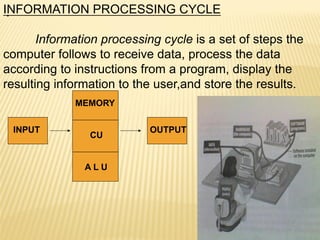
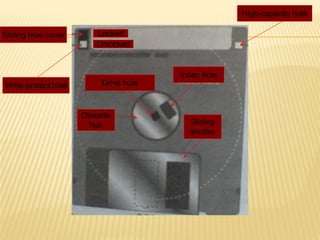
The document provides a comprehensive overview of computer systems, defining a computer and categorizing its types, such as personal computers, mainframes, minicomputers, and supercomputers. It explains essential components including hardware, software, and the information processing cycle, along with details about input and output devices. Additionally, the document outlines various operating systems and data storage methods, highlighting the functions of processors, memory types, and different printing technologies.