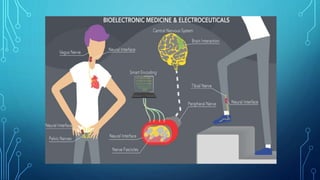
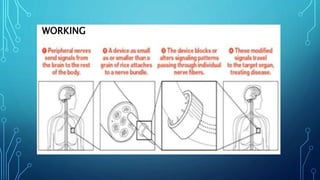
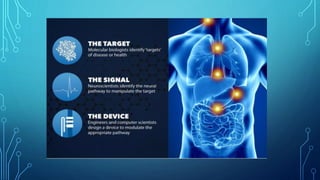
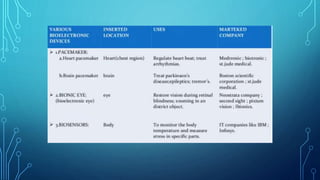
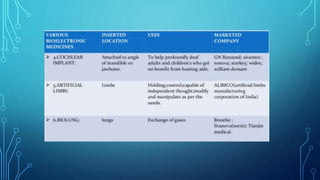
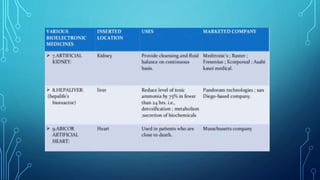
Bioelectronic medicine involves using tiny implanted devices to treat diseases by modulating neural signals between organs. It works by transmitting electrical impulses along nerve fibers unlike drugs which act through molecular mechanisms. Advantages include targeted treatment with minimal side effects. Applications include diabetes monitoring and cancer treatment. However, high costs and risks of electrical shock remain challenges. Recent advances include vagus nerve implants to regulate the immune system and contact lenses to monitor glucose levels.