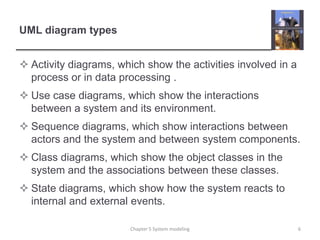
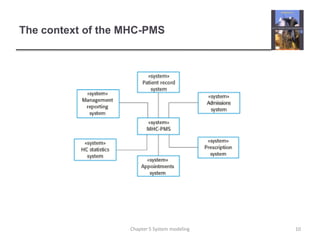
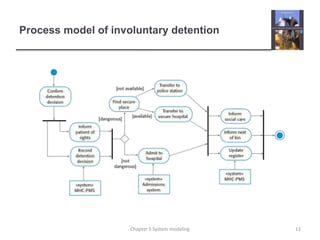
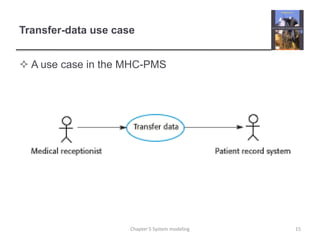
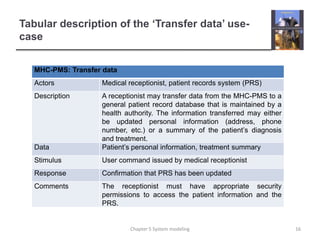
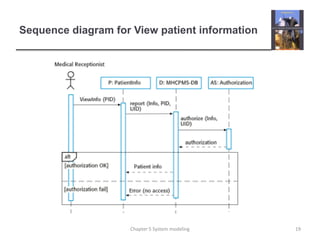
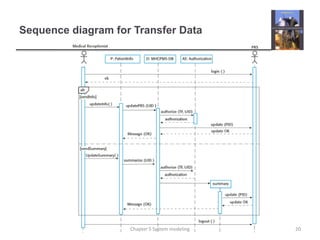
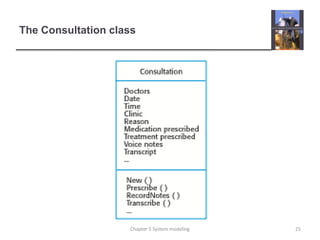
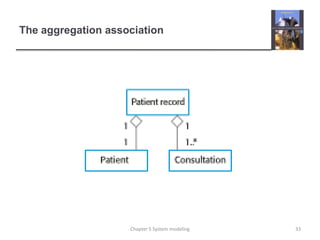
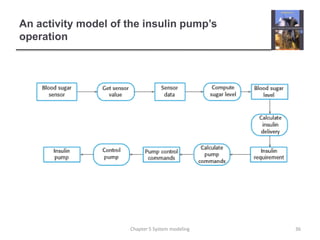
System modeling involves creating abstract models of a system from different perspectives, such as context, interactions, structure, and behavior. These models help analysts understand system functionality and communicate with customers. Context models show a system's external environment and relationships. Interaction models, such as use case and sequence diagrams, depict how users and systems interact. Structural models, like class diagrams, represent a system's internal organization. Behavioral models, including activity and state diagrams, illustrate a system's dynamic response to events or data. Model-driven engineering aims to generate implementation from system models.