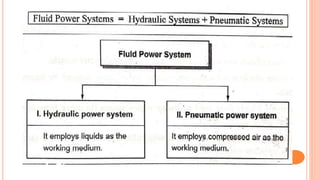
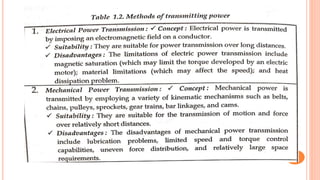
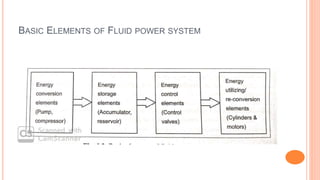
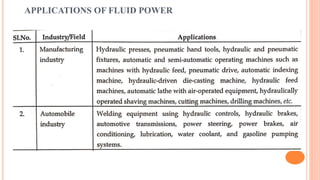
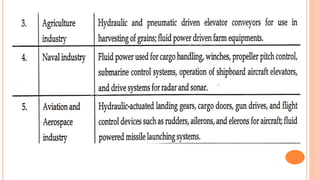
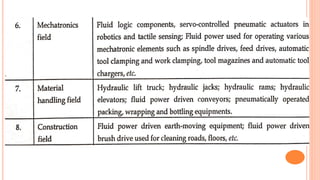
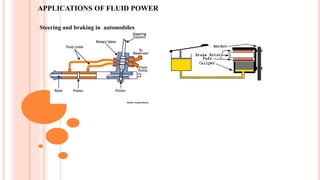
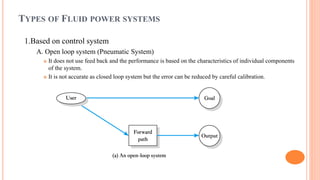
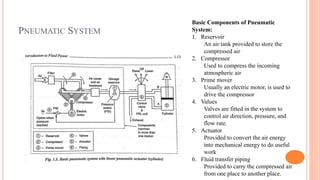
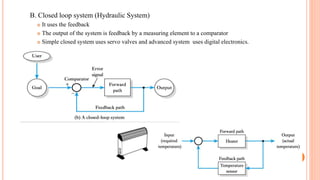
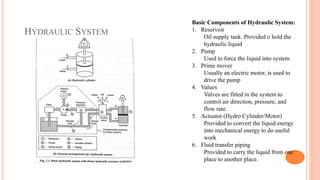
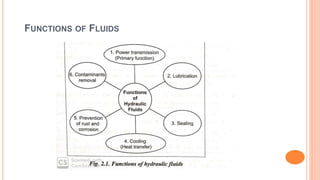
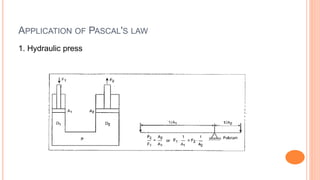
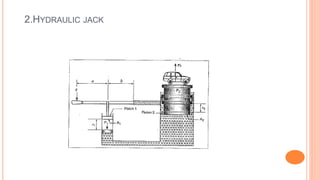
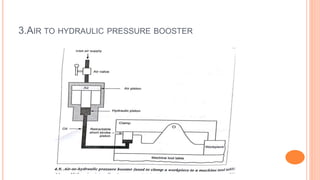
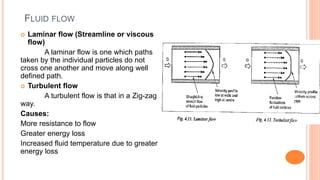
This document discusses the fundamentals of fluid power systems including hydraulics and pneumatics. It covers topics such as the basic principles of hydraulics including Pascal's law, types of hydraulic fluids and their properties, hydraulic components like pumps, actuators and control valves. It also discusses pneumatic systems, fluid logic control, applications of fluid power systems in various industries and troubleshooting of hydraulic and pneumatic circuits. The document appears to be part of a course curriculum on hydraulics and pneumatics.