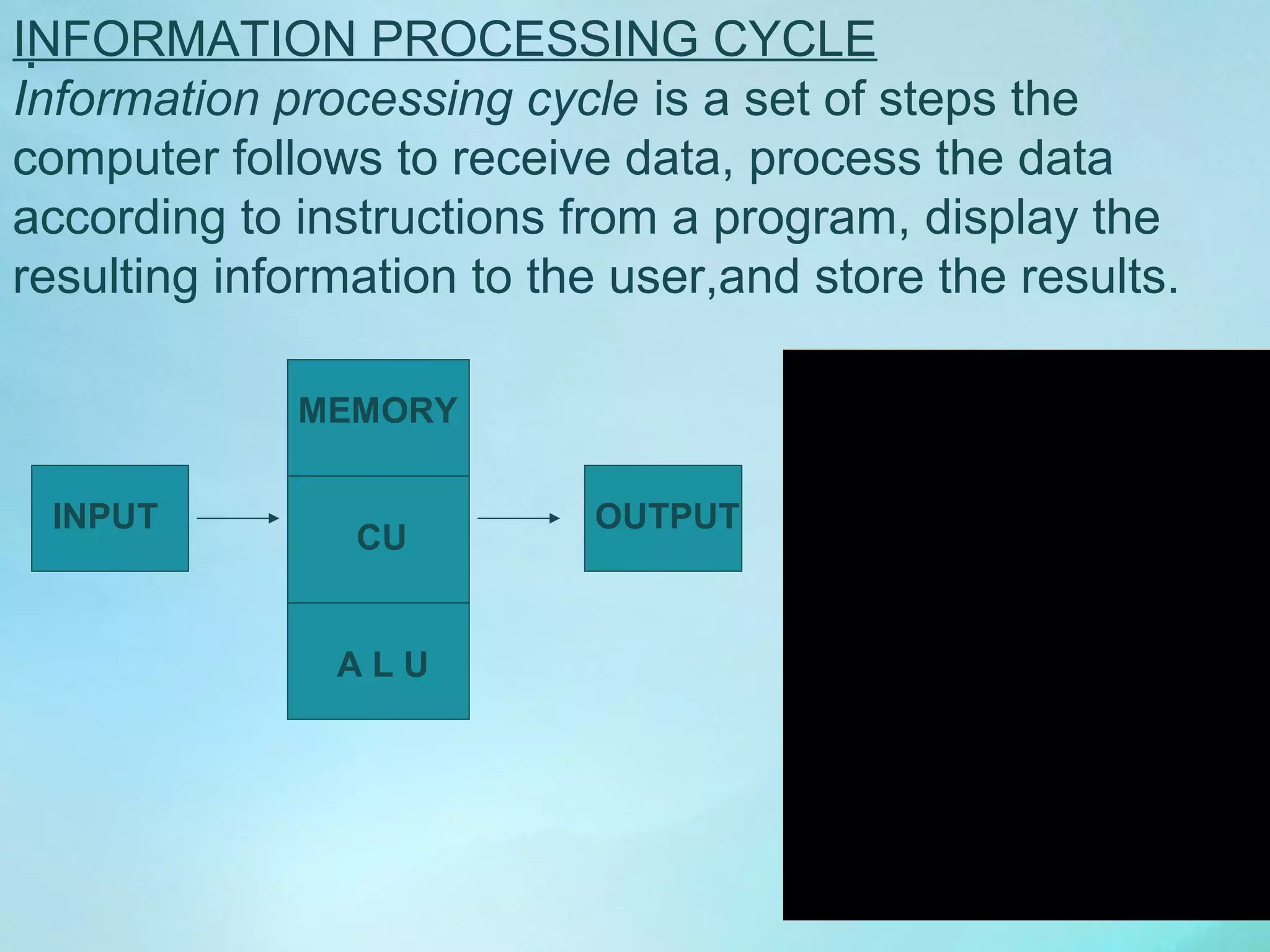
The document provides an overview of various types of computers, including personal, mainframe, minicomputer, and supercomputer, along with their functions and components. It explains the essential parts of a computer system—hardware, software, data, and users—while detailing the information processing cycle and the roles of input and output devices. Additionally, it highlights the importance of operating systems and storage devices in managing and retaining data for computer functionality.