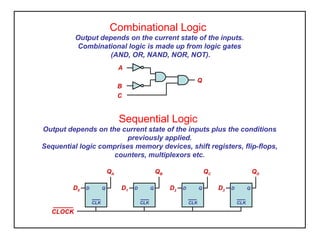
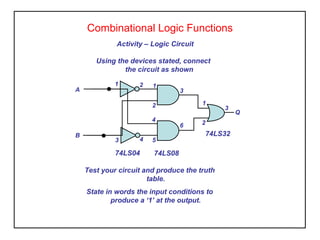
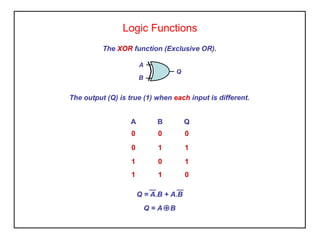
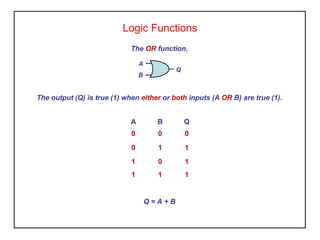
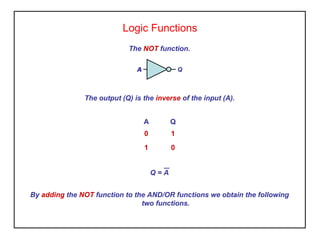
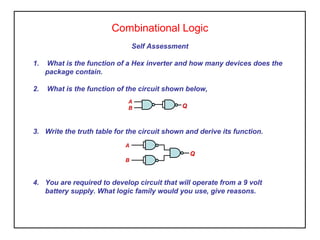
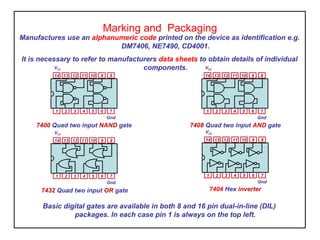
Digital logic circuits have two states - on or off (1 or 0, true or false). TTL uses bipolar transistors and operates at 5V but requires more power, while CMOS uses MOSFETs, operates at 3-15V, and consumes very little power, making it suitable for portable equipment. Sequential logic has an output dependent on current and previous inputs, while combinational logic only depends on current inputs. Basic logic gates include AND, OR, NAND, NOR, NOT, XOR, and XNOR.