Compounds and mixtures
•
0 likes•330 views
This document summarizes key concepts about elements, compounds, mixtures and chemical reactions. It explains that elements are made of only one type of atom, while compounds contain two or more elements bonded together. Compounds have distinct properties from their constituent elements. Chemical reactions form new substances and are represented by word equations. Physical changes do not form new substances and can usually be reversed. Mixtures are easier to separate than compounds.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Matter r1

Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. [1] All matter is composed of tiny particles that are in constant motion and have spaces between them. [2] The temperature of matter determines the average energy of its particles and its phase (solid, liquid, or gas). [3] Physical changes alter a substance's state without changing its chemical makeup, while chemical changes produce new substances through chemical reactions.
Matter (audio) r1

Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. [1] All matter is composed of tiny particles that are in constant motion and have spaces between them. [2] As temperature increases, the average energy of particles increases, determining the phase or state of matter - solid, liquid, gas or plasma. [3] Physical changes alter the form of a substance without changing its chemical makeup, while chemical changes produce new substances through chemical reactions.
Density Common Chemical Changes Q And A

This document discusses physical and chemical properties and changes in matter. It provides examples of physical properties including state, size, mass, density, and magnetic properties. Examples of physical changes include changes in state, dissolving, and changes in shape. Chemical properties include ability to burn and examples of chemical changes are burning and rusting. The document also discusses signs that a chemical change has occurred such as release of energy, change in odor or color, and formation of gases or solids.
Elements, Compounds And Mixtures

Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further. They consist of only one type of particle, such as atoms. Compounds are formed when two or more elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio. Compounds have unique properties different from their constituent elements. Mixtures are physical combinations of substances that retain their individual properties and can often be separated using various techniques like distillation or magnetism.
Ch 4 elements_compounds_and_mixtures

Elements, compounds, and mixtures are discussed. Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further, while compounds are formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together. Compounds have unique properties and can be broken down into their constituent elements through chemical or electrolytic processes. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids based on their physical properties such as conductivity.
Elements, compound and mixture

This document discusses the classification and properties of matter. It defines the four states of matter as solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Matter is classified as either elements, compounds, or mixtures based on its chemical constitution. Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further, while compounds contain two or more elements chemically bonded together. Compounds have distinct properties from their constituent elements. The document provides examples of elements and compounds, and discusses their distinguishing physical and chemical properties. Redox reactions are described as reactions where both oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
chemical reaction

This chapter discusses chemical reactions and bonds. It explains that chemical bonds form when atoms exchange or share electrons, forming ionic bonds or covalent bonds. Chemical reactions involve reactants changing into products, and require activation energy to break existing bonds. Photosynthesis is highlighted as the key reaction that harnesses solar energy to produce glucose and oxygen, storing energy in chemical bonds and removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Elements And Compounds Middle School

The document discusses the basic concepts of elements, compounds, atoms, molecules, and chemical reactions. It explains that elements are made of only one type of atom, while compounds are made of two or more elements chemically bonded together. Atoms can bond by sharing or transferring electrons to form molecules or ionic compounds with new properties. A chemical reaction occurs when bonds in reactants are broken and new bonds form, creating different products while conserving mass. Energy is either absorbed or released in chemical reactions.
Recommended
Matter r1

Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. [1] All matter is composed of tiny particles that are in constant motion and have spaces between them. [2] The temperature of matter determines the average energy of its particles and its phase (solid, liquid, or gas). [3] Physical changes alter a substance's state without changing its chemical makeup, while chemical changes produce new substances through chemical reactions.
Matter (audio) r1

Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. [1] All matter is composed of tiny particles that are in constant motion and have spaces between them. [2] As temperature increases, the average energy of particles increases, determining the phase or state of matter - solid, liquid, gas or plasma. [3] Physical changes alter the form of a substance without changing its chemical makeup, while chemical changes produce new substances through chemical reactions.
Density Common Chemical Changes Q And A

This document discusses physical and chemical properties and changes in matter. It provides examples of physical properties including state, size, mass, density, and magnetic properties. Examples of physical changes include changes in state, dissolving, and changes in shape. Chemical properties include ability to burn and examples of chemical changes are burning and rusting. The document also discusses signs that a chemical change has occurred such as release of energy, change in odor or color, and formation of gases or solids.
Elements, Compounds And Mixtures

Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further. They consist of only one type of particle, such as atoms. Compounds are formed when two or more elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio. Compounds have unique properties different from their constituent elements. Mixtures are physical combinations of substances that retain their individual properties and can often be separated using various techniques like distillation or magnetism.
Ch 4 elements_compounds_and_mixtures

Elements, compounds, and mixtures are discussed. Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further, while compounds are formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together. Compounds have unique properties and can be broken down into their constituent elements through chemical or electrolytic processes. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids based on their physical properties such as conductivity.
Elements, compound and mixture

This document discusses the classification and properties of matter. It defines the four states of matter as solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Matter is classified as either elements, compounds, or mixtures based on its chemical constitution. Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further, while compounds contain two or more elements chemically bonded together. Compounds have distinct properties from their constituent elements. The document provides examples of elements and compounds, and discusses their distinguishing physical and chemical properties. Redox reactions are described as reactions where both oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
chemical reaction

This chapter discusses chemical reactions and bonds. It explains that chemical bonds form when atoms exchange or share electrons, forming ionic bonds or covalent bonds. Chemical reactions involve reactants changing into products, and require activation energy to break existing bonds. Photosynthesis is highlighted as the key reaction that harnesses solar energy to produce glucose and oxygen, storing energy in chemical bonds and removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Elements And Compounds Middle School

The document discusses the basic concepts of elements, compounds, atoms, molecules, and chemical reactions. It explains that elements are made of only one type of atom, while compounds are made of two or more elements chemically bonded together. Atoms can bond by sharing or transferring electrons to form molecules or ionic compounds with new properties. A chemical reaction occurs when bonds in reactants are broken and new bonds form, creating different products while conserving mass. Energy is either absorbed or released in chemical reactions.
Chemical rections(complete)

The key ways to prevent rancidity mentioned in the passage are:
(A) Adding antioxidants, which are substances that prevent oxidation
(B) Refrigeration
(C) Storing the food in air-tight containers to prevent exposure to oxygen in the air
The correct answer is A, B, and C - adding antioxidants, refrigeration, and storing in air-tight containers all help prevent oxidation and thus rancidity.
Chemical reaction

The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants.
Chemical reaction and equations

A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction using formulas and symbols. Balanced chemical equations show the same number and type of atoms on both sides of the reaction through the use of coefficients. There are several types of chemical reactions including synthesis reactions where elements or compounds combine, decomposition reactions where a compound breaks down, displacement reactions where a more reactive element replaces a less reactive one, and double displacement reactions where ions switch places between reactants.
solids, liquids and gases

The document provides information about the states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases. It explains that all substances are made up of particles and the key difference between the three states is how strongly the particles are attracted to each other and how much they move. Solids have particles that are strongly attracted and do not move around much. Liquids have particles that are less strongly attracted and can move past each other. Gases have particles that move freely and are rarely touching. The document also discusses diffusion, which is the spreading out of particles, and provides examples of how smells diffuse through the air or liquids.
Elements and compounds

Elements are substances made of only one type of atom, while compounds are made of two or more elements that are chemically bonded together. The chemical formula of a compound shows which elements it contains. Compounds have different properties than their constituent elements. Common table salt, or NaCl, is a compound formed from the elements sodium and chlorine bonding together, even though on their own sodium is a metal and chlorine is a gas. Compounds form when atoms bond by sharing, gaining or losing electrons.
MCQ on Chemical Reactions and Equations PDF

The PDF file contains MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) related to Chemical Reactions and Equations. Chemical Reactions and Equations is the Chapter 1 of Class 10 Science (Chemistry).
Element,compound and mixture

The document discusses elements, compounds, and mixtures. It defines each term and provides examples. Elements cannot be broken down further through chemical reactions, while compounds can be broken down into their constituent elements. Mixtures do not undergo chemical reactions and can be separated into their original substances. Compounds are uniform throughout while mixtures can be heterogeneous or homogeneous.
03 Chemical Reactions

This document provides an overview of chemical reactions and changes. It defines a chemical reaction as a process that changes one set of chemicals into another. It discusses reagents (reactants) and products. It distinguishes between physical and chemical changes, providing examples of each. Signs of a chemical change are described as the formation of a precipitate, color change, bubbles, temperature change, or new odor. The law of conservation of mass is explained. Chemical equations are introduced and the importance of balancing equations is described through an example. Finally, practice problems are provided to test understanding of these concepts.
Changing matter

There are two types of matter changes: physical changes and chemical changes. Physical changes alter the physical properties of matter without changing its chemical composition, such as changes in state from solid to liquid to gas. Chemical changes form new chemical substances through rearrangement of atoms, such as burning or rusting. Chemical changes are identified through evidence like gas formation, color change, or energy transfer, and matter is conserved before and after the reaction according to the law of conservation of mass.
Ch06 elements, compounds & mixtures

This document discusses the classification of matter into elements, compounds, and mixtures. It defines elements as the simplest form of matter that cannot be broken down further through chemical reactions. Compounds are formed via chemical reactions and consist of two or more chemically bonded elements. Mixtures are physical combinations of elements and/or compounds that are not chemically bonded and can be separated using physical means. The document provides examples and properties to distinguish among these three classifications of matter.
IGCSE 11.1.5

The document discusses endothermic reactions. It states that endothermic reactions absorb thermal energy, causing a decrease in temperature. Examples of endothermic reactions given include thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate in a blast furnace, photosynthesis, some types of electrolysis, and the melting of sherbet.
Matter

All matter can undergo physical and chemical changes. A physical change alters the appearance but not the chemical composition, such as water freezing. A chemical change forms new substances with different properties, like reactions with acids or bases. Substances have characteristic intensive properties that identify them and extensive properties that depend on amount.
COMPOUNDS

A compound is a pure substance composed of two or more elements chemically bonded together, such as sodium chloride or water. Compounds can only be broken down or formed through a chemical reaction that breaks and rearranges bonds between atoms. Some common compounds found in homes include sodium chloride, water, glucose, and other substances containing ionically or covalently bonded elements.
Elements, molecules, compounds_and_mixtures

The document lists common elements and materials including water, iron, crude oil, wood, plastic, oxygen, brick, air, copper, gold, clay, and aluminium. It then provides definitions for element, molecule, compound, and mixture as well as examples that match each definition. The key terms are distinguished based on whether they contain only one type of atom, have a chemical symbol, involve two or more chemically combined elements, or have components that are not chemically combined.
Hazardoous symbol

This document provides a revision guide for the GCSE Science module on chemistry. It summarizes key concepts about atoms, the periodic table, chemical groups and their properties, chemical symbols and equations, and factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions. Concepts are explained concisely with examples given for many topics.
Unit 4 Chemical Properties

1) An atom is made up of protons, electrons, and neutrons. When two or more atoms combine chemically, it forms a molecule.
2) A chemical reaction is the rearrangement of atoms to form new molecules. Some reactions release or absorb energy.
3) Chemical properties can only be observed when substances change into different substances, such as through flammability or reactivity.
Elements, Compounds & Mixtures Slides

1) Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further by chemical processes. They are represented by chemical symbols on the periodic table.
2) Compounds are pure substances composed of two or more elements chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio. Their properties are different from the original elements.
3) Mixtures are physical combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded and can be separated by physical means like filtration or distillation. Their properties are similar to the original substances.
Basic concept of Chemistry

Presentation is for the first chapter of class 11th Chemistry CBSE board. Presentation is having detailed description for some of the basic concepts like mole concept, matter in our surrounding etc.
Keynote; ch. 2; nature of matter

All matter is made of atoms. Atoms of different elements have unique physical and chemical properties. Matter can be made of a single element or a combination of elements chemically bonded together to form compounds or mixtures. Compounds have different properties than their individual elements. Chemical and physical properties can be used to identify substances and chemical reactions which rearrange atoms but conserve total matter.
Element and compound baroe

Here are the key points about homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures:
- Homogeneous mixtures have uniform composition and appearance throughout. Common examples include solutions.
- Heterogeneous mixtures have visibly distinct parts that can be seen without using a microscope. The substances do not dissolve or blend uniformly.
- Homogeneous mixtures are examples of single phase systems while heterogeneous mixtures contain two or more phases (solid, liquid, gas).
- Sugar solution is an example of a homogeneous mixture where sugar is dissolved uniformly throughout the water. Water and oil is an example of a heterogeneous mixture since the substances do not dissolve in each other and remain as separate visible layers.
The key difference is that homogeneous mixtures appear uniform while heterogeneous mixtures have distinct parts
Grade 8 night 2012

The document provides an agenda and information for a Grade 8 Parents' Night at Ridgemont High School. It outlines the various course and program options available to students in Grade 9, including academic, applied, and essential streams for core subjects like math, science, and English. It also highlights extracurricular activities like arts, athletics, clubs and the peer mentoring program. The document aims to help parents learn about pathways and course selections for their children as they transition to high school.
Food and digestion

We need a balanced diet with carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients to provide our bodies with the materials needed. Food is digested in the gut through mechanical and chemical breakdown. Digestive juices and enzymes in the mouth, stomach, and intestines break foods into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and used by cells. The small intestine plays a key role in absorbing digested nutrients into the bloodstream to be used for energy, growth, and other functions.
More Related Content
What's hot
Chemical rections(complete)

The key ways to prevent rancidity mentioned in the passage are:
(A) Adding antioxidants, which are substances that prevent oxidation
(B) Refrigeration
(C) Storing the food in air-tight containers to prevent exposure to oxygen in the air
The correct answer is A, B, and C - adding antioxidants, refrigeration, and storing in air-tight containers all help prevent oxidation and thus rancidity.
Chemical reaction

The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants.
Chemical reaction and equations

A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of a chemical reaction using formulas and symbols. Balanced chemical equations show the same number and type of atoms on both sides of the reaction through the use of coefficients. There are several types of chemical reactions including synthesis reactions where elements or compounds combine, decomposition reactions where a compound breaks down, displacement reactions where a more reactive element replaces a less reactive one, and double displacement reactions where ions switch places between reactants.
solids, liquids and gases

The document provides information about the states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases. It explains that all substances are made up of particles and the key difference between the three states is how strongly the particles are attracted to each other and how much they move. Solids have particles that are strongly attracted and do not move around much. Liquids have particles that are less strongly attracted and can move past each other. Gases have particles that move freely and are rarely touching. The document also discusses diffusion, which is the spreading out of particles, and provides examples of how smells diffuse through the air or liquids.
Elements and compounds

Elements are substances made of only one type of atom, while compounds are made of two or more elements that are chemically bonded together. The chemical formula of a compound shows which elements it contains. Compounds have different properties than their constituent elements. Common table salt, or NaCl, is a compound formed from the elements sodium and chlorine bonding together, even though on their own sodium is a metal and chlorine is a gas. Compounds form when atoms bond by sharing, gaining or losing electrons.
MCQ on Chemical Reactions and Equations PDF

The PDF file contains MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) related to Chemical Reactions and Equations. Chemical Reactions and Equations is the Chapter 1 of Class 10 Science (Chemistry).
Element,compound and mixture

The document discusses elements, compounds, and mixtures. It defines each term and provides examples. Elements cannot be broken down further through chemical reactions, while compounds can be broken down into their constituent elements. Mixtures do not undergo chemical reactions and can be separated into their original substances. Compounds are uniform throughout while mixtures can be heterogeneous or homogeneous.
03 Chemical Reactions

This document provides an overview of chemical reactions and changes. It defines a chemical reaction as a process that changes one set of chemicals into another. It discusses reagents (reactants) and products. It distinguishes between physical and chemical changes, providing examples of each. Signs of a chemical change are described as the formation of a precipitate, color change, bubbles, temperature change, or new odor. The law of conservation of mass is explained. Chemical equations are introduced and the importance of balancing equations is described through an example. Finally, practice problems are provided to test understanding of these concepts.
Changing matter

There are two types of matter changes: physical changes and chemical changes. Physical changes alter the physical properties of matter without changing its chemical composition, such as changes in state from solid to liquid to gas. Chemical changes form new chemical substances through rearrangement of atoms, such as burning or rusting. Chemical changes are identified through evidence like gas formation, color change, or energy transfer, and matter is conserved before and after the reaction according to the law of conservation of mass.
Ch06 elements, compounds & mixtures

This document discusses the classification of matter into elements, compounds, and mixtures. It defines elements as the simplest form of matter that cannot be broken down further through chemical reactions. Compounds are formed via chemical reactions and consist of two or more chemically bonded elements. Mixtures are physical combinations of elements and/or compounds that are not chemically bonded and can be separated using physical means. The document provides examples and properties to distinguish among these three classifications of matter.
IGCSE 11.1.5

The document discusses endothermic reactions. It states that endothermic reactions absorb thermal energy, causing a decrease in temperature. Examples of endothermic reactions given include thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate in a blast furnace, photosynthesis, some types of electrolysis, and the melting of sherbet.
Matter

All matter can undergo physical and chemical changes. A physical change alters the appearance but not the chemical composition, such as water freezing. A chemical change forms new substances with different properties, like reactions with acids or bases. Substances have characteristic intensive properties that identify them and extensive properties that depend on amount.
COMPOUNDS

A compound is a pure substance composed of two or more elements chemically bonded together, such as sodium chloride or water. Compounds can only be broken down or formed through a chemical reaction that breaks and rearranges bonds between atoms. Some common compounds found in homes include sodium chloride, water, glucose, and other substances containing ionically or covalently bonded elements.
Elements, molecules, compounds_and_mixtures

The document lists common elements and materials including water, iron, crude oil, wood, plastic, oxygen, brick, air, copper, gold, clay, and aluminium. It then provides definitions for element, molecule, compound, and mixture as well as examples that match each definition. The key terms are distinguished based on whether they contain only one type of atom, have a chemical symbol, involve two or more chemically combined elements, or have components that are not chemically combined.
Hazardoous symbol

This document provides a revision guide for the GCSE Science module on chemistry. It summarizes key concepts about atoms, the periodic table, chemical groups and their properties, chemical symbols and equations, and factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions. Concepts are explained concisely with examples given for many topics.
Unit 4 Chemical Properties

1) An atom is made up of protons, electrons, and neutrons. When two or more atoms combine chemically, it forms a molecule.
2) A chemical reaction is the rearrangement of atoms to form new molecules. Some reactions release or absorb energy.
3) Chemical properties can only be observed when substances change into different substances, such as through flammability or reactivity.
Elements, Compounds & Mixtures Slides

1) Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further by chemical processes. They are represented by chemical symbols on the periodic table.
2) Compounds are pure substances composed of two or more elements chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio. Their properties are different from the original elements.
3) Mixtures are physical combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded and can be separated by physical means like filtration or distillation. Their properties are similar to the original substances.
Basic concept of Chemistry

Presentation is for the first chapter of class 11th Chemistry CBSE board. Presentation is having detailed description for some of the basic concepts like mole concept, matter in our surrounding etc.
Keynote; ch. 2; nature of matter

All matter is made of atoms. Atoms of different elements have unique physical and chemical properties. Matter can be made of a single element or a combination of elements chemically bonded together to form compounds or mixtures. Compounds have different properties than their individual elements. Chemical and physical properties can be used to identify substances and chemical reactions which rearrange atoms but conserve total matter.
Element and compound baroe

Here are the key points about homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures:
- Homogeneous mixtures have uniform composition and appearance throughout. Common examples include solutions.
- Heterogeneous mixtures have visibly distinct parts that can be seen without using a microscope. The substances do not dissolve or blend uniformly.
- Homogeneous mixtures are examples of single phase systems while heterogeneous mixtures contain two or more phases (solid, liquid, gas).
- Sugar solution is an example of a homogeneous mixture where sugar is dissolved uniformly throughout the water. Water and oil is an example of a heterogeneous mixture since the substances do not dissolve in each other and remain as separate visible layers.
The key difference is that homogeneous mixtures appear uniform while heterogeneous mixtures have distinct parts
What's hot (20)
Viewers also liked
Grade 8 night 2012

The document provides an agenda and information for a Grade 8 Parents' Night at Ridgemont High School. It outlines the various course and program options available to students in Grade 9, including academic, applied, and essential streams for core subjects like math, science, and English. It also highlights extracurricular activities like arts, athletics, clubs and the peer mentoring program. The document aims to help parents learn about pathways and course selections for their children as they transition to high school.
Food and digestion

We need a balanced diet with carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients to provide our bodies with the materials needed. Food is digested in the gut through mechanical and chemical breakdown. Digestive juices and enzymes in the mouth, stomach, and intestines break foods into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and used by cells. The small intestine plays a key role in absorbing digested nutrients into the bloodstream to be used for energy, growth, and other functions.
Digestive system

The document summarizes the human digestive system. It describes how food is broken down as it passes through the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon. Key steps include chewing and mixing with saliva in the mouth, peristalsis to move food through the esophagus, churning and breaking down of proteins in the acidic stomach, further breakdown of nutrients by enzymes in the small intestine, and water absorption with waste formation in the colon. The end products are then excreted from the body.
Chapter 27 Nutrition and Digestion

Nutrition and digestion allow animals to take in nutrients from food, break the food down, absorb it, and use it for energy and growth. Nutrition includes ingestion, digestion, absorption, storage, and use of nutrients. Digestion is the breakdown of food into absorbable particles through chemical and mechanical means. There are many feeding strategies like herbivory, predation, deposit feeding, and fluid feeding as well as continuous and discontinuous feeding. Digestive structures also vary from protozoa to invertebrates to vertebrates.
Food And Digestion Concept Map

The document presents a concept map about human digestion. It outlines the main food groups - proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins and minerals, fibre, and water. It describes how each food group provides cell growth, energy, health, digestion, or hydration. The concept map also details common examples for each food group and explains how enzymes break down large food molecules for absorption. Laboratory tests for identifying sugars, starches, fats, and proteins in food are outlined as well.
Food digestion

The document summarizes the process of digestion in humans. It begins with food being chewed in the mouth and then traveling to the stomach where acids and enzymes break it down further. The partially digested food then moves to the small intestine, where nutrients are absorbed and waste is sorted to be passed to the large intestine and eventually excreted from the body. The document includes links to diagrams and a video about digestion.
Digestion!

Digestion uses both mechanical and chemical processes to break down food. Mechanical digestion physically breaks down food pieces while chemical digestion uses acids and enzymes to digest food at a molecular level. The major steps of digestion are: 1) Mouth - chewing and saliva begin breakdown, 2) Esophagus - food is pushed to stomach by peristalsis, 3) Stomach - food is further broken down by hydrochloric acid and churned, 4) Small Intestine - fingerlike villi and digestive enzymes from pancreas and liver complete digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs, 5) Large Intestine - water is absorbed and waste is excreted.
Digestive system

The digestive system breaks down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and used by the body. It consists of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. Food is mechanically and chemically broken down at each stage as it moves through the system. The mouth chews food, the stomach churns and adds acid, and the intestines further break down food with enzymes before nutrients are absorbed and waste is eliminated.
Chapter 3 NUTR

The document summarizes the key aspects of digestion, absorption, and transport. It describes the anatomy and functions of the digestive tract, including the roles of muscles, secretions, and hormones in breaking down food. Absorption occurs in the small intestine, where nutrients pass through the intestinal walls. Transported nutrients are then circulated via the hepatic portal system and lymphatic vessels. Homeostasis and gut flora also help regulate the healthy functioning of the GI system. Common digestive issues like diarrhea, constipation, and ulcers are discussed.
Food, nutrition and digestion

This presentation is created by www.gyanbikash.com for the students of Science group of class Nine to Ten
Chapter 18- nutrition, digestion, excretion

This document provides information about nutrition, digestion, and excretion. It discusses the six major nutrients - carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals, and water. It describes the digestive system and the roles of the main organs involved in ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination. Key digestive organs mentioned are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, pancreas, liver and gallbladder. Enzymes produced in these organs help break down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and used by the body.
FOOD AND DIGESTION

This presentation and activites are designed to assist students to understand how to get the most credit in this topic. Please email comments and suggestions to whysciencetutors@yahoo.com or vist us at
www.sciencetutors.zoomshare.com for other resources
Digestion and absorption of food 

This document discusses digestion and absorption of food. It begins by outlining the biological and medical importance of digestion and absorption. The major sites of digestion in the gastrointestinal tract and the digestive juices involved are described. Carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids are broken down into smaller molecules so they can be absorbed. Carbohydrates are digested into monosaccharides like glucose and galactose. Proteins are digested into amino acids through the action of proteases. Lipids are broken into fatty acids and glycerol. The absorbed nutrients are then transported through the intestinal mucosa and into circulation. Clinical conditions related to deficiencies in digestion and absorption are also mentioned.
Sistem pencernaan 1

The document summarizes the key stages and processes of digestion. It describes the functions of the main parts of the digestive system including the mouth, stomach, small intestine, liver, gallbladder and pancreas. It explains the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food as well as the roles of enzymes and hormones in digesting carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Absorption and motility in the small intestine is also summarized.
Food and digestion - grade 4

The document discusses the process of digestion and a balanced diet. It explains that food is broken down in the digestive system, with chemicals being transported through the bloodstream. The seven types of chemicals that make up food can provide a balanced diet. It then outlines the five stages of digestion - chewing, swallowing, breaking down in the stomach, further breakdown in the small intestine aided by bile, and absorption of nutrients in the large intestine with waste excretion. Finally, it lists some of the food groups that should be included in a balanced diet such as bread, meat, and dairy.
Digestion

This document summarizes the human digestive system. It describes how digestion involves both mechanical and chemical breakdown of food. Mechanical digestion begins in the mouth through chewing, while chemical digestion occurs through enzymes secreted in the mouth, stomach, pancreas, and intestines. The digestive system is made up of the digestive tract, which includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. Food moves through this tract as it is broken down and nutrients are absorbed for use by the body.
Section 1, chapter 17: digestive system

The digestive system breaks down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by cells. It consists of the alimentary canal (mouth to anus) and accessory glands. The alimentary canal wall has four layers - mucosa, submucosa, muscular layer, and serosa. Muscles in the walls provide segmentation to mix foods and peristalsis to propel foods through the canal. Accessory glands like the salivary glands secrete chemicals to aid digestion. The mouth is the beginning of the alimentary canal and contains the teeth, tongue, and palate to mechanically break down foods. Saliva from the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual
8 a food & digestion (boardworks)

Humans need a balanced diet containing carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. Digestion begins in the mouth and stomach and is completed in the small intestine, where nutrients are absorbed. Undigested waste then moves to the large intestine and rectum to be excreted. Digestive enzymes break down food molecules into smaller absorbable pieces, including carbohydrase for carbohydrates, protease for proteins, and lipase for fats.
What specialised feature of small intestine account for

The specialized features of the small intestine that enable efficient absorption of digested food include villi and microvilli. The villi are finger-like projections lining the ileum that are richly supplied with blood capillaries and lacteals. The microvilli further increase the absorptive surface area. Sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids are absorbed into the bloodstream or lacteals by diffusion or active transport. Fats are recombined into lipoproteins within the villi and transported to the bloodstream.
Food and Digestion Year 9

The document provides information about food and nutrition for a Year 9 class. It begins with learning objectives about appreciating a balanced diet and introduces the reasons why humans need food, such as for energy storage, growth, and chemical reactions. It then discusses energy balance and input versus output. The document provides success criteria for students and links to additional online resources. It addresses topics like food groups, dietary intake, nutrition, digestion, and adaptations that aid the digestive system.
Viewers also liked (20)
What specialised feature of small intestine account for

What specialised feature of small intestine account for
Similar to Compounds and mixtures
Chemical Reactions CD

The document discusses several key chemistry concepts:
- Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. An element is made of a single type of atom.
- Compounds are made of two or more elements chemically bonded together. Chemical reactions involve breaking and forming bonds to change one substance into another.
- Physical changes alter a substance's properties like shape or state but not its chemical makeup. Chemical reactions alter the substance's chemical identity and atomic/molecular structure.
Interactive textbook ch. 14 chemical reactions

A chemical reaction occurs when substances break apart or combine to form new substances with different chemical properties. A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction using chemical symbols and formulas, with reactants written before an arrow and products written after. It is important that chemical equations are balanced to obey the law of conservation of mass, which states the total mass is the same for reactants and products.
Elements, Compounds, Mixtures

This document discusses the classification of matter into elements, compounds, and mixtures. It defines each term and provides examples. Elements are pure substances made of only one type of atom that cannot be broken down further. Compounds are pure substances composed of two or more elements chemically bonded together in fixed ratios to form new substances with different properties from the original elements. Mixtures are physical combinations of elements or compounds that are not chemically bonded and can be separated by physical means such as filtration or evaporation.
Introduction to chemistry

Chemistry deals with the properties and structure of matter, as well as changes in matter. There are over 100 known elements, which were formed either during the Big Bang or within stars. Elements combine to form compounds with distinct properties. Matter exists as either pure substances like elements and compounds, or as mixtures of substances. Pure substances cannot be separated into other substances by physical means alone, while mixtures can be separated into their individual parts physically.
CHEMISTRY, ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS

An element is the simplest form of matter that has unique properties and includes all substances on the periodic table, while a compound contains two or more elements bonded together and can be broken down into simpler substances through chemical means. Compounds have different properties from their constituent elements, as sodium is an explosive metal, chlorine is toxic gas, but together they form the compound sodium chloride, which is table salt. Chemical changes involve the formation or breakdown of compounds through chemical reactions that conserve mass according to the law of conservation of mass.
5 1.1 Matter Powerpoint Part A Classification Of Matter

The document provides an overview of classifying and studying matter. It defines matter as anything having mass and volume. It discusses the basic units of matter being atoms and classifies matter as either pure substances (elements or compounds) or mixtures. Elements contain only one type of atom, while compounds are made of two or more different elements that are chemically combined. Mixtures are combinations of substances that are not chemically combined and can be separated physically. Mixtures are either homogeneous, appearing uniform throughout, or heterogeneous, visibly different throughout. Examples and diagrams are provided to illustrate these key concepts.
The Chemistry of Life

The document discusses the four states of matter - solids, liquids, gases, and plasma. It describes the properties of each state and how they differ in terms of particle movement and energy. It then explains that changing between states requires the addition or removal of energy, giving examples like ice melting into water. The document also briefly covers the nature of matter, chemical bonds, water properties, and organic compounds.
evidence of a chemical reaction

All chemical bonds contain potential energy that is changed during chemical reactions when old bonds break and new bonds form. There are several evidences that can indicate if a chemical reaction has occurred, including the emission of light, evolution of a gas, and changes in temperature, color, or the formation of a precipitate. Chemical equations are used to represent chemical reactions, and they must be balanced by ensuring equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides of the reaction.
Chapters 2&3

This document provides a summary of basic chemistry concepts covered in chapters 2 and 3 of a unit 1 notes document. It discusses the following key points in 3 sentences:
Matter is anything that takes up space and has specific physical and chemical properties. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter and consist of a nucleus with protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons. Compounds are formed when two or more elements chemically combine, resulting in new substances with different properties than the individual elements.
Chemical Bonding

This document provides an overview of chemical bonding concepts including ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. It discusses how ionic bonds form via the transfer of electrons between metals and nonmetals to form oppositely charged ions. Covalent bonds are described as the sharing of electrons between nonmetals. Metallic bonding is explained as a "sea of electrons" that holds positively charged metal ions in a lattice structure. The properties of ionic compounds, covalent compounds, and metals are contrasted. Examples of giant covalent structures like diamond and graphite are analyzed in terms of their bonding and properties. Learning outcomes are stated throughout to guide the reader.
Chemical Bonding

This document provides an overview of chemical bonding and different types of bonds. It begins by explaining ionic bonds which are formed by the transfer of electrons between metals and non-metals. Sodium chloride is given as an example. Covalent bonds are then introduced and involve the sharing of electrons between non-metals like hydrogen and oxygen. The properties of ionic and covalent compounds are contrasted. Ionic compounds have high melting points and conduct electricity when molten or dissolved, while covalent compounds have lower melting points and do not conduct electricity. Metallic bonding is described involving positive metal ions in a "sea of electrons". Finally, macromolecular structures like diamond and graphite are discussed and how their different bonding structures
Unit 4 Power Point

1) An atom is made up of protons, electrons, and neutrons. When two or more atoms combine chemically, it forms a molecule.
2) A chemical reaction is the rearrangement of atoms to form new molecules. Some reactions release or absorb energy.
3) Chemical properties can only be observed when substances change into different substances, such as through flammability or reactivity.
Chapter 14

The document discusses different types of changes in matter:
1. Physical changes alter the form or appearance of a substance without changing its chemical makeup, such as water evaporating or a rock being broken into pieces.
2. Chemical changes result in one or more new substances forming through the breaking or forming of chemical bonds, such as hydrogen and oxygen combining to form water.
3. Chemical reactions can be classified as synthesis, decomposition, or replacement reactions depending on whether they involve the combining of substances, breaking of substances, or replacing of elements.
chemistry background

- Radiopharmacology is the science of drugs used in radiology for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. It is a branch of pharmacology.
- The lecture discusses key concepts in chemistry including the structure of atoms, types of chemical bonds, states of matter, and organic chemistry basics.
- Mixtures and solutions are introduced, where a solution is a homogeneous mixture of a solute dissolved in a solvent. Important electrolytes in solutions include acids and bases.
Science Indicators (changing matter)

This document discusses different types of chemical reactions including synthesis reactions where substances join to form new compounds, decomposition reactions where compounds break down into simpler substances, replacement reactions where one element replaces another in a compound, and combustion reactions where oxygen combines with other compounds to form water and carbon dioxide. It also describes exothermic reactions which release heat and endothermic reactions which absorb heat. Neutralization reactions involve acids and bases canceling each other out.
some basic concept of chemistry.pdf

This chapter is tell you about all the concepts of equilibrium where how the says how the surroundings are created
Some basic concepts of chemistry

This document provides an overview of basic chemistry concepts including:
- Matter can be classified as mixtures or pure substances. Pure substances have a definite composition while mixtures do not.
- Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further, and are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Compounds are also pure substances but have elements combined in fixed proportions.
- Chemical properties describe reactions that change a substance's composition, while physical properties can be observed without chemical changes.
Chemistry 1 yousef berbar

1) Chemical reactions can be endothermic or exothermic depending on whether heat energy is absorbed or released during the reaction.
2) The organization and disorder of particles changes as matter changes form - gases have more disorder than solids or liquids.
3) Balanced chemical equations follow the law of conservation of matter, with the same number and type of atoms on both sides of the equation.
Chemical Reactions and Equations

Chemical reactions involve the transformation of one or more substances into different substances and can be represented by chemical equations. Chemical equations show the reactants on the left and products on the right of the arrow and must be balanced according to the law of conservation of mass. There are several types of chemical reactions including combination reactions where two or more substances combine to form one product, decomposition reactions where one compound breaks down into multiple products usually with heat, and substitution reactions where a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive one.
Chemical reactions and equations class 10

The document discusses various physical and chemical changes that occur in everyday life. It provides examples of physical changes such as changes in state from liquid to gas, and chemical changes where new substances are formed. The key differences between physical and chemical changes are explained, with chemical changes resulting in the formation of new substances with different properties compared to the original reactants. Specific chemical reactions and observations that indicate chemical changes, such as gas evolution, temperature change, and color change, are also outlined.
Similar to Compounds and mixtures (20)
5 1.1 Matter Powerpoint Part A Classification Of Matter

5 1.1 Matter Powerpoint Part A Classification Of Matter
More from themassmaker
Growing microbes

1. The student was asked to grow an uncontaminated culture of microbes. The method provided involved sterilizing equipment, heating an inoculating loop, spreading bacteria onto agar jelly in a petri dish, and incubating the dish at 25°C.
2. The student tested the effectiveness of four antibiotic solutions by placing sterile paper discs dipped in each solution onto agar with growing bacteria. After two days of incubation, different sized regions with no bacterial growth were observed around each disc.
3. The least effective antibiotic produced the smallest region without bacteria, as the size of this region indicates how strongly the antibiotic inhibited bacterial growth. Calculations of the area of the bacterial-free zones would be inaccurate
Antibiotic resistance ms

Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a bacterium that causes difficult-to-treat infections in humans. MRSA developed from a similar strain called Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) that was treatable with antibiotics. Through natural selection, some MSSA bacteria gained mutations that made them resistant to antibiotics. Those resistant bacteria survived exposure to antibiotics and passed on the resistance genes through asexual reproduction, leading to the emergence of the MRSA strain.
Antibiotic resistance

The document discusses antibiotic resistance, specifically Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). MRSA infections are difficult to treat with antibiotics that previously worked. This is because MRSA developed from a strain called Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus that was susceptible to antibiotics, through natural selection whereby bacteria resistant to antibiotics survived and passed on those resistance genes. New treatments are needed to kill MRSA since existing antibiotics are no longer effective.
Semmelweiss ms

The document summarizes data from a hospital in the 1800s that showed higher death rates for women giving birth in Ward A compared to Ward B. After 1840, only doctors worked in Ward A while only midwives worked in Ward B, resulting in a much lower death rate in Ward B. In 1847, Semmelweis required doctors to wash their hands with chloride of lime before childbirth. This led to a significant reduction in the Ward A death rate in 1848-1849, bringing it closer to the rate in Ward B. The hand washing killed bacteria that doctors were transmitting from autopsies to women during childbirth.
Semmelweiss

The document summarizes data from the 1800s that showed death rates of women giving birth in two hospital wards: Ward A and Ward B. Before 1840, both wards had similar high death rates as doctors and midwives worked in both. After 1840, Ward A had only doctors while Ward B had only midwives, and Ward B saw significantly lower death rates. Dr. Semmelweis later required doctors to wash their hands in chloride of lime solution before deliveries in Ward A, which further reduced Ward A's death rate to match Ward B's lower level.
Defense against diseases

Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium. When someone with TB coughs or sneezes, the bacteria are expelled into the air and can be inhaled by others. If breathed in, the bacteria initially infect the lungs. In the lungs, the bacteria can multiply and cause lesions and inflammation. Other types of microorganisms besides bacteria, such as viruses, can also cause infectious disease. When the body is exposed to TB bacteria, it mounts an immune response to fight the infection by using white blood cells, antibodies, and other mechanisms of defense.
Diet and exercise ms

The document discusses diet, exercise, and metabolic rate. It defines metabolic rate as the rate of chemical reactions in the body. While genes affect metabolic rate, exercise can increase it. A balanced diet with carbohydrates, proteins, and fats provides energy, builds cells, and stores energy. An imbalanced diet can lead to malnutrition by providing too much or too little energy compared to what the body needs. The document questions an advert claiming quick weight loss from a program, as it lacks long-term data and sample size details.
Diet and exercise

The document discusses diet, exercise, and weight management. It defines metabolic rate as the rate at which the body burns calories and explains that some people have naturally low metabolic rates. It recommends exercise as a way to increase metabolic rate. Diet components like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats serve important functions, and an imbalanced diet can lead to malnutrition. The document questions the validity of an advert claiming quick weight loss from a "Dropweight" program based on reported one-day results.
Defense against diseases ms

Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium. When people with TB cough or sneeze, they expel the bacteria into the air. If others breathe these bacteria in, they can become infected. The bacteria first infect the lungs or bronchioles. In the body, the bacteria produce toxins that damage cells. The body fights the infection through white blood cells that engulf and destroy bacteria and produce antibodies and antitoxins. Vaccines work by exposing the body to an inactive form of the disease-causing microbe, allowing it to develop antibodies without risk of illness. These antibodies then provide future protection against the live microbe.
P2 checklist

1) The document is a revision checklist for additional GCSE science covering topics in physics including forces, motion, braking, terminal velocity, elasticity, energy, momentum, static electricity, electrical circuits, household electricity, current, charge, power, atomic structure, radiation, nuclear fission, and nuclear fusion.
2) It lists key terms, concepts, and formulas to define and explanations to provide for each topic.
3) The checklist provides resources for students to review physics content and ensure they understand the essential information for their GCSE exam.
P1 checklist

This document contains a revision checklist for the GCSE Core Science P1 Physics exam. It lists several topics and subtopics that students should review in preparation for the exam, including: infrared radiation; states of matter; conduction, convection, and evaporation/condensation as methods of heat transfer; factors affecting the rate of heat transfer; solar panels; specific heat capacity; energy efficiency and Sankey diagrams; electrical appliances and calculating energy transfers; methods of generating electricity including alternative sources; the National Grid; waves including transverse/longitudinal waves, electromagnetic spectrum, reflection, refraction, and diffraction of waves; and Doppler effect and evidence for the Big Bang theory.
C2 checklist

This document provides an overview of the content covered in additional science C2: chemistry. It outlines several key topics in chemistry including structure and bonding, atomic structure and quantitative chemistry, rates of reaction, endo/exothermic reactions, acids bases and salts, and electrolysis. For each topic, it lists the main concepts, definitions, and processes that students are expected to understand at a higher level, such as describing bonding using diagrams, calculating relative formula mass, explaining how factors affect reaction rates, writing equations for acid-base reactions, and describing electrolysis processes and products. The document serves as a revision checklist for students to ensure they have learned the essential high-level information and skills for the additional chemistry content.
C1 checklist

This document is a revision checklist for GCSE core science covering various topics in chemistry. It provides a list of key concepts and processes to review for each topic, including fundamental chemistry ideas like atomic structure, limestone and building materials, metals and their uses, crude oil and fuels, and changes to the Earth's atmosphere. For each item, it indicates related videos, exam questions, and whether it is core or higher content.
B2 checklist

This document provides an outline of topics covered in Additional Science B2: Biology. It includes sections on cells and transport, tissues and organ systems, photosynthesis, organisms and their environment, aerobic and anaerobic respiration, cell division and inheritance, speciation, and includes learning objectives for each section such as describing processes like diffusion, the roles of organs in the digestive system, the process of photosynthesis, and more. It also provides exam questions, activities, and checkpoints to evaluate understanding of the material.
B1 checklist1

This document provides an overview of topics covered in a biology course, including:
- The components of a balanced diet and how exercise affects health.
- How pathogens make us ill and how the body protects against them.
- The development and testing of medical drugs, and issues around drug dependence.
- Genetic variation, inheritance, and different types of reproduction.
- Evolution by natural selection and genetic variation over generations.
- Ecological concepts like food chains, nutrient cycling, and indicator species.
Aqa p3-checklist

X-rays have a short wavelength and can cause ionization. They are used in medicine for diagnosis and treatment, but precautions must be taken when operating X-ray machines. Ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves above the human hearing range. The waves reflect off boundaries and the time of reflections can be used to determine distances between interfaces in different media. Lenses refract light to form images. A convex lens brings parallel rays to a focus at its principal focus, defined by the focal length. The nature of images depends on size, orientation, and whether real or virtual.
Aqa c3-checklist

The document summarizes key concepts in chemistry including the periodic table, properties of groups in the periodic table, hard and soft water, chemical reactions, and organic compounds. It describes how elements are arranged in the modern periodic table by electronic structure and properties of groups such as metals, nonmetals, and halogens. It also discusses chemical tests and reactions including flame tests, precipitation reactions, acid-base titrations, and the production of ammonia via the Haber process.
Aqa b3-checklist

This document provides information on various biology topics including:
- Diffusion and osmosis, the movement of substances through membranes. Active transport requires energy.
- Exchange surfaces are effective with large surface area, thinness, good blood supply and ventilation like in alveoli and villi.
- During breathing, the ribcage and diaphragm work to decrease thoracic pressure and draw air into the lungs. Artificial aids can help breathing.
- In plants, carbon dioxide enters leaves and water and minerals are absorbed by roots, transported by xylem and phloem.
- The heart has four chambers and pumps blood through two circulation systems. Blood flows through arteries, veins
AQA GCSE Economics Revision unit - 12

The document discusses key economic concepts related to government objectives and the functioning of the economy. It covers topics such as different types of economies, market failures including externalities and public goods, the economic cycle, fiscal and monetary policies, and the role of the EU. The key points are that candidates should understand the principal objectives of governments in terms of economic growth, employment, prices and trade balances. They should also be aware of how markets can fail to allocate resources efficiently and the roles of government and central banks in addressing these issues.
AQA GCSE Economics Revision unit - 11

The document outlines a specification for teaching personal finance concepts. It covers understanding the personal lifecycle and how needs and wants change throughout different stages of life. Students will learn to make financial decisions by weighing costs and benefits and considering opportunity costs. They will also explore concepts related to spending, saving, borrowing money, and managing personal finances. The specification also addresses topics related to work, including rewards, labor markets, unemployment, and the impact of globalization. Finally, it covers understanding international trade, exchange rates, and the influence of consumers on national and global economies.
More from themassmaker (20)
Compounds and mixtures
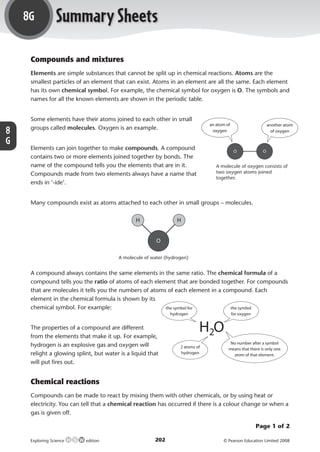
- 1. 8G Summary Sheets Compounds and mixtures Elements are simple substances that cannot be split up in chemical reactions. Atoms are the smallest particles of an element that can exist. Atoms in an element are all the same. Each element has its own chemical symbol. For example, the chemical symbol for oxygen is O. The symbols and names for all the known elements are shown in the periodic table. Some elements have their atoms joined to each other in small an atom of another atom groups called molecules. Oxygen is an example. 8 oxygen of oxygen G Elements can join together to make compounds. A compound O O contains two or more elements joined together by bonds. The name of the compound tells you the elements that are in it. A molecule of oxygen consists of Compounds made from two elements always have a name that two oxygen atoms joined together. ends in ‘-ide’. Many compounds exist as atoms attached to each other in small groups – molecules. H H O A molecule of water (hydrogen) A compound always contains the same elements in the same ratio. The chemical formula of a compound tells you the ratio of atoms of each element that are bonded together. For compounds that are molecules it tells you the numbers of atoms of each element in a compound. Each element in the chemical formula is shown by its chemical symbol. For example: the symbol for the symbol hydrogen for oxygen The properties of a compound are different from the elements that make it up. For example, H2O hydrogen is an explosive gas and oxygen will No number after a symbol 2 atoms of means that there is only one relight a glowing splint, but water is a liquid that hydrogen atom of that element. will put fires out. Chemical reactions Compounds can be made to react by mixing them with other chemicals, or by using heat or electricity. You can tell that a chemical reaction has occurred if there is a colour change or when a gas is given off. Page 1 of 2 Exploring Science edition 202 © Pearson Education Limited 2008 M07_ES_AB_Y8_5415_U8G.indd 202 28/8/08 12:49:23
- 2. 8G Summary Sheets (continued) Most chemical reactions also involve an energy change. This is usually in the form of heat, for example in burning (combustion). In a chemical reaction a new substance is always formed. Most chemical reactions are not easily reversed (they are irreversible). Some chemical reactions take place just by mixing substances together. (e.g. when a solid (a precipitate) forms by mixing two liquids in a precipitation reaction). Other chemical reactions need energy to start them off. (e.g. when some compounds are broken up, decomposed, by 8 heat). G Word equations show what happens in a chemical reaction. The chemicals that you start with are called the reactants. The chemicals at the end are called the products. For example: magnesium + oxygen magnesium oxide { Physical changes reactants { In a physical change no new substance is formed and the product melting evaporating changes are usually easily reversed. Melting, evaporating, ice water steam condensing and freezing are all examples of physical changes. freezing condensing Mixtures Elements and compounds can also be mixed together. A mixture is easier to separate than the elements in a compound. Soil, river water and sea water are examples of mixtures that occur naturally. A pure substance contains a single substance, element or compound, nothing else. Elements and compounds melt and boil at a fixed temperature. Mixtures do not have definite melting points and boiling points. Alloys Alloys are mixtures of metals with one or more other elements. Alloys have different properties from the pure metal. Pure gold is too soft for making jewellery. An alloy of gold mixed with other metals, like copper or silver, is used because it is stronger. The original method used to measure the purity of gold alloys was the carat system. One carat is 1 part in 24. So pure gold is 24 carats and 12 carat gold contains 50% gold. Page 2 of 2 Exploring Science edition 203 © Pearson Education Limited 2008 M07_ES_AB_Y8_5415_U8G.indd 203 28/8/08 12:49:24