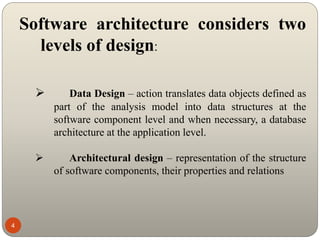
This document discusses architectural styles and patterns. It defines architectural styles as abstract frameworks that provide solutions to recurring problems and improve design partitioning and reuse. Styles define how components interact and are parameterized for different contexts. Architectural patterns are reusable solutions to common problems and are documented similarly to software design patterns. Patterns specify element types, relationships, and interaction mechanisms, while styles are more general without an associated problem.