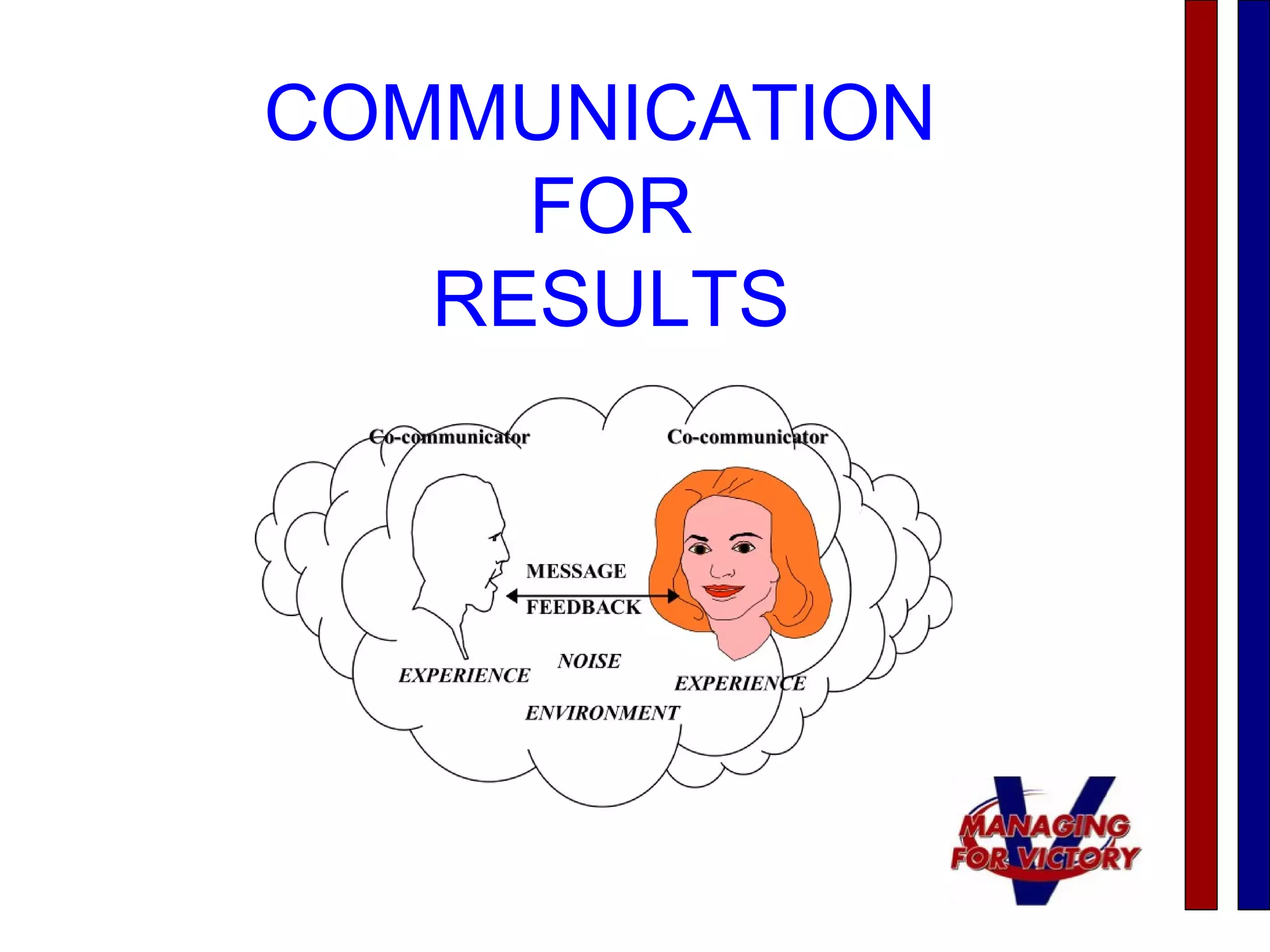
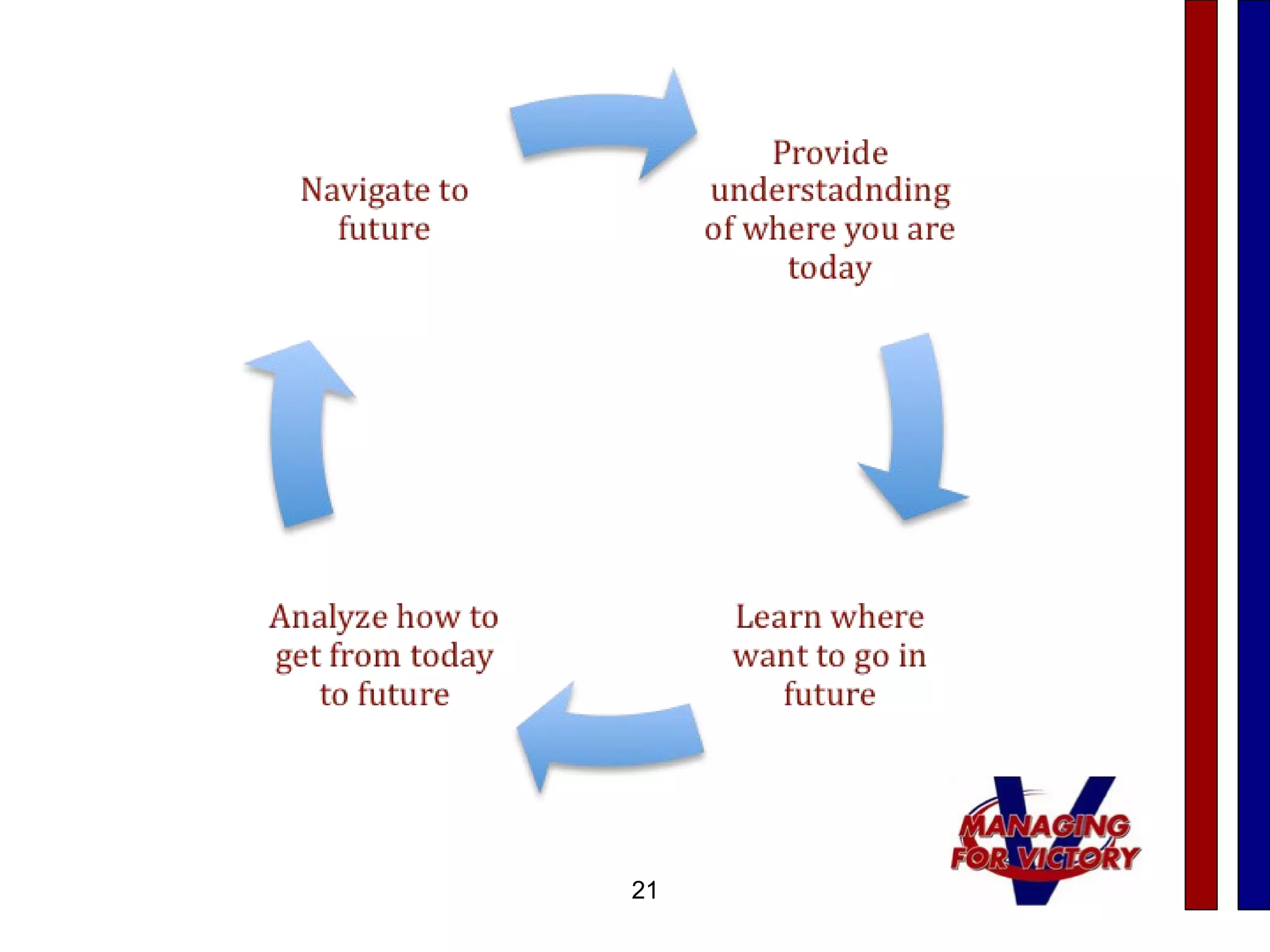
This document discusses effective communication techniques. It emphasizes the importance of listening, providing feedback, and developing action plans. Some key points covered include clarifying your message, observing body language, focusing on understanding other points of view, nurturing feelings, and emphasizing listening. Barriers to good communication mentioned are having a bad attitude, avoiding real issues, and being unwilling to be open and honest. The document provides guidelines for both giving and receiving feedback in a considerate manner.