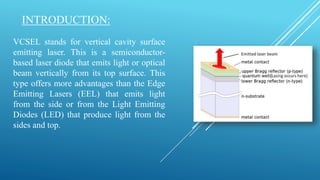
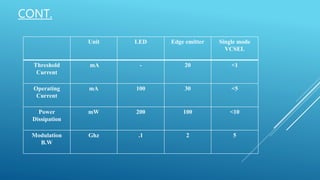
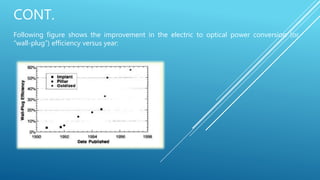
This document discusses vertical cavity surface emitting lasers (VCSELs). It begins by introducing VCSELs and their advantages over edge emitting lasers and LEDs. Key points include that VCSELs emit light perpendicular to the surface, allowing thousands to be processed at once on a wafer. VCSELs can also be tested throughout production to check for issues. The document then covers the history and development of VCSELs, their materials and wavelengths, operating characteristics, structure, applications, and concludes that VCSELs are now commonly used for short-range fiber optic communication due to their lower costs and higher reliability compared to edge emitters.