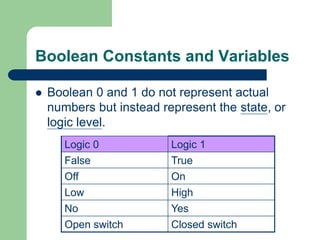
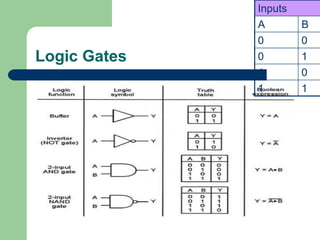
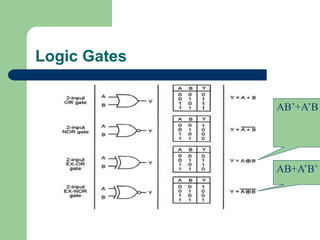
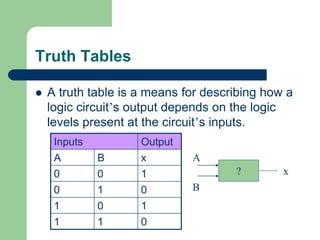
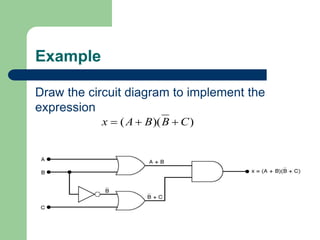
This document discusses digital logic gates and Boolean algebra. It defines the objectives as performing basic logic operations, describing AND, NAND, OR and NOR gates using truth tables, writing Boolean expressions, and implementing logic circuits. It explains Boolean constants and variables, the three basic logic operations (OR, AND, NOT), logic gates and their truth tables, gate IC numbers, and gives examples of implementing Boolean expressions as logic circuits.