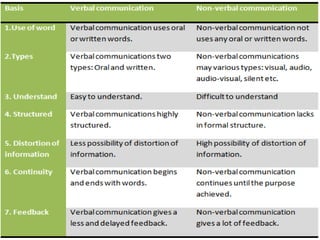
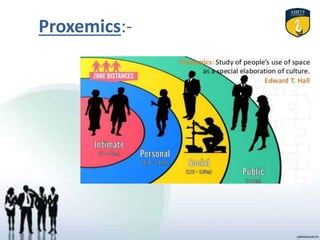
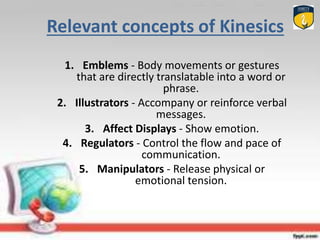
Non-verbal communication refers to communicating through body language and other non-verbal cues rather than words. It includes various modes such as paralanguage, proxemics, kinesics, oculesics, chronemics, haptics, color, and artifacts. Effective non-verbal communication supports and reinforces verbal messages, conveys feelings, and indicates intentions. It plays an important role in interpersonal interactions and relationships. However, non-verbal cues can also be imprecise or culturally dependent. Developing non-verbal communication skills involves practices like maintaining eye contact, facial expressions, personal space, posture, and tone of voice.