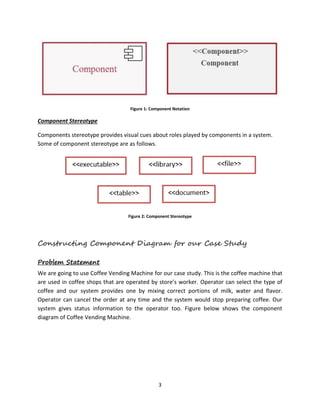
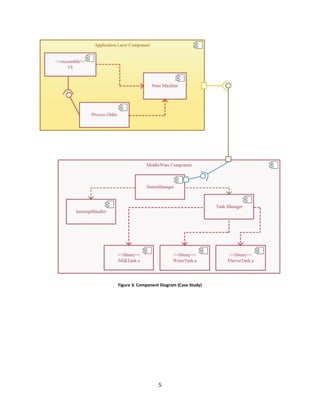
The document outlines the significance of component diagrams in representing the physical implementation of software designs, categorizing components into deployment, work product, and execution components. It uses a coffee vending machine case study to illustrate the construction of a component diagram, detailing the functionalities of each component in both application and middleware layers. Key elements and notations for creating component diagrams are also highlighted, emphasizing the visual cues provided by component stereotypes.