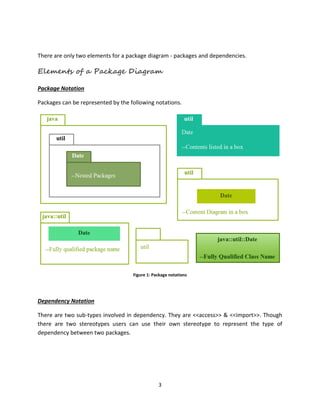
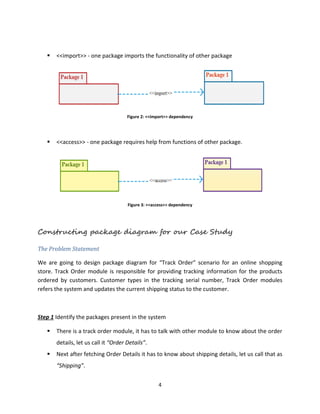
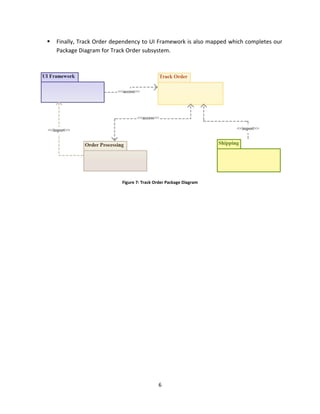
The document discusses package diagrams in UML. It explains that package diagrams show the high-level organization of systems and can contain other UML diagrams. Package diagrams use packages and dependencies. Packages represent modules and can contain classes, diagrams, and other elements. Dependencies show relationships between packages like import and access relationships. The document then provides an example of constructing a package diagram for an online order tracking system.