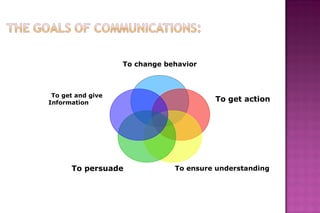
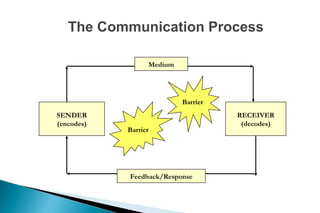
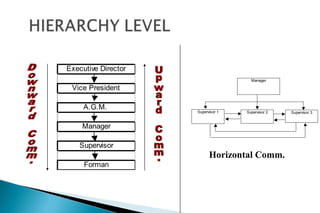
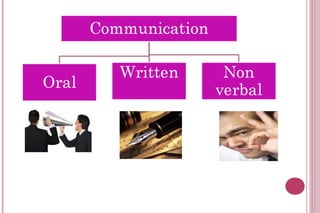
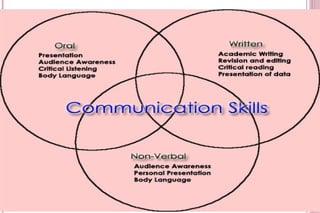
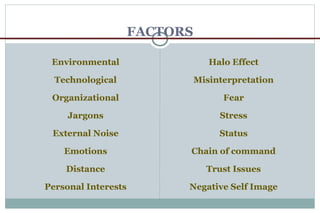
The document discusses effective communication skills. It defines communication as the process of exchanging information through various means, including speech, writing, and behavior. The document outlines different types of communication, such as oral, written, and nonverbal communication. It also discusses barriers to communication, such as physical, semantic, socio-psychological, organizational, and cross-cultural barriers. The document provides tips to overcome these barriers and improve communication skills.