This document provides an overview of ultrasound imaging systems. It discusses how ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to visualize internal organs and tissues. Key points include:
- Ultrasound uses sound waves above the range of human hearing (above 20 kHz) for medical imaging. It provides 2D, 3D, and 4D images of anatomy.
- The physics of ultrasound involves the longitudinal transmission of sound waves through tissues at different speeds depending on density and elasticity. Reflections at tissue boundaries create echoes that form images.
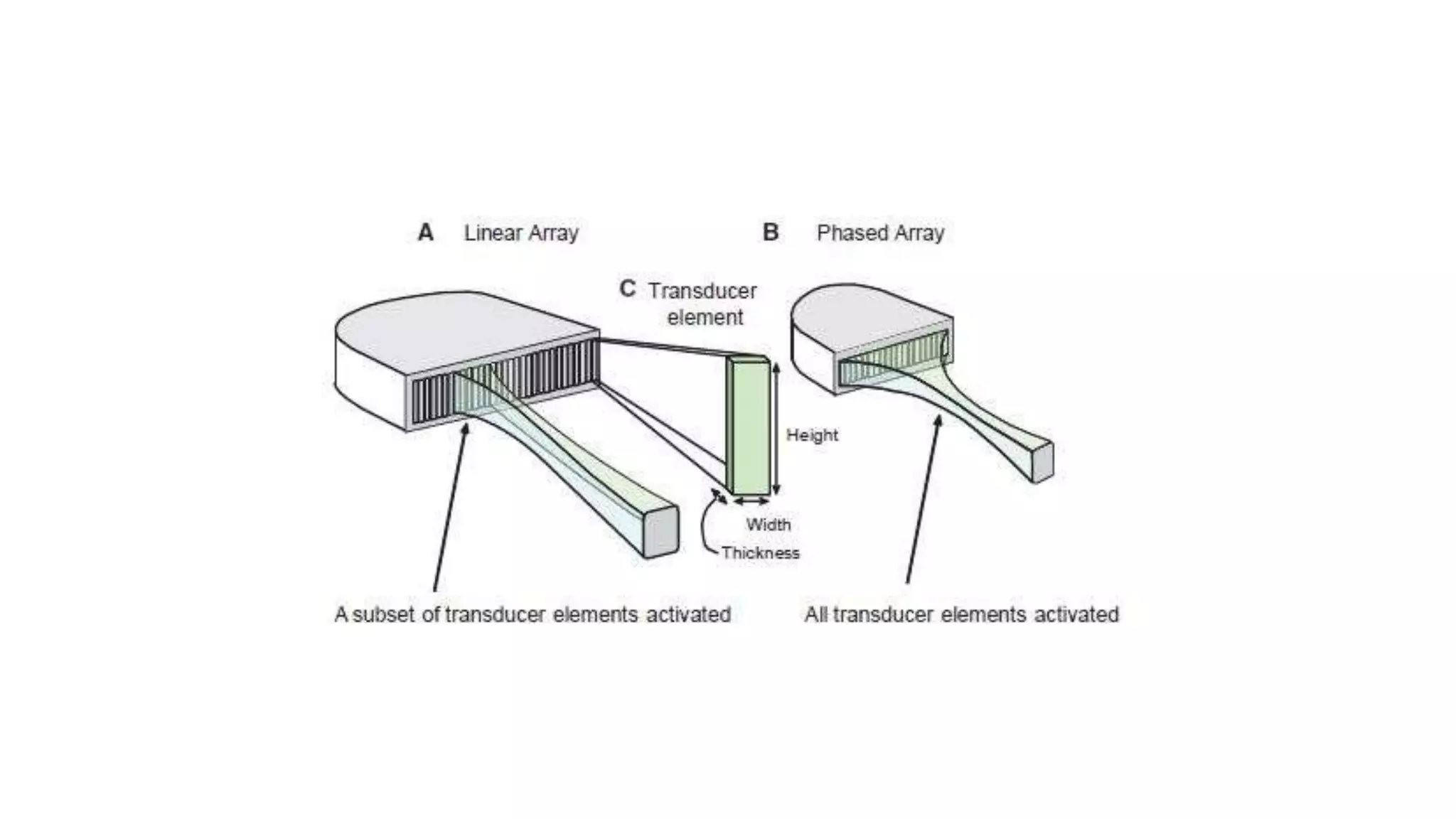
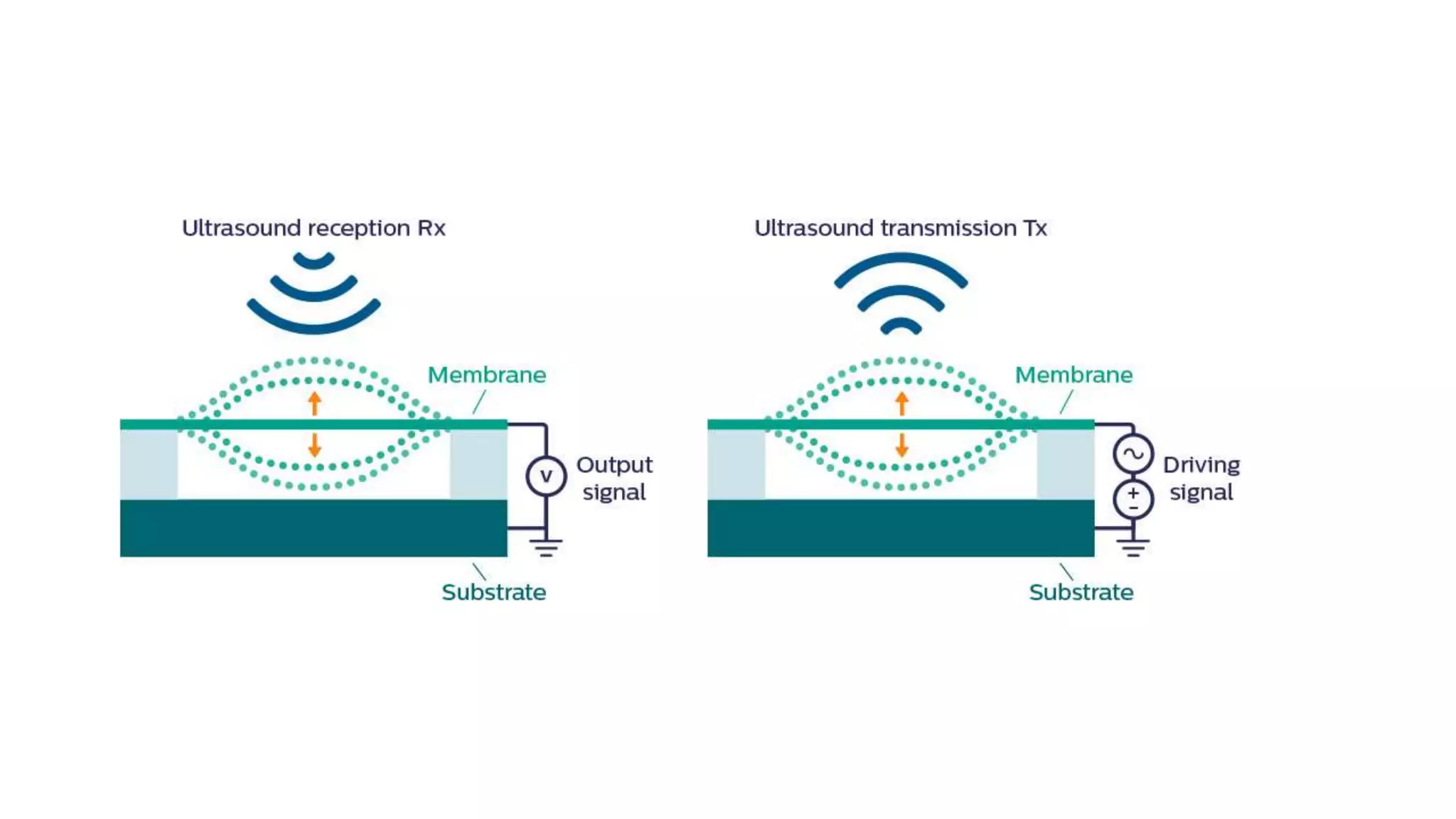
- Ultrasound transducers use piezoelectric materials like quartz or PZT to transmit sound and detect reflections. Array transducers with multiple elements beamform the ultrasound for