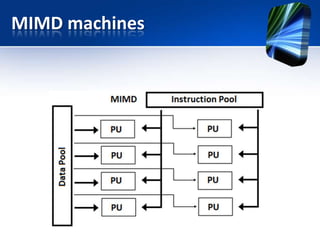
This document discusses low cost supercomputing using Linux clusters. It begins with an introduction to parallel processing and clustering. Clusters offer a way to use multiple computers together as a single system for higher performance and lower costs. The document then covers parallel processing schemes and provides a conceptual overview of clusters. It discusses cluster design considerations including topology, hardware specifications, and software requirements. Linux is identified as a suitable operating system for clustering. The document outlines features and benefits of clustering, such as data sharing and parallel processing. It provides examples of clustering applications in fields like web serving, simulation, and science.