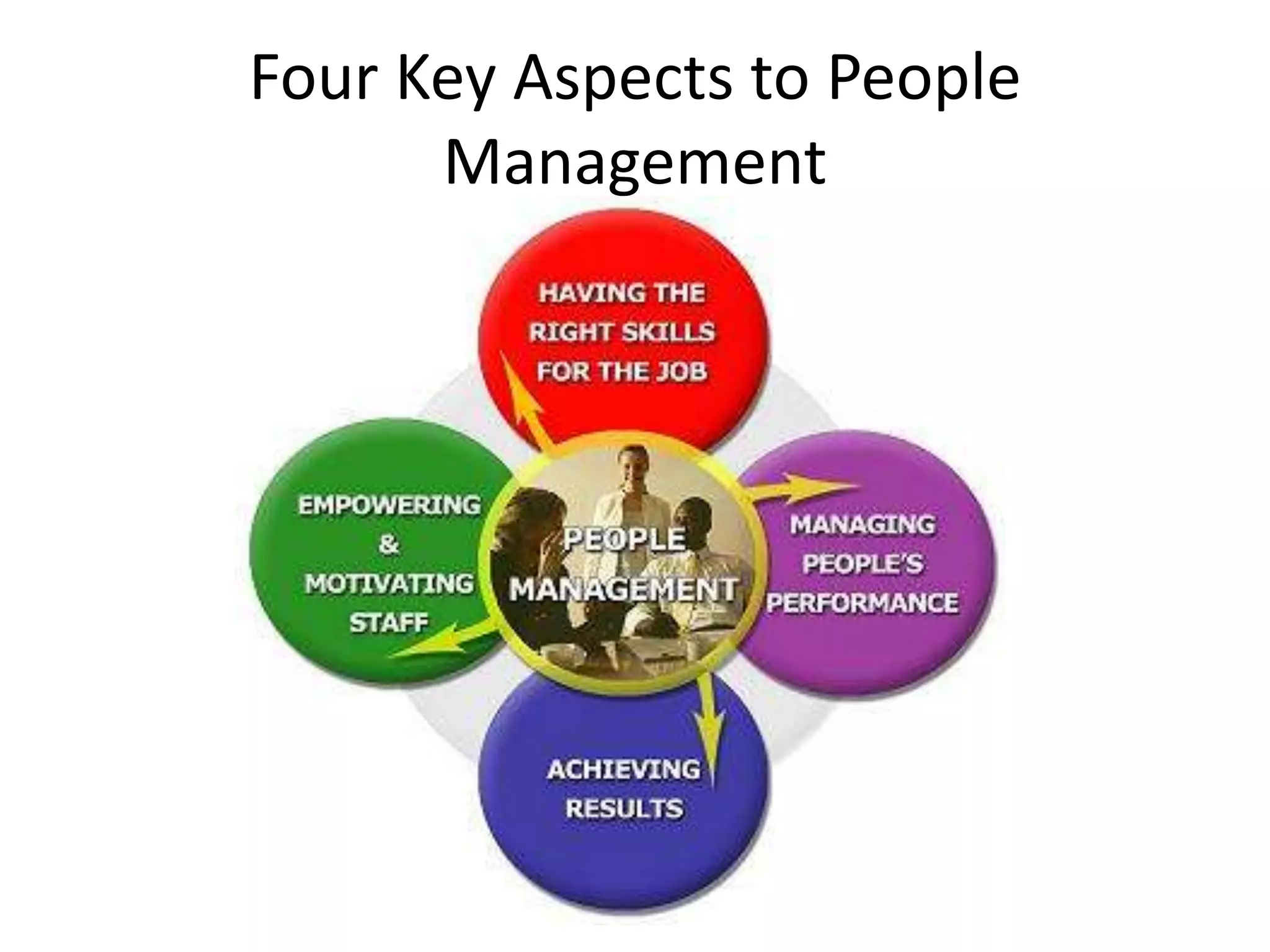
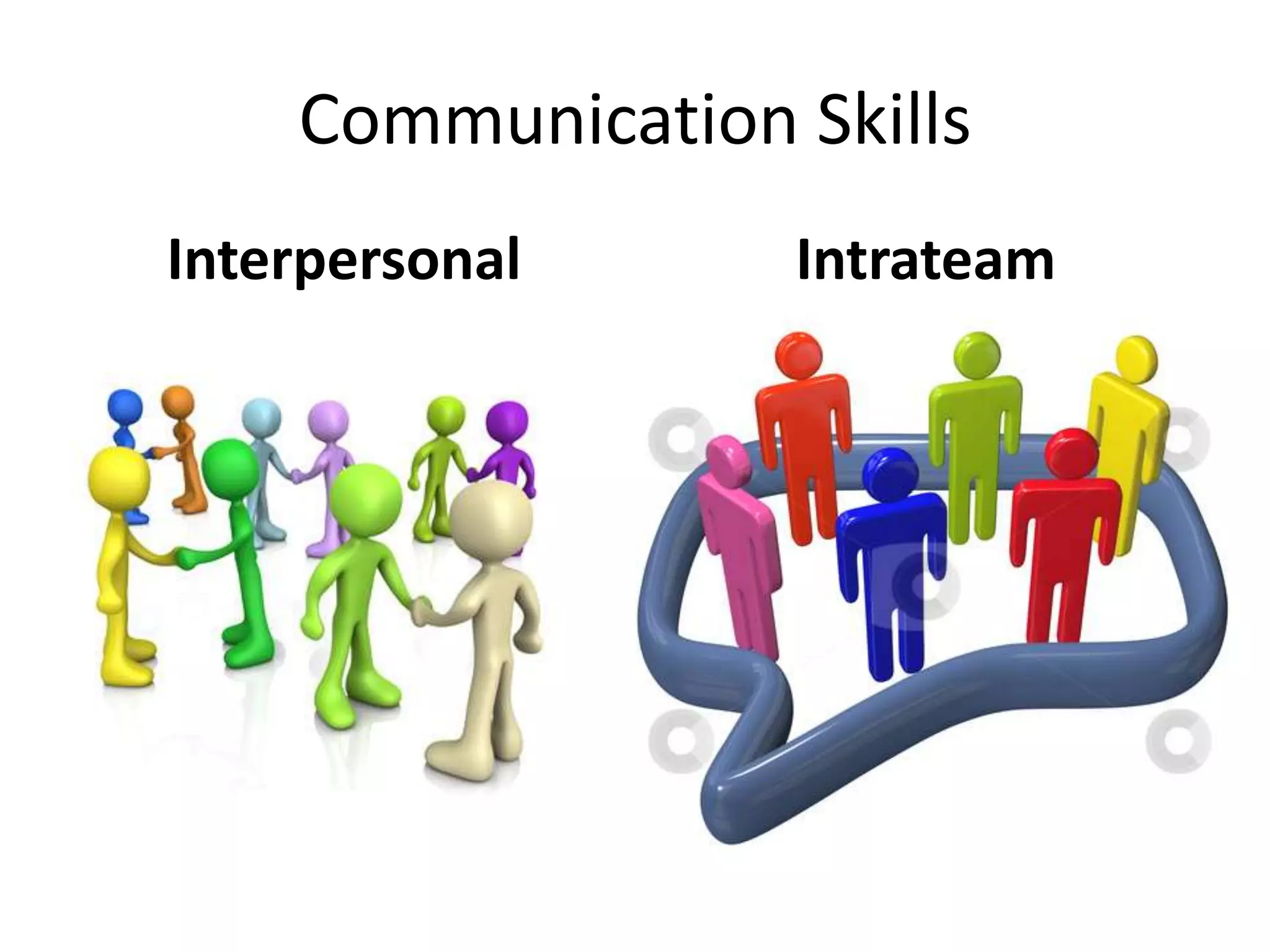
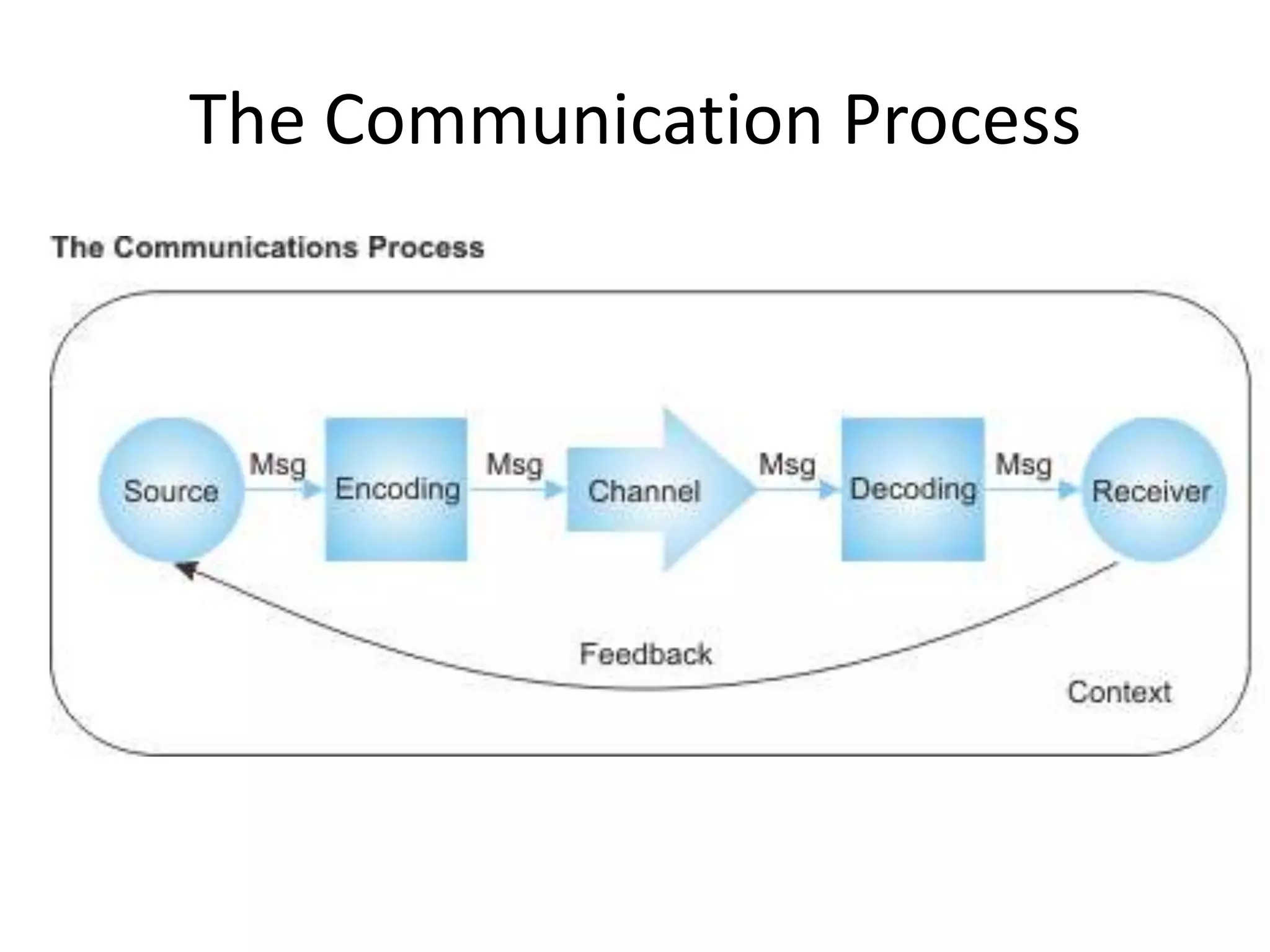
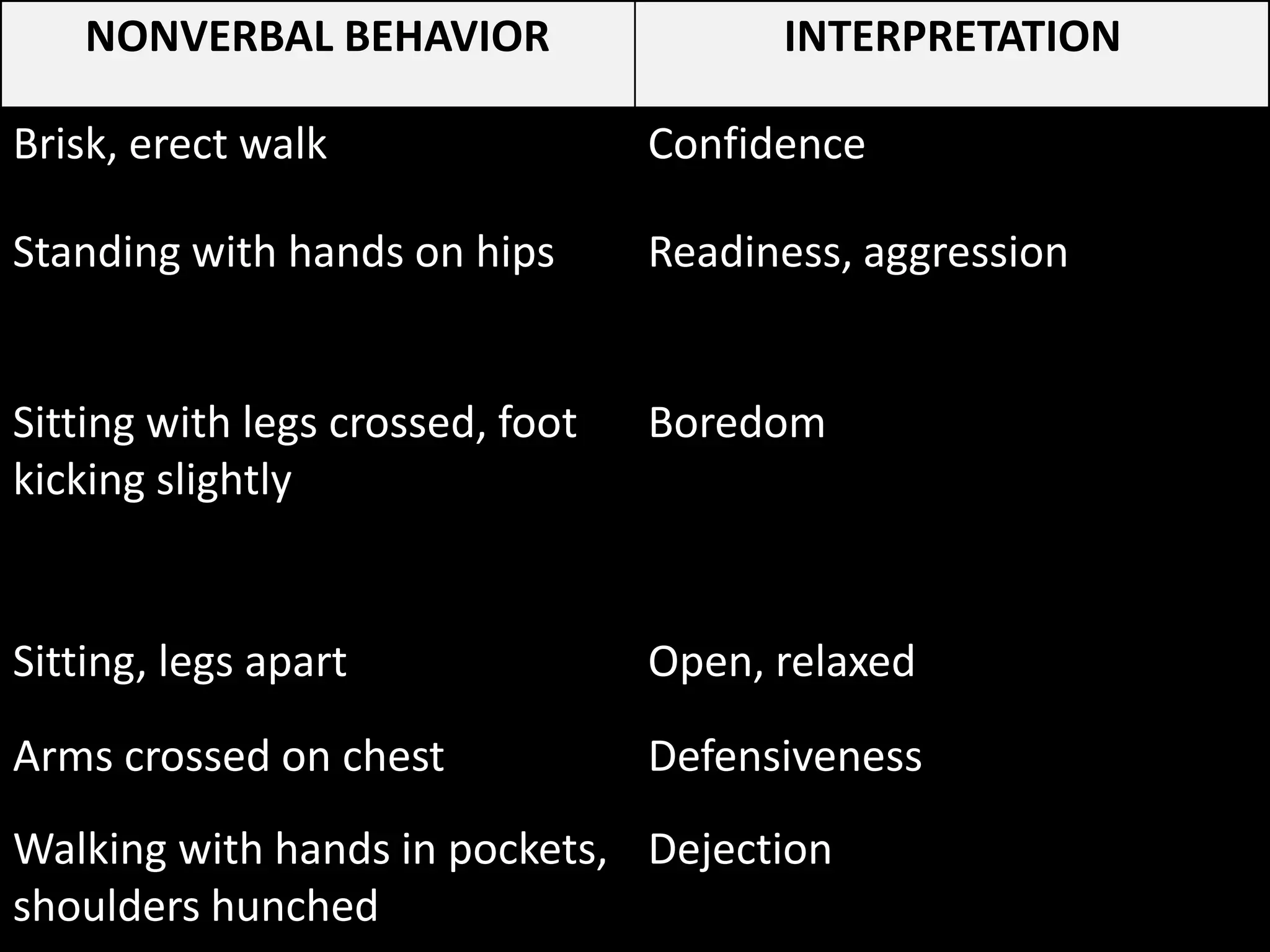
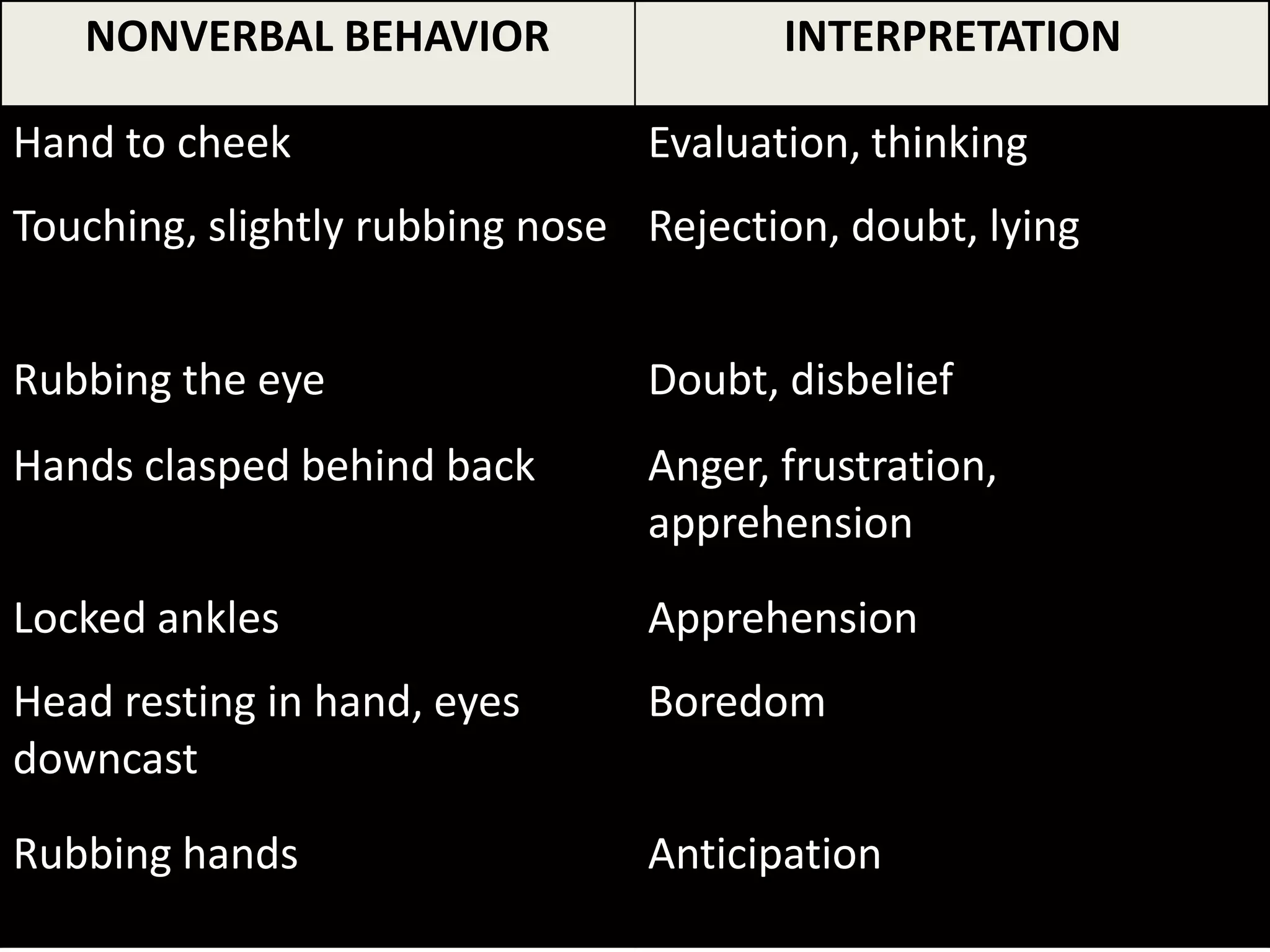
The document outlines key aspects of people management and communication skills, focusing on interpersonal and intrateam communication. It discusses effective communication techniques, nonverbal cues, barriers to communication, and strategies for improvement. The importance of active listening, giving and receiving constructive feedback, and recognizing nonverbal behavior is emphasized throughout.