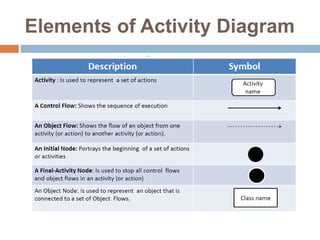
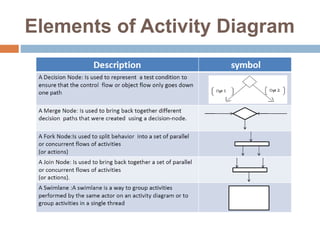
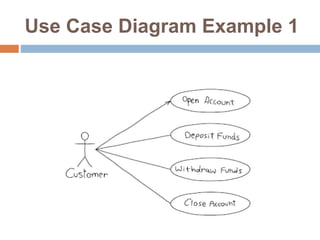
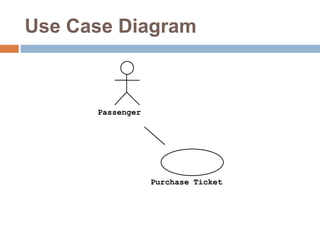
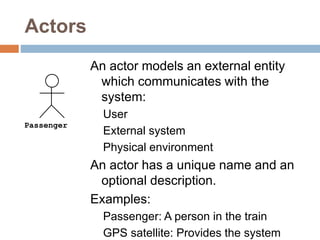
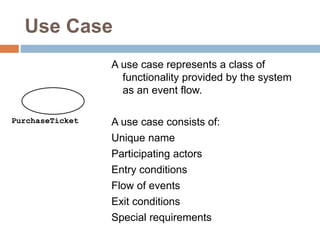
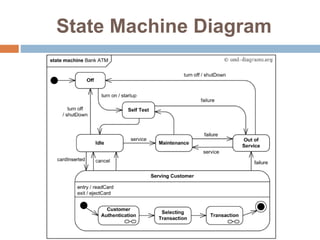
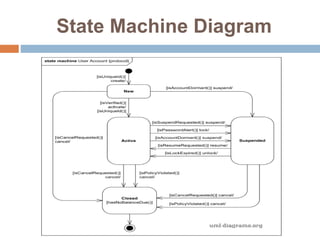
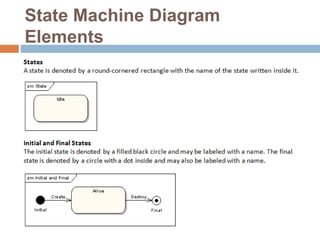
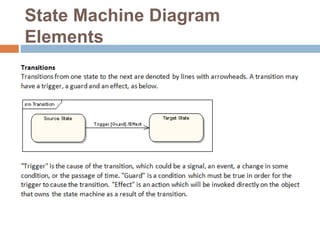
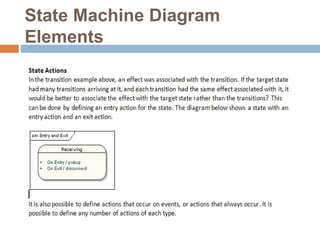
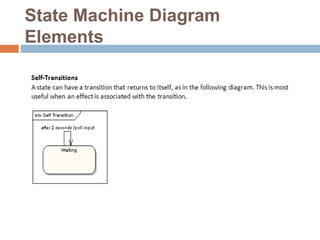
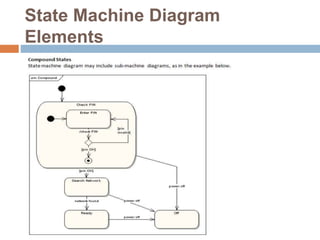
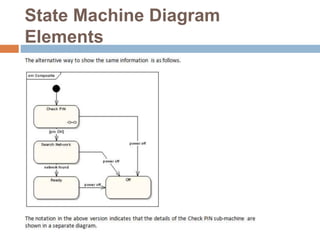
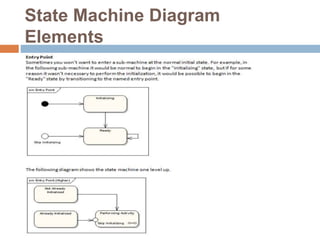
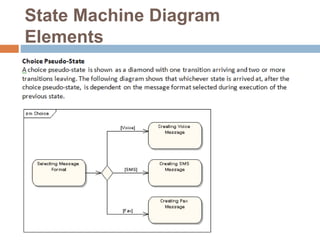
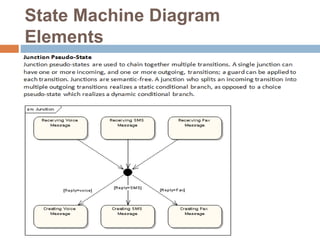
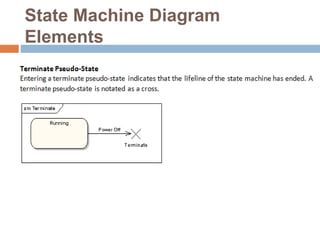
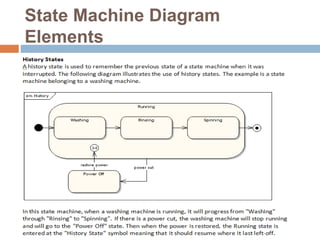
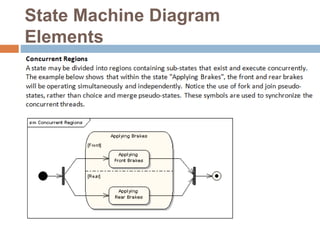
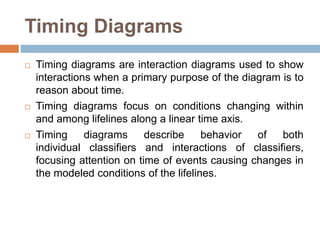
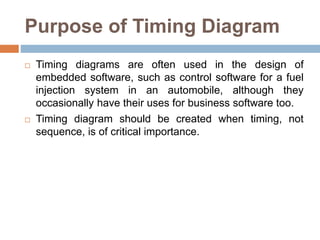
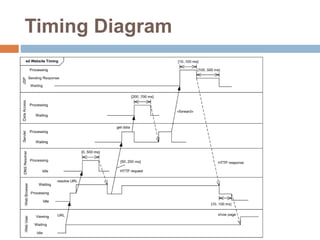
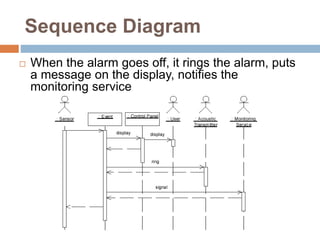
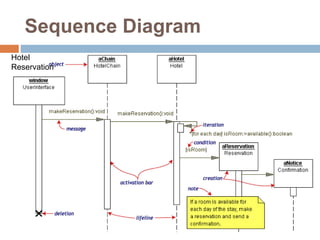
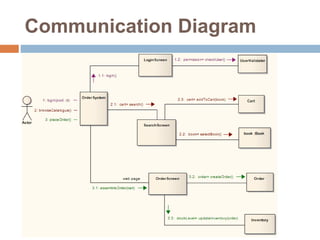
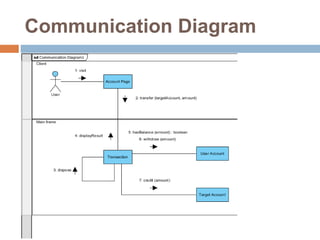
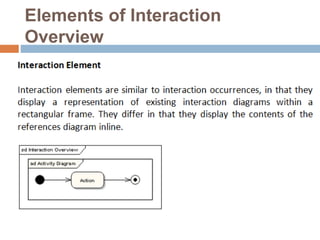
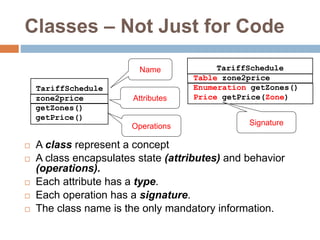
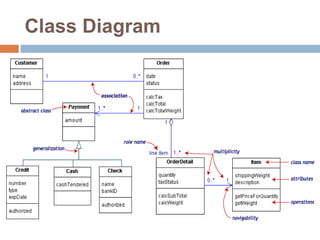
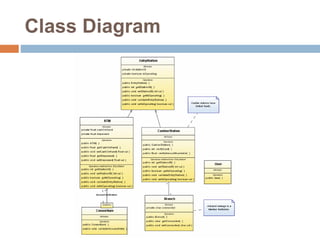
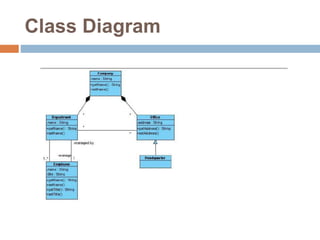
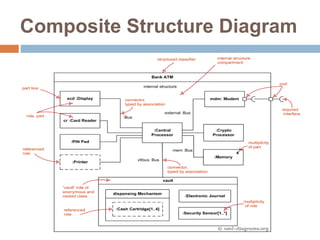
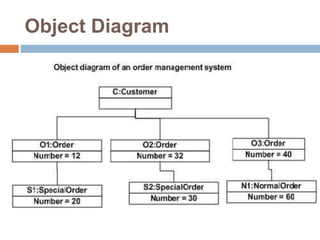
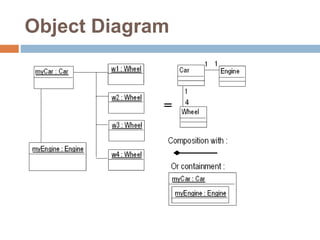
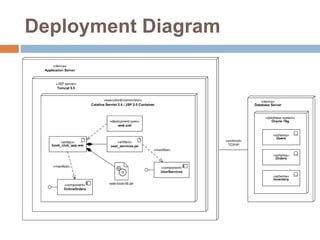
The document provides an overview of various UML diagrams used in software engineering, including activity, state machine, use case, communication, and timing diagrams. It explains their purposes, elements, and advantages in system design and analysis, emphasizing how they aid in understanding functional requirements and interactions within the system. Additionally, it outlines structural diagrams like class and deployment diagrams, highlighting their role in illustrating relationships and internal structures of software components.