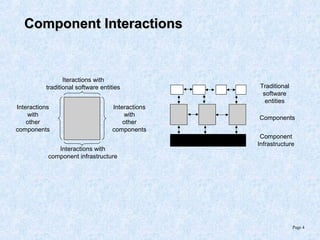
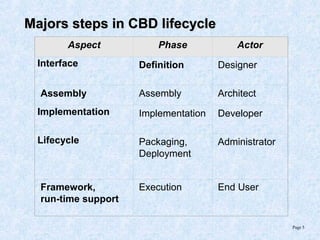
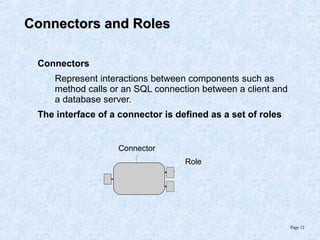
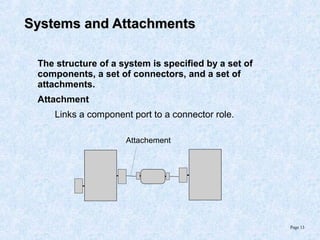
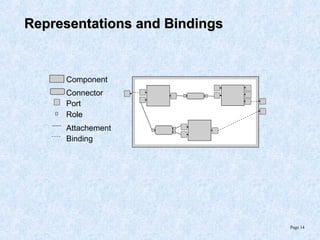
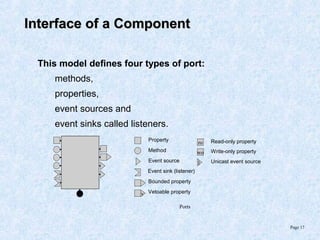
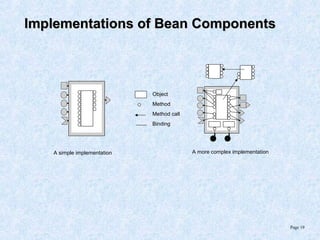
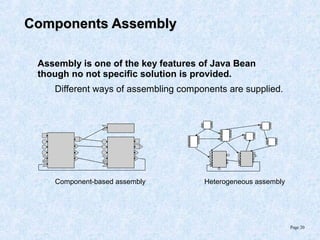
This document discusses various component models and technologies, including ACME, Java Beans, COM/DCOM/MTS, CORBA, .NET, and OSGi. It covers topics such as component interfaces, connections, interactions, lifecycles, architectures, and specific models like Java Beans. The Java Bean component model is described in more detail, including its key features around reusable software components, interfaces focusing on methods, properties, events, and implementations as simple Java objects or more complex wrappers.